Abstract
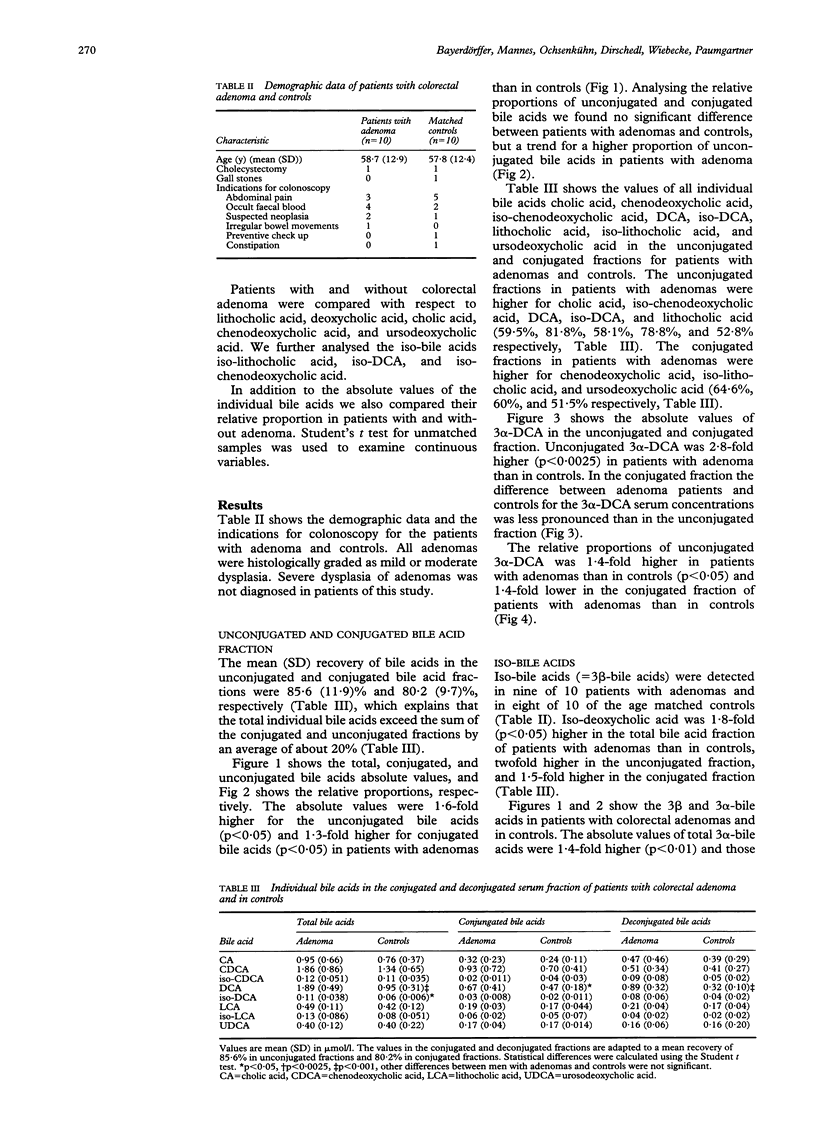
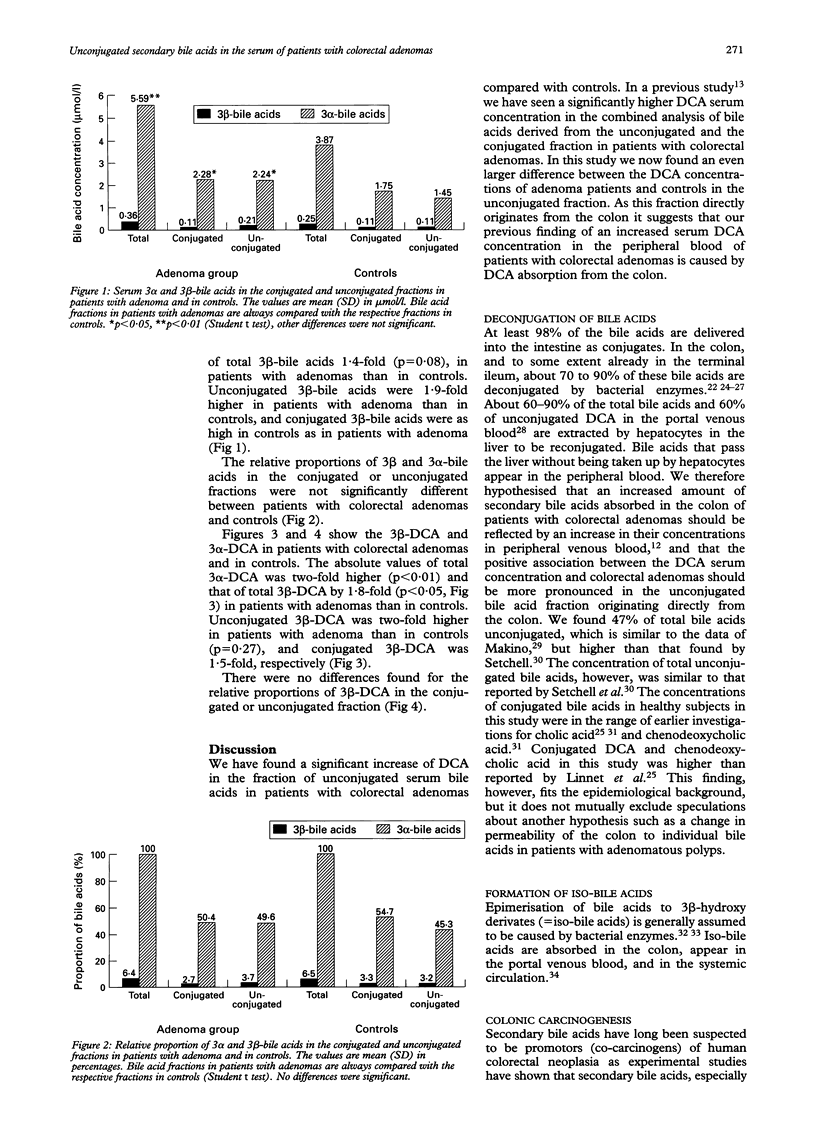
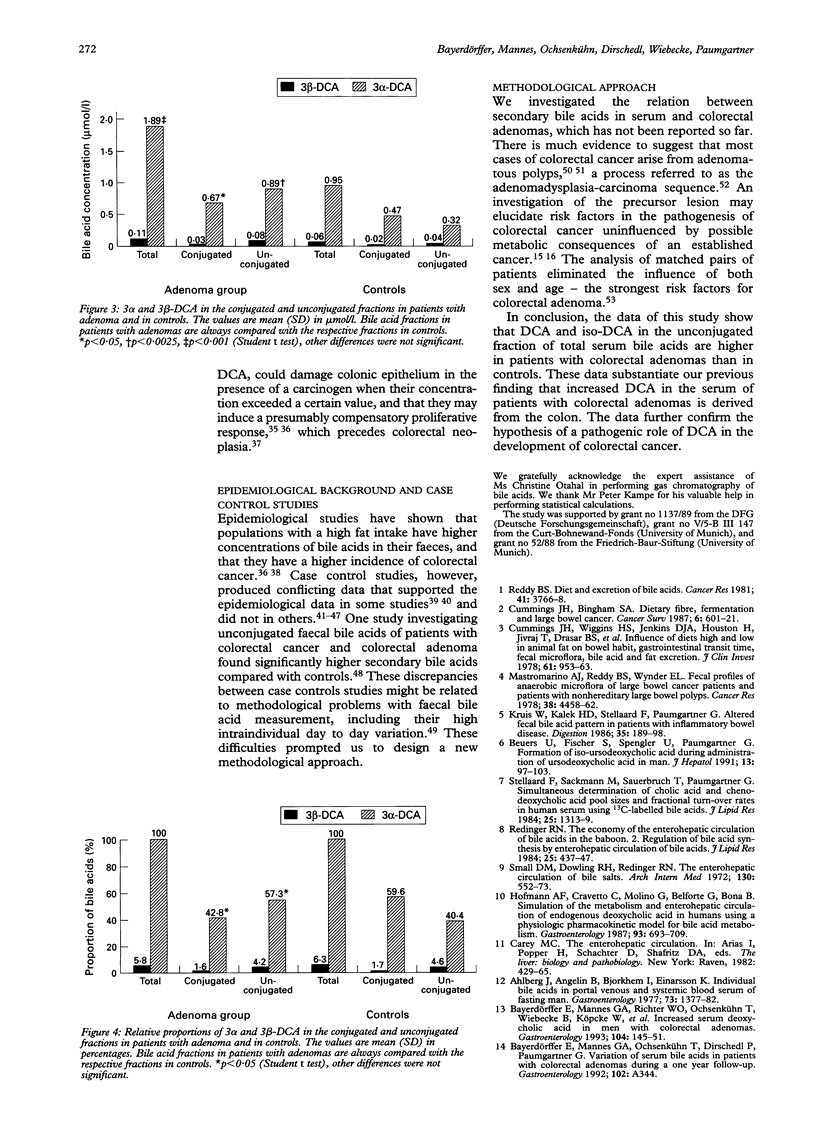
A positive association between deoxcholic acid (DCA) in the serum and colorectal adenomas, the precursors of colorectal cancer has recently been found, which supported the hypothesis of a pathogenic role of DCA in colonic carcinogenesis. This approach was based on the hypothesis that DCA formed in the colon is absorbed into the portal venous blood and exhibits a constant spillover to the systemic circulation. To further substantiate this hypothesis this study investigated whether in the serum of adenoma patients DCA was higher in the unconjugated fraction, which originates directly from the colon. DCA was found to be 2.8-fold higher in the unconjugated fraction of patients with colorectal adenomas than in controls (0.89 v 0.32 mumol/l, p < 0.0025), 1.9-fold in the total DCA fraction (1.89 v 0.95 mumol/l, p < 0.0001), and 1.4-fold in the conjugated fraction (0.67 v 0.47 mumol/l, p < 0.05). It was further found that the bacterial isomerisation product 3 beta-DCA was twofold higher in the unconjugated fraction of adenoma patients than in controls (0.08 v 0.04 mumol/l, p = 0.27), 1.8-fold in the total iso-DCA fraction (0.11 v 0.06 mumol/l, p < 0.05), and 1.5-fold in the conjugated iso-DCA fraction (0.03 v 0.02 mumol/l, p = 0.68). The data suggest that the positive association between the serum DCA concentration and colorectal adenoma as described previously results from the DCA fraction that is absorbed from the colon. This further supports a pathogenic role of DCA in the carcinogenesis of colorectal cancer.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ahlberg J., Angelin B., Björkhem I., Einarsson K. Individual bile acids in portal venous and systemic blood serum of fasting man. Gastroenterology. 1977 Dec;73(6):1377–1382. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Angelin B., Björkhem I., Einarsson K., Ewerth S. Hepatic uptake of bile acids in man. Fasting and postprandial concentrations of individual bile acids in portal venous and systemic blood serum. J Clin Invest. 1982 Oct;70(4):724–731. doi: 10.1172/JCI110668. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bayerdörffer E., Mannes G. A., Richter W. O., Ochsenkühn T., Wiebecke B., Köpcke W., Paumgartner G. Increased serum deoxycholic acid levels in men with colorectal adenomas. Gastroenterology. 1993 Jan;104(1):145–151. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(93)90846-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beuers U., Fischer S., Spengler U., Paumgartner G. Formation of iso-ursodeoxycholic acid during administration of ursodeoxycholic acid in man. J Hepatol. 1991 Jul;13(1):97–103. doi: 10.1016/0168-8278(91)90870-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breuer N. F., Jaekel S., Dommes P., Goebell H. Fecal bile acids in patients with adenomatous polyps of the colon. Case-control study. Digestion. 1986;34(2):87–92. doi: 10.1159/000199315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cambien F., Ducimetiere P., Richard J. Total serum cholesterol and cancer mortality in a middle-aged male population. Am J Epidemiol. 1980 Sep;112(3):388–394. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a113004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cummings J. H., Bingham S. A. Dietary fibre, fermentation and large bowel cancer. Cancer Surv. 1987;6(4):601–621. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cummings J. H., Wiggins H. S., Jenkins D. J., Houston H., Jivraj T., Drasar B. S., Hill M. J. Influence of diets high and low in animal fat on bowel habit, gastrointestinal transit time, fecal microflora, bile acid, and fat excretion. J Clin Invest. 1978 Apr;61(4):953–963. doi: 10.1172/JCI109020. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deschner E. E., Cohen B. I., Raicht R. F. Acute and chronic effect of dietary cholic acid on colonic epithelial cell proliferation. Digestion. 1981;21(6):290–296. doi: 10.1159/000198579. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hikasa Y., Tanida N., Ohno T., Shimoyama T. Faecal bile acid profiles in patients with large bowel cancer in Japan. Gut. 1984 Aug;25(8):833–838. doi: 10.1136/gut.25.8.833. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hofmann A. F., Cravetto C., Molino G., Belforte G., Bona B. Simulation of the metabolism and enterohepatic circulation of endogenous deoxycholic acid in humans using a physiologic pharmacokinetic model for bile acid metabolism. Gastroenterology. 1987 Oct;93(4):693–709. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(87)90430-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imray C. H., Radley S., Davis A., Barker G., Hendrickse C. W., Donovan I. A., Lawson A. M., Baker P. R., Neoptolemos J. P. Faecal unconjugated bile acids in patients with colorectal cancer or polyps. Gut. 1992 Sep;33(9):1239–1245. doi: 10.1136/gut.33.9.1239. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jensen O. M., MacLennan R., Wahrendorf J. Diet, bowel function, fecal characteristics, and large bowel cancer in Denmark and Finland. Nutr Cancer. 1982;4(1):5–19. doi: 10.1080/01635588209513733. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaibara N., Sasaki T., Ikeguchi M., Koga S., Ikawa S. Fecal bile acids and neutral sterols in Japanese with large bowel carcinoma. Oncology. 1983;40(4):255–258. doi: 10.1159/000225738. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karlaganis G., Paumgartner G. Determination of bile acids in serum by capillary gas-liquid chromatography. Clin Chim Acta. 1979 Feb 15;92(1):19–26. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(79)90391-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korpela J. T., Fotsis T., Adlercreutz H. Multicomponent analysis of bile acids in faeces by anion exchange and capillary column gas-liquid chromatography: application in oxytetracycline treated subjects. J Steroid Biochem. 1986 Aug;25(2):277–284. doi: 10.1016/0022-4731(86)90429-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kruis W., Kalek H. D., Stellaard F., Paumgartner G. Altered fecal bile acid pattern in patients with inflammatory bowel disease. Digestion. 1986;35(4):189–198. doi: 10.1159/000199367. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linnet K., Andersen J. R., Hesselfeldt P. Concentrations of glycine- and taurine-conjugated bile acids in portal and systemic venous serum in man. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1984 Jun;19(4):575–578. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macdonald I. A., Bokkenheuser V. D., Winter J., McLernon A. M., Mosbach E. H. Degradation of steroids in the human gut. J Lipid Res. 1983 Jun;24(6):675–700. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Makino I., Nakagawa S., Mashimo K. Conjugated and unconjugated serum bile acid levels n patients with hepatobiliary diseases. Gastroenterology. 1969 Jun;56(6):1033–1039. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mannes G. A., Maier A., Thieme C., Wiebecke B., Paumgartner G. Relation between the frequency of colorectal adenoma and the serum cholesterol level. N Engl J Med. 1986 Dec 25;315(26):1634–1638. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198612253152602. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mannes G. A., Stellaard F., Paumgartner G. Diagnostic sensitivity of fasting and postprandial serum bile acids determined by different methods. Clin Chim Acta. 1987 Jan 30;162(2):147–154. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(87)90446-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mastromarino A. J., Reddy B. S., Wynder E. L. Fecal profiles of anaerobic microflora of large bowel cancer patients and patients with nonhereditary large bowel polyps. Cancer Res. 1978 Dec;38(12):4458–4462. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moskovitz M., White C., Barnett R. N., Stevens S., Russell E., Vargo D., Floch M. H. Diet, fecal bile acids, and neutral sterols in carcinoma of the colon. Dig Dis Sci. 1979 Oct;24(10):746–751. doi: 10.1007/BF01317206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mower H. F., Ray R. M., Shoff R., Stemmermann G. N., Nomura A., Glober G. A., Kamiyama S., Shimada A., Yamakawa H. Fecal bile acids in two Japanese populations with different colon cancer risks. Cancer Res. 1979 Feb;39(2 Pt 1):328–331. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mudd D. G., McKelvey S. T., Norwood W., Elmore D. T., Roy A. D. Faecal bile acid concentration of patients with carcinoma or increased risk of carcinoma in the large bowel. Gut. 1980 Jul;21(7):587–590. doi: 10.1136/gut.21.7.587. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muto T., Bussey H. J., Morson B. C. The evolution of cancer of the colon and rectum. Cancer. 1975 Dec;36(6):2251–2270. doi: 10.1002/cncr.2820360944. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Narisawa T., Magadia N. E., Weisburger J. H., Wynder E. L. Promoting effect of bile acids on colon carcinogenesis after intrarectal instillation of N-methyl-N'-nitro-N-nitrosoguanidine in rats. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1974 Oct;53(4):1093–1097. doi: 10.1093/jnci/53.4.1093. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Northfield T. C., McColl I. Postprandial concentrations of free and conjugated bile acids down the length of the normal human small intestine. Gut. 1973 Jul;14(7):513–518. doi: 10.1136/gut.14.7.513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reddy B. S. Diet and excretion of bile acids. Cancer Res. 1981 Sep;41(9 Pt 2):3766–3768. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reddy B. S. Dietary fat and its relationship to large bowel cancer. Cancer Res. 1981 Sep;41(9 Pt 2):3700–3705. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reddy B. S., Wynder E. L. Metabolic epidemiology of colon cancer. Fecal bile acids and neutral sterols in colon cancer patients and patients with adenomatous polyps. Cancer. 1977 Jun;39(6):2533–2539. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(197706)39:6<2533::aid-cncr2820390634>3.0.co;2-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Redinger R. N. The economy of the enterohepatic circulation of bile acids in the baboon. 2. Regulation of bile acid synthesis by enterohepatic circulation of bile acids. J Lipid Res. 1984 May;25(5):437–447. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schalm S. W., LaRusso N. F., Hofmann A. F., Hoffman N. E., van Berge-Henegouwen G. P., Korman M. G. Diurnal serum levels of primary conjugated bile acids. Assessment by specific radioimmunoassays for conjugates of cholic and chenodeoxycholic acid. Gut. 1978 Nov;19(11):1006–1014. doi: 10.1136/gut.19.11.1006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Setchell K. D., Ives J. A., Cashmore G. C., Lawson A. M. On the homogeneity of stools with respect to bile acid composition and normal day-to-day variations: a detailed qualitative and quantitative study using capillary column gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. Clin Chim Acta. 1987 Feb 15;162(3):257–275. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(87)90045-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Setchell K. D., Lawson A. M., Blackstock E. J., Murphy G. M. Diurnal changes in serum unconjugated bile acids in normal man. Gut. 1982 Aug;23(8):637–642. doi: 10.1136/gut.23.8.637. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Setchell K. D., Matsui A. Serum bile acid analysis. Clin Chim Acta. 1983 Jan 7;127(1):1–17. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(83)90070-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Setchell K. D., Worthington J. A rapid method for the quantitative extraction of bile acids and their conjugates from serum using commercially available reverse-phase octadecylsilane bonded silica cartridges. Clin Chim Acta. 1982 Oct 27;125(2):135–144. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(82)90190-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shafritz D. A., Shouval D., Zern M. A. Recombinant DNA and the liver: studies with albumin, alpha-fetoprotein, hepatitis B virus, and other DNA probes. Prog Liver Dis. 1982;7:429–449. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shefer S., Salen G., Hauser S., Dayal B., Batta A. K. Metabolism of iso-bile acids in the rat. J Biol Chem. 1982 Feb 10;257(3):1401–1406. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Small D. M., Dowling R. H., Redinger R. N. The enterohepatic circulation of bile salts. Arch Intern Med. 1972 Oct;130(4):552–573. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stellaard F., Paumgartner G. Measurement of isotope ratios in organic compounds at picomole quantities by capillary gas chromatography/quadrupole electron impact mass spectrometry. Biomed Mass Spectrom. 1985 Sep;12(9):560–564. doi: 10.1002/bms.1200120920. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stellaard F., Sackmann M., Sauerbruch T., Paumgartner G. Simultaneous determination of cholic acid and chenodeoxycholic acid pool sizes and fractional turnover rates in human serum using 13C-labeled bile acids. J Lipid Res. 1984 Dec 1;25(12):1313–1319. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stellaard F., Sauerbruch T., Luderschmidt C. H., Leisner B., Paumgartner G. Intestinal involvement in progressive systemic sclerosis detected by increased unconjugated serum bile acids. Gut. 1987 Apr;28(4):446–450. doi: 10.1136/gut.28.4.446. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanida N., Hikasa Y., Shimoyama T., Setchell K. D. Comparison of faecal bile acid profiles between patients with adenomatous polyps of the large bowel and healthy subjects in Japan. Gut. 1984 Aug;25(8):824–832. doi: 10.1136/gut.25.8.824. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas C. B., Duszynski K. R., Shaffer J. W. Cholesterol levels in young adulthood and subsequent cancer: a preliminary note. Johns Hopkins Med J. 1982 Mar;150(3):89–94. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



