Abstract
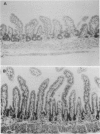
Rotavirus infection is the most common cause of acute diarrhoea in children worldwide. The structural and functional consequences of mammalian rotavirus infection in the small intestine have been incompletely studied and the mechanism of enterocyte damage poorly defined. This study used a neonatal rat model of group B rotavirus infection to study the natural history, clinical features, and the structural and functional consequences of infection in the small intestine. Group B rotavirus infection in eight day old neonatal rats produced diarrhoea by 24-36 hours, which was accompanied by weight loss during the early stages of infection. By seven days the diarrhoea had ceased and body weight was similar to noninfected controls. Rotavirus could be recovered in faeces from 24-72 hours. Light microscopy and morphometry confirmed reduction in villous height in both jejunum and ileum, with a reduction in total mucosal thickness indicating true flat mucosa. Increase in crypt depth followed villous shortening and continued as villous height progressively increased between 96-168 hours. Steady state perfusion of the entire small intestine with a plasma electrolyte solution confirmed the presence of a net secretory state for water between 12-48 hours, with a parallel reduction in sodium absorption. Group B rotavirus infection produces a self limiting acute diarrhoeal illness in neonatal rats similar to human rotavirus infection. Infection causes a reversible flat mucosa resulting from enterocyte loss associated with a net secretory state for water and impaired sodium absorption as a functional correlate. These findings may have relevance for the pathogenesis of human rotavirus infection.
Full text
PDF

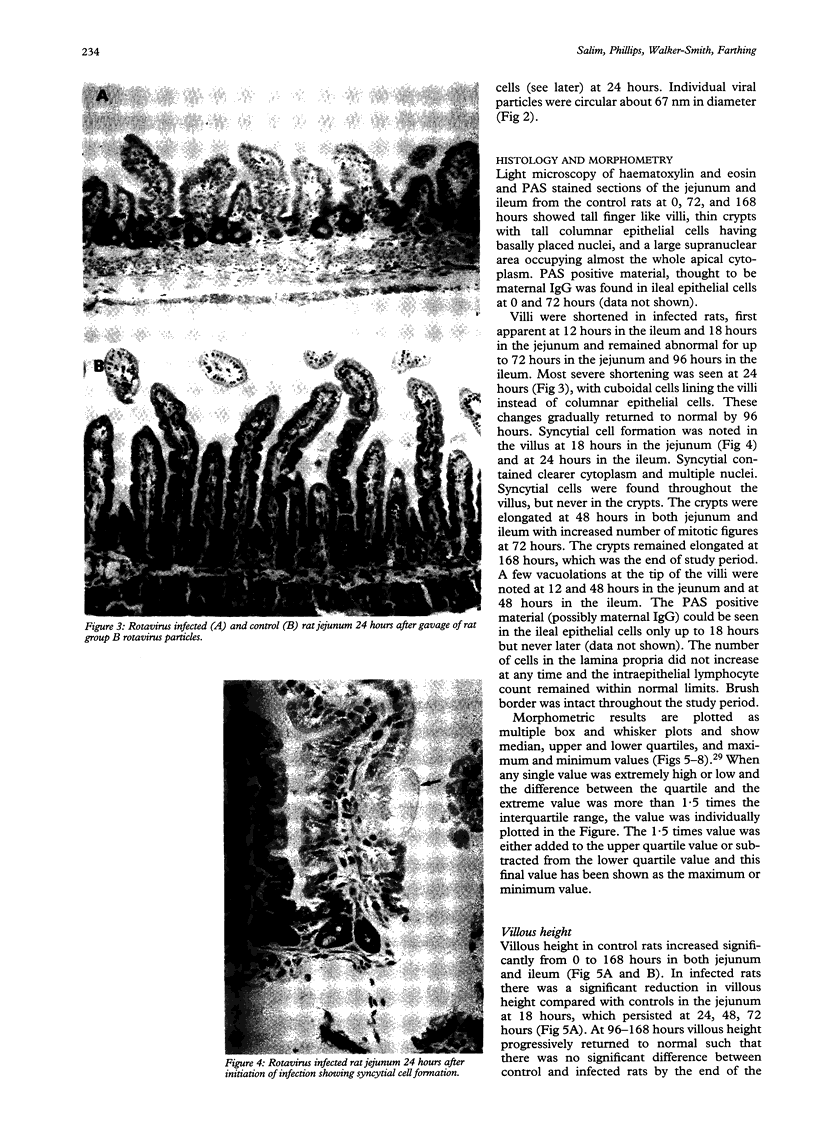
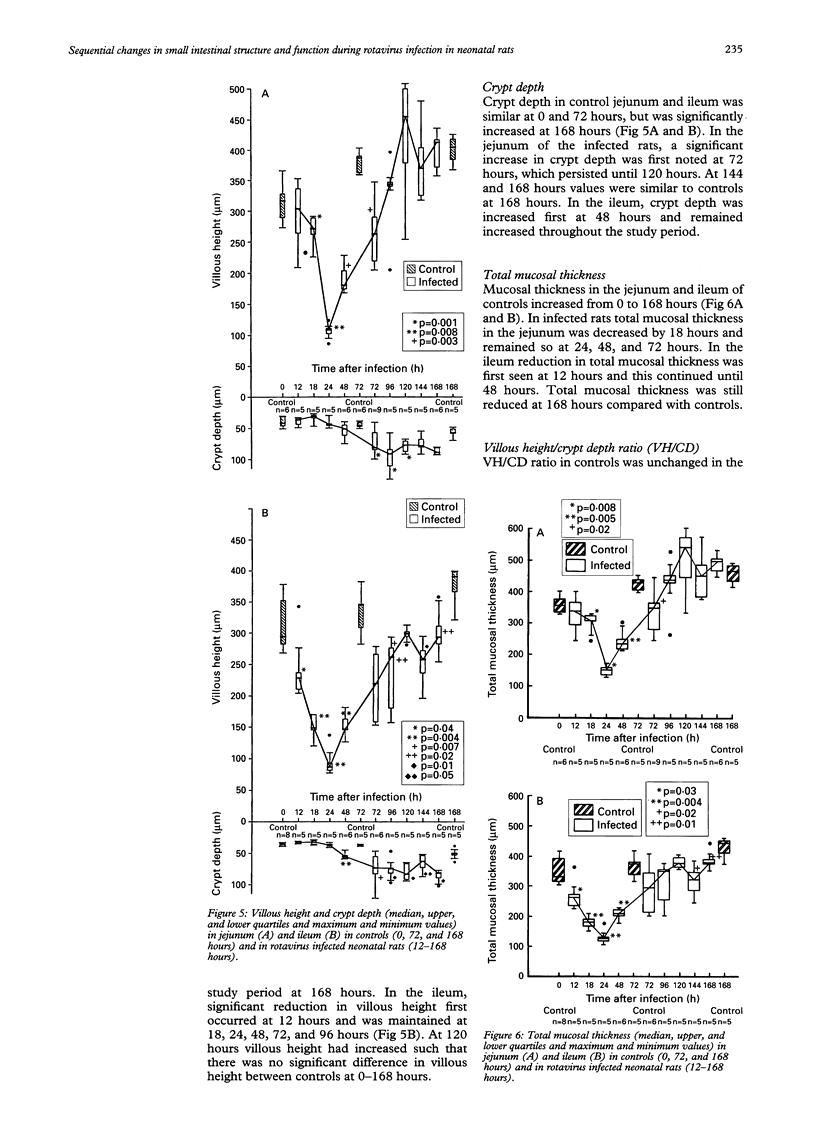
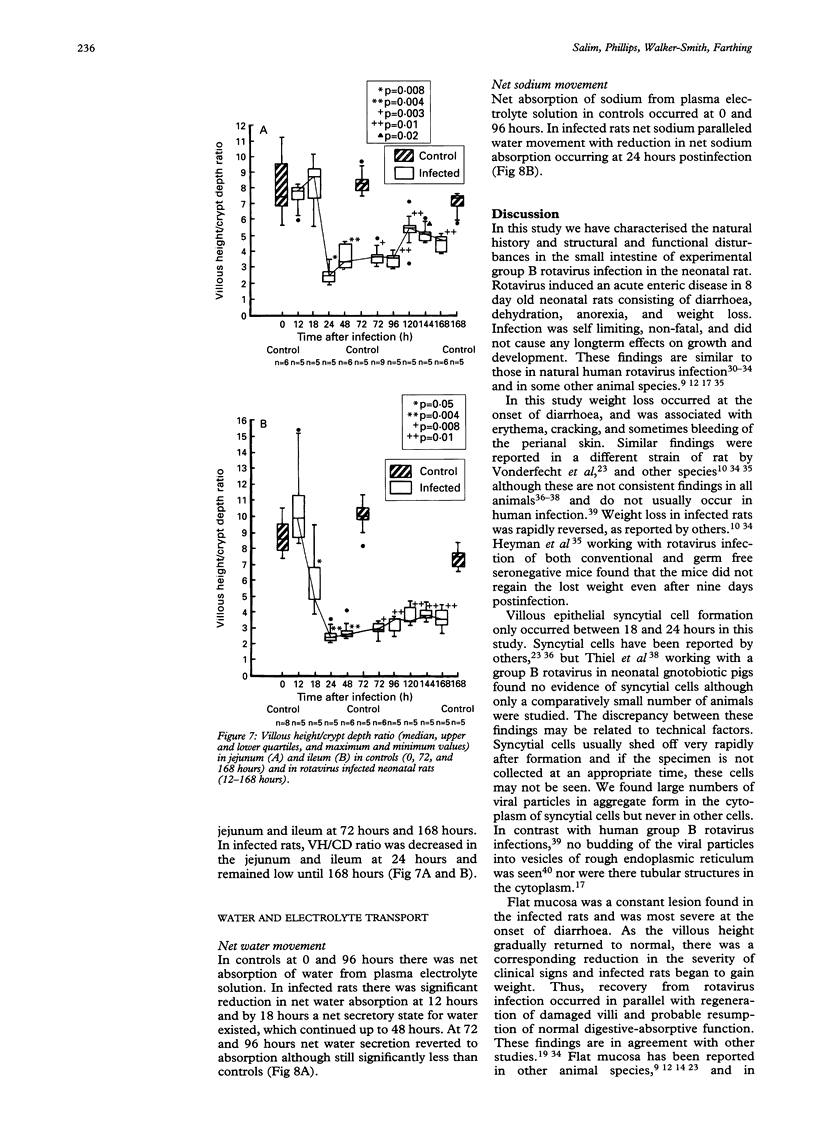
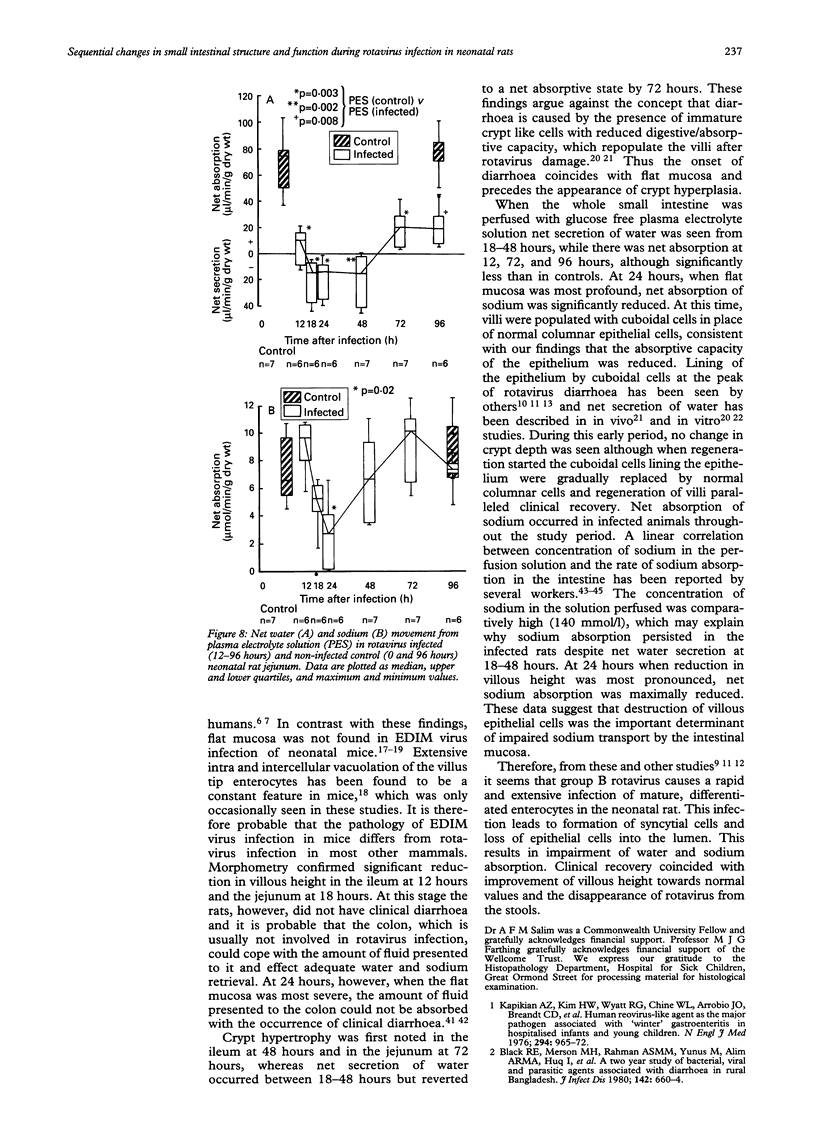

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams W. R., Kraft L. M. Electron-Microscopic Study of the Intestinal Epithelium of Mice Infected with the Agent of Epizootic Diarrhea of Infant Mice (EDIM Virus). Am J Pathol. 1967 Jul;51(1):39–60. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Askaa J., Bloch B. Infection in piglets with a porcine rotavirus-like virus. Experimental inoculation and ultrastructural examination. Arch Virol. 1984;80(4):291–303. doi: 10.1007/BF01311220. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bishop R. F., Davidson G. P., Holmes I. H., Ruck B. J. Virus particles in epithelial cells of duodenal mucosa from children with acute non-bacterial gastroenteritis. Lancet. 1973 Dec 8;2(7841):1281–1283. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(73)92867-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Black R. E., Merson M. H., Rahman A. S., Yunus M., Alim A. R., Huq I., Yolken R. H., Curlin G. T. A two-year study of bacterial, viral, and parasitic agents associated with diarrhea in rural Bangladesh. J Infect Dis. 1980 Nov;142(5):660–664. doi: 10.1093/infdis/142.5.660. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown R. A., Beck J. S. Statistics on microcomputers. A non-algebraic guide to their appropriate use in biomedical research and pathology practice. 3. Analysis of variance and distribution-free methods. J Clin Pathol. 1988 Dec;41(12):1256–1262. doi: 10.1136/jcp.41.12.1256. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CURRAN P. F., SOLOMON A. K. Ion and water fluxes in the ileum of rats. J Gen Physiol. 1957 Sep 20;41(1):143–168. doi: 10.1085/jgp.41.1.143. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coelho K. I., Bryden A. S., Hall C., Flewett T. H. Pathology of rotavirus infection in suckling mice: A study by conventional histology, immunofluorescence, ultrathin sections, and scanning electron microscopy. Ultrastruct Pathol. 1981 Jan-Mar;2(1):59–80. doi: 10.3109/01913128109031504. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conner M. E., Estes M. K., Graham D. Y. Rabbit model of rotavirus infection. J Virol. 1988 May;62(5):1625–1633. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.5.1625-1633.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crouch C. F., Woode G. N. Serial studies of virus multiplication and intestinal damage in gnotobiotic piglets infected with rotavirus. J Med Microbiol. 1978 Aug;11(3):325–334. doi: 10.1099/00222615-11-3-325. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davidson G. P., Barnes G. L. Structural and functional abnormalities of the small intestine in infants and young children with rotavirus enteritis. Acta Paediatr Scand. 1979 Mar;68(2):181–186. doi: 10.1111/j.1651-2227.1979.tb04986.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davidson G. P., Gall D. G., Petric M., Butler D. G., Hamilton J. R. Human rotavirus enteritis induced in conventional piglets. Intestinal structure and transport. J Clin Invest. 1977 Dec;60(6):1402–1409. doi: 10.1172/JCI108901. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eiden J., Vonderfecht S., Yolken R. H. Evidence that a novel rotavirus-like agent of rats can cause gastroenteritis in man. Lancet. 1985 Jul 6;2(8445):8–11. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(85)90057-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elliott E. J., Watson A. J., Walker-Smith J. A., Farthing M. J. Effect of bicarbonate on efficacy of oral rehydration therapy: studies in an experimental model of secretory diarrhoea. Gut. 1988 Aug;29(8):1052–1057. doi: 10.1136/gut.29.8.1052. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gouvea V. S., Alencar A. A., Barth O. M., de Castro L., Fialho A. M., Araújo H. P., Majerowicz S., Pereira H. G. Diarrhoea in mice infected with a human rotavirus. J Gen Virol. 1986 Mar;67(Pt 3):577–581. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-67-3-577. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heyman M., Corthier G., Petit A., Meslin J. C., Moreau C., Desjeux J. F. Intestinal absorption of macromolecules during viral enteritis: an experimental study on rotavirus-infected conventional and germ-free mice. Pediatr Res. 1987 Jul;22(1):72–78. doi: 10.1203/00006450-198707000-00017. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hjelt K., Krasilnikoff P. A., Grauballe P. C., Rasmussen S. W. Clinical features in hospitalised children with acute gastroenteritis. Does the rotavirus syndrome exist? Acta Paediatr Scand. 1985 Jan;74(1):96–101. doi: 10.1111/j.1651-2227.1985.tb10927.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hung T., Chen G. M., Wang C. G., Yao H. L., Fang Z. Y., Chao T. X., Chou Z. Y., Ye W., Chang X. J., Den S. S. Waterborne outbreak of rotavirus diarrhoea in adults in China caused by a novel rotavirus. Lancet. 1984 May 26;1(8387):1139–1142. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunt J. B., Thillainayagam A. V., Salim A. F., Carnaby S., Elliott E. J., Farthing M. J. Water and solute absorption from a new hypotonic oral rehydration solution: evaluation in human and animal perfusion models. Gut. 1992 Dec;33(12):1652–1659. doi: 10.1136/gut.33.12.1652. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson C. A., Snider T. G., 3rd, Henk W. G., Fulton R. W. A scanning and transmission electron microscopic study of rotavirus-induced intestinal lesions in neonatal gnotobiotic dogs. Vet Pathol. 1986 Jul;23(4):443–453. doi: 10.1177/030098588602300415. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kapikian A. Z., Kim H. W., Wyatt R. G., Cline W. L., Arrobio J. O., Brandt C. D., Rodriguez W. J., Sack D. A., Chanock R. M., Parrott R. H. Human reovirus-like agent as the major pathogen associated with "winter" gastroenteritis in hospitalized infants and young children. N Engl J Med. 1976 Apr 29;294(18):965–972. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197604292941801. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerzner B., Kelly M. H., Gall D. G., Butler D. G., Hamilton J. R. Transmissible gastroenteritis: sodium transport and the intestinal epithelium during the course of viral enteritis. Gastroenterology. 1977 Mar;72(3):457–461. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kovacs A., Chan L., Hotrakitya C., Overturf G., Portnoy B. Rotavirus gastroenteritis. Clinical and laboratory features and use of the Rotazyme test. Am J Dis Child. 1987 Feb;141(2):161–166. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1987.04460020051025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maluenda C., Phillips A. D., Briddon A., Walker-Smith J. A. Quantitative analysis of small intestinal mucosa in cow's milk-sensitive enteropathy. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 1984 Jun;3(3):349–356. doi: 10.1097/00005176-198406000-00008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McAdaragh J. P., Bergeland M. E., Meyer R. C., Johnshoy M. W., Stotz I. J., Benfield D. A., Hammer R. Pathogenesis of rotaviral enteritis in gnotobiotic pigs: a microscopic study. Am J Vet Res. 1980 Oct;41(10):1572–1581. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mebus C. A., Newman L. E. Scanning electron, light, and immunofluorescent microscopy of intestine of gnotobiotic calf infected with reovirus-like agent. Am J Vet Res. 1977 May;38(5):553–558. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy A. M., Albrey M. B., Crewe E. B. Rotavirus infections of neonates. Lancet. 1977 Dec 3;2(8049):1149–1150. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(77)91538-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mäki M. A prospective clinical study of rotavirus diarrhoea in young children. Acta Paediatr Scand. 1981 Jan;70(1):107–113. doi: 10.1111/j.1651-2227.1981.tb07181.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osborne M. P., Haddon S. J., Spencer A. J., Collins J., Starkey W. G., Wallis T. S., Clarke G. J., Worton K. J., Candy D. C., Stephen J. An electron microscopic investigation of time-related changes in the intestine of neonatal mice infected with murine rotavirus. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 1988 Mar-Apr;7(2):236–248. doi: 10.1097/00005176-198803000-00014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips A. D. Small intestinal mucosa in childhood in health and disease. Scand J Gastroenterol Suppl. 1981;70:65–85. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Read N. W. Diarrhoea: the failure of colonic salvage. Lancet. 1982 Aug 28;2(8296):481–483. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(82)90504-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saif L. J., Theil K. W., Bohl E. H. Morphogenesis of porcine rotavirus in porcine kidney cell cultures and intestinal epithelial cells. J Gen Virol. 1978 May;39(2):205–217. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-39-2-205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shepherd R. W., Truslow S., Walker-Smith J. A., Bird R., Cutting W., Darnell R., Barker C. M. Infantile gastroenteritis: a clinical study of reovirus-like agent infection. Lancet. 1975 Nov 29;2(7944):1082–1084. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(75)90446-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snodgrass D. R., Angus K. W., Gray E. W. Rotavirus infection in lambs: pathogenesis and pathology. Arch Virol. 1977;55(4):263–274. doi: 10.1007/BF01315048. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snodgrass D. R., Ferguson A., Allan F., Angus K. W., Mitchell B. Small intestinal morphology and epithelial cell kinetics in lamb rotavirus infections. Gastroenterology. 1979 Mar;76(3):477–481. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Starkey W. G., Candy D. C., Thornber D., Collins J., Spencer A. J., Osborne M. P., Stephen J. An in vitro model to study aspects of the pathophysiology of murine rotavirus-induced diarrhoea. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 1990 Apr;10(3):361–370. doi: 10.1097/00005176-199004000-00017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Starkey W. G., Collins J., Wallis T. S., Clarke G. J., Spencer A. J., Haddon S. J., Osborne M. P., Candy D. C., Stephen J. Kinetics, tissue specificity and pathological changes in murine rotavirus infection of mice. J Gen Virol. 1986 Dec;67(Pt 12):2625–2634. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-67-12-2625. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki H., Konno T. Reovirus-like particles in jejunal mucosa of a Japanese infant with acute infectious non-bacterial gastroenteritis. Tohoku J Exp Med. 1975 Mar;115(3):199–211. doi: 10.1620/tjem.115.199. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tallett S., MacKenzie C., Middleton P., Kerzner B., Hamilton R. Clinical, laboratory, and epidemiologic features of a viral gastroenteritis in infants and children. Pediatrics. 1977 Aug;60(2):217–222. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Theil K. W., Bohl E. H., Cross R. F., Kohler E. M., Agnes A. G. Pathogenesis of porcine rotaviral infection in experimentally inoculated gnotobiotic pigs. Am J Vet Res. 1978 Feb;39(2):213–220. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Theil K. W., Saif L. J., Moorhead P. D., Whitmoyer R. E. Porcine rotavirus-like virus (group B rotavirus): characterization and pathogenicity for gnotobiotic pigs. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Mar;21(3):340–345. doi: 10.1128/jcm.21.3.340-345.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vonderfecht S. L., Huber A. C., Eiden J., Mader L. C., Yolken R. H. Infectious diarrhea of infant rats produced by a rotavirus-like agent. J Virol. 1984 Oct;52(1):94–98. doi: 10.1128/jvi.52.1.94-98.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]