Abstract
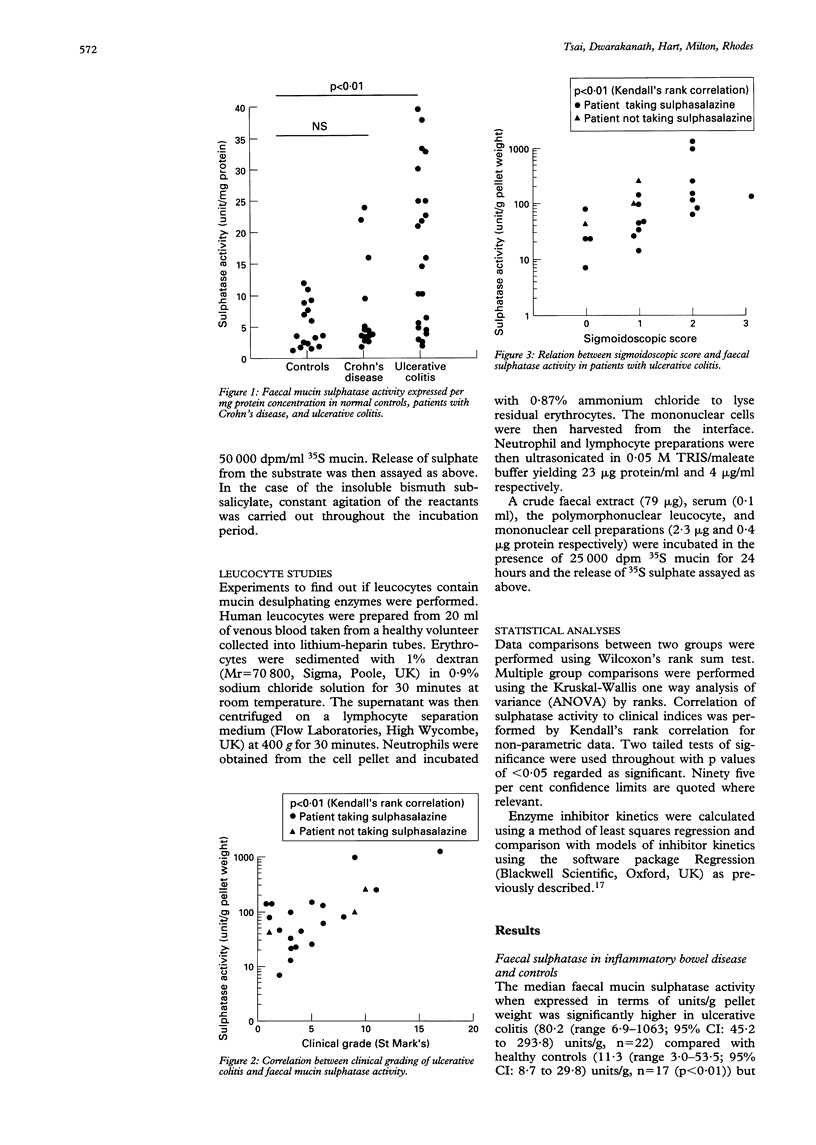
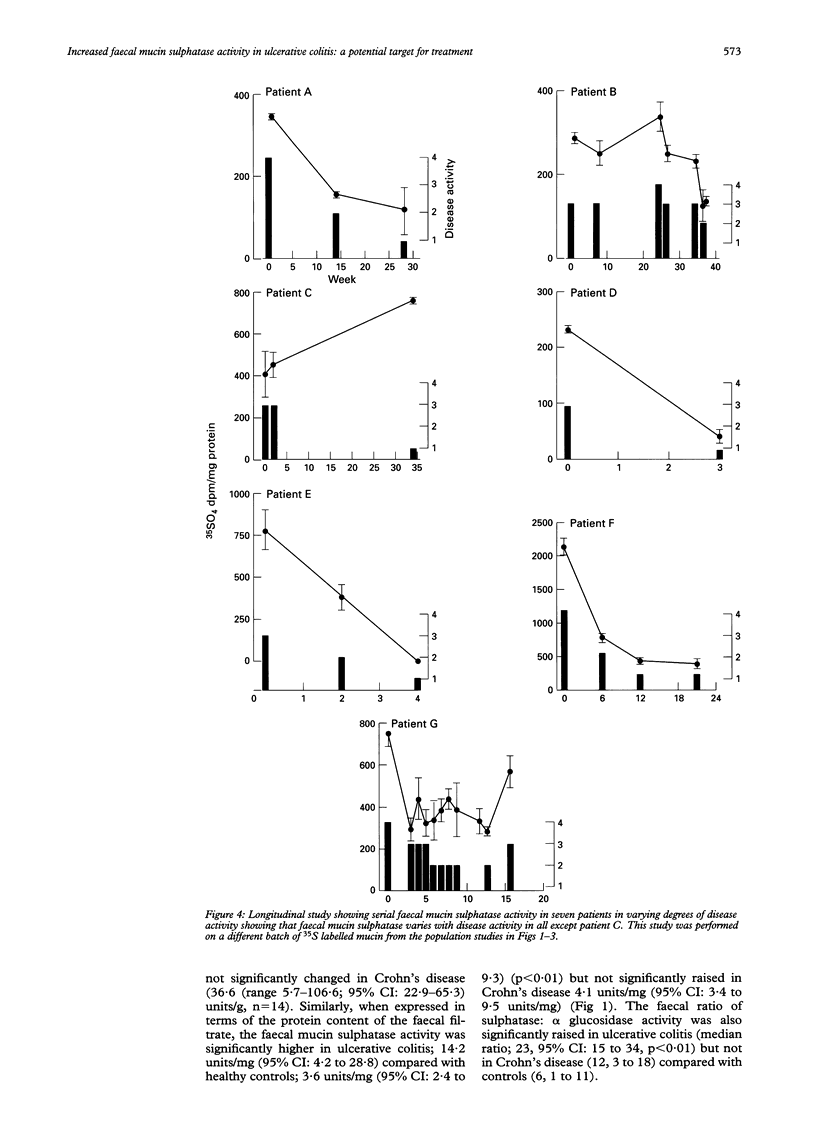
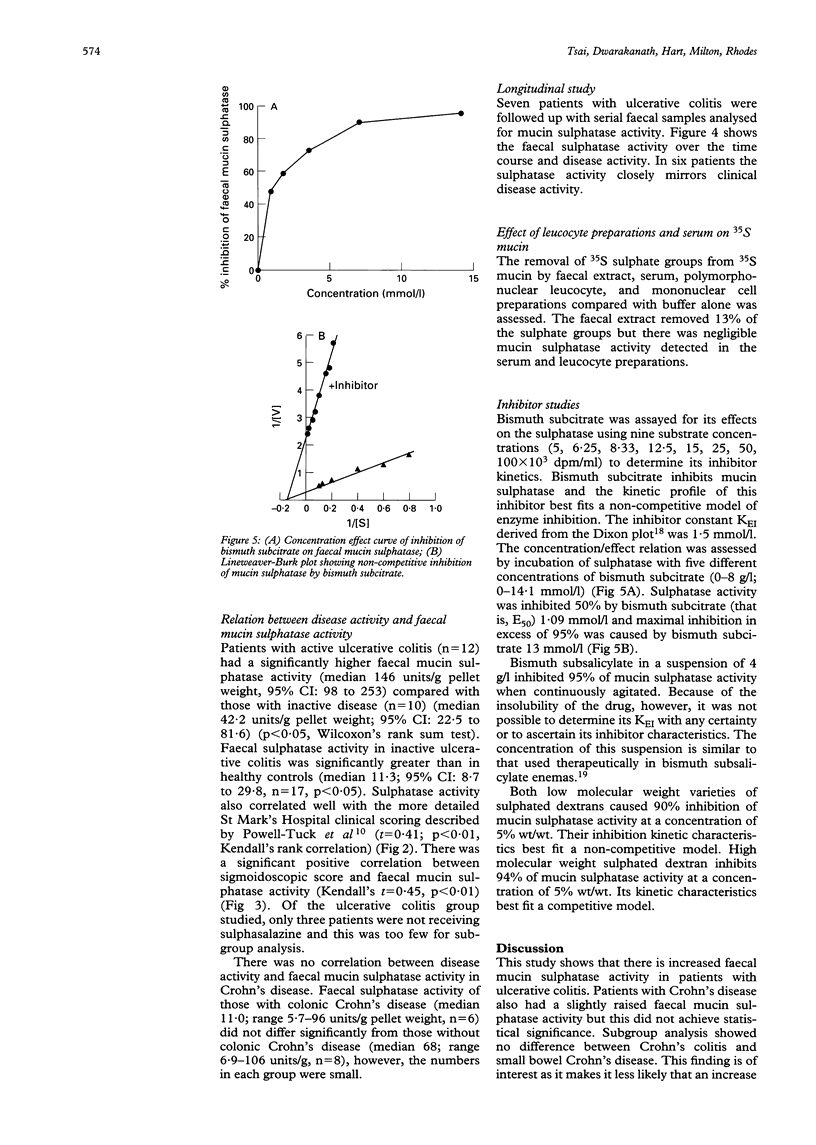
Colonic mucin is heavily sulphated and it has been shown that enzymatic desulphation by faecal bacterial sulphatases greatly increases its susceptibility to degradation by faecal glycosidases. A possible role for faecal mucin sulphatase in the pathogenesis of inflammatory bowel disease has therefore been explored. Faecal mucin sulphatase activity assayed using 35S mucin as substrate was increased in ulcerative colitis (median 80.2 units/g pellet weight (range 6.9-1063; 95% confidence intervals (CI): 45.2 to 293.8, n = 22) compared with 11.3 units/g (range 3.0-53.5; 95% CI: 8.7 to 29.8, n = 17) in healthy controls (p < 0.01), where one unit released 1000 dpm free sulphate/hour from 35S mucin (1680 dpm/microgram). Patients with active ulcerative colitis had higher sulphatase activity (median 146; 95% CI: 98 to 253 units/g, n = 10) than those with inactive ulcerative colitis (median 42.2; CI: 22.5 to 81.6 units/g, n = 12) (p < 0.05). Longitudinal studies in patients with ulcerative colitis show fluctuations of faecal mucin sulphatase activity corresponding to clinical disease activity in six of seven patients. Faecal mucin sulphatase activity was not significantly increased in Crohn's disease (median 36.6, range 5.7-106.6; 95% CI: 22.9 to 65.3 units/g, n = 14). The bismuth salts, bismuth subcitrate and bismuth subsalicylate were found to inhibit faecal mucin sulphatase activity at concentrations achievable therapeutically. The increased faecal mucin sulphatase activity in ulcerative colitis could be the result of greater intraluminal substrate (mucin) availability leading to bacterial enzyme induction, but would probably result in more rapid degradation of secreted mucin and represents a potential target for treatment.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Burke D. A., Axon A. T., Clayden S. A., Dixon M. F., Johnston D., Lacey R. W. The efficacy of tobramycin in the treatment of ulcerative colitis. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 1990 Apr;4(2):123–129. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2036.1990.tb00456.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chapman R. W., Selby W. S., Jewell D. P. Controlled trial of intravenous metronidazole as an adjunct to corticosteroids in severe ulcerative colitis. Gut. 1986 Oct;27(10):1210–1212. doi: 10.1136/gut.27.10.1210. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corfield A. P., Wagner S. A., O'Donnell L. J., Durdey P., Mountford R. A., Clamp J. R. The roles of enteric bacterial sialidase, sialate O-acetyl esterase and glycosulfatase in the degradation of human colonic mucin. Glycoconj J. 1993 Feb;10(1):72–81. doi: 10.1007/BF00731190. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corfield A. P., Williams A. J., Clamp J. R., Wagner S. A., Mountford R. A. Degradation by bacterial enzymes of colonic mucus from normal subjects and patients with inflammatory bowel disease: the role of sialic acid metabolism and the detection of a novel O-acetylsialic acid esterase. Clin Sci (Lond) 1988 Jan;74(1):71–78. doi: 10.1042/cs0740071. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Creeth J. M. Constituents of mucus and their separation. Br Med Bull. 1978 Jan;34(1):17–24. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.bmb.a071454. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dickinson R. J., O'Connor H. J., Pinder I., Hamilton I., Johnston D., Axon A. T. Double blind controlled trial of oral vancomycin as adjunctive treatment in acute exacerbations of idiopathic colitis. Gut. 1985 Dec;26(12):1380–1384. doi: 10.1136/gut.26.12.1380. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FELSEN J., WOLARSKY W. Acute and chronic bacillary dysentery and chronic ulcerative colitis. J Am Med Assoc. 1953 Nov 21;153(12):1069–1072. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Filipe M. I., Dawson I. The diagnostic value of mucosubstances in rectal biopsies from patients with ulcerative colitis and Crohn's disease. Gut. 1970 Mar;11(3):229–234. doi: 10.1136/gut.11.3.229. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Filipe M. I. Mucins in the human gastrointestinal epithelium: a review. Invest Cell Pathol. 1979 Jul-Sep;2(3):195–216. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gomes P., du Boulay C., Smith C. L., Holdstock G. Relationship between disease activity indices and colonoscopic findings in patients with colonic inflammatory bowel disease. Gut. 1986 Jan;27(1):92–95. doi: 10.1136/gut.27.1.92. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorbach S. L., Nahas L., Plaut A. G., Weinstein L., Patterson J. F., Levitan R. Studies of intestinal microflora. V. Fecal microbial ecology in ulcerative colitis and regional enteritis: relationship to severity of disease and chemotherapy. Gastroenterology. 1968 Apr;54(4):575–587. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harvey R. F., Bradshaw J. M. A simple index of Crohn's-disease activity. Lancet. 1980 Mar 8;1(8167):514–514. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(80)92767-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoskins L. C., Agustines M., McKee W. B., Boulding E. T., Kriaris M., Niedermeyer G. Mucin degradation in human colon ecosystems. Isolation and properties of fecal strains that degrade ABH blood group antigens and oligosaccharides from mucin glycoproteins. J Clin Invest. 1985 Mar;75(3):944–953. doi: 10.1172/JCI111795. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mian N., Anderson C. E., Kent P. W. Effect of O-sulphate groups in lactose and N-acetylneuraminyl-lactose on their enzymic hydrolysis. Biochem J. 1979 Aug 1;181(2):387–399. doi: 10.1042/bj1810387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller R. S., Hoskins L. C. Mucin degradation in human colon ecosystems. Fecal population densities of mucin-degrading bacteria estimated by a "most probable number" method. Gastroenterology. 1981 Oct;81(4):759–765. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Onderdonk A. B., Hermos J. A., Dzink J. L., Bartlett J. G. Protective effect of metronidazole in experimental ulcerative colitis. Gastroenterology. 1978 Mar;74(3):521–526. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker N., Finnie I. A., Raouf A. H., Ryder S. D., Campbell B. J., Tsai H. H., Iddon D., Milton J. D., Rhodes J. M. High performance gel filtration using monodisperse highly cross-linked agarose as a one-step system for mucin purification. Biomed Chromatogr. 1993 Mar-Apr;7(2):68–74. doi: 10.1002/bmc.1130070204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Potier M., Mameli L., Bélisle M., Dallaire L., Melançon S. B. Fluorometric assay of neuraminidase with a sodium (4-methylumbelliferyl-alpha-D-N-acetylneuraminate) substrate. Anal Biochem. 1979 Apr 15;94(2):287–296. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(79)90362-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powell-Tuck J., Bown R. L., Lennard-Jones J. E. A comparison of oral prednisolone given as single or multiple daily doses for active proctocolitis. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1978;13(7):833–837. doi: 10.3109/00365527809182199. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pullan R. D., Thomas G. A., Rhodes M., Newcombe R. G., Williams G. T., Allen A., Rhodes J. Thickness of adherent mucus gel on colonic mucosa in humans and its relevance to colitis. Gut. 1994 Mar;35(3):353–359. doi: 10.1136/gut.35.3.353. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raouf A. H., Tsai H. H., Parker N., Hoffman J., Walker R. J., Rhodes J. M. Sulphation of colonic and rectal mucin in inflammatory bowel disease: reduced sulphation of rectal mucus in ulcerative colitis. Clin Sci (Lond) 1992 Nov;83(5):623–626. doi: 10.1042/cs0830623. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raouf A., Parker N., Iddon D., Ryder S., Langdon-Brown B., Milton J. D., Walker R., Rhodes J. M. Ion exchange chromatography of purified colonic mucus glycoproteins in inflammatory bowel disease: absence of a selective subclass defect. Gut. 1991 Oct;32(10):1139–1145. doi: 10.1136/gut.32.10.1139. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhodes J. M., Black R. R., Gallimore R., Savage A. Histochemical demonstration of desialation and desulphation of normal and inflammatory bowel disease rectal mucus by faecal extracts. Gut. 1985 Dec;26(12):1312–1318. doi: 10.1136/gut.26.12.1312. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberton A. M., McKenzie C. G., Sharfe N., Stubbs L. B. A glycosulphatase that removes sulphate from mucus glycoprotein. Biochem J. 1993 Aug 1;293(Pt 3):683–689. doi: 10.1042/bj2930683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roediger W. E. What sequence of pathogenetic events leads to acute ulcerative colitis? Dis Colon Rectum. 1988 Jun;31(6):482–487. doi: 10.1007/BF02552623. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roy A. B. Sulphatases, lysosomes and disease. Aust J Exp Biol Med Sci. 1976 Apr;54(2):111–135. doi: 10.1038/icb.1976.13. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryder S. D., Walker R. J., Jones H., Rhodes J. M. Rectal bismuth subsalicylate as therapy for ulcerative colitis. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 1990 Aug;4(4):333–338. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2036.1990.tb00480.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith P. K., Krohn R. I., Hermanson G. T., Mallia A. K., Gartner F. H., Provenzano M. D., Fujimoto E. K., Goeke N. M., Olson B. J., Klenk D. C. Measurement of protein using bicinchoninic acid. Anal Biochem. 1985 Oct;150(1):76–85. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(85)90442-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spicer S. S., Leppi T. J., Stoward P. J. Suggestions for a histochemical terminology of carbohydrate-rich tissue components. J Histochem Cytochem. 1965 Sep-Oct;13(7):599–603. doi: 10.1177/13.7.599. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trier J. S. Organ-culture methods in the study of gastrointestinal-mucosal function and development. N Engl J Med. 1976 Jul 15;295(3):150–155. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197607152950308. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai H. H. Statistical analyses of enzyme inhibitor kinetics: a hierarchical model-dependent approach. Biochem Int. 1991 Jan;23(1):75–81. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai H. H., Sunderland D., Gibson G. R., Hart C. A., Rhodes J. M. A novel mucin sulphatase from human faeces: its identification, purification and characterization. Clin Sci (Lond) 1992 Apr;82(4):447–454. doi: 10.1042/cs0820447. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Silva H. J., Millard P. R., Kettlewell M., Mortensen N. J., Prince C., Jewell D. P. Mucosal characteristics of pelvic ileal pouches. Gut. 1991 Jan;32(1):61–65. doi: 10.1136/gut.32.1.61. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Wiel-Korstanje J. A., Winkler K. C. The faecal flora in ulcerative colitis. J Med Microbiol. 1975 Nov;8(4):491–501. doi: 10.1099/00222615-8-4-491. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


