Abstract
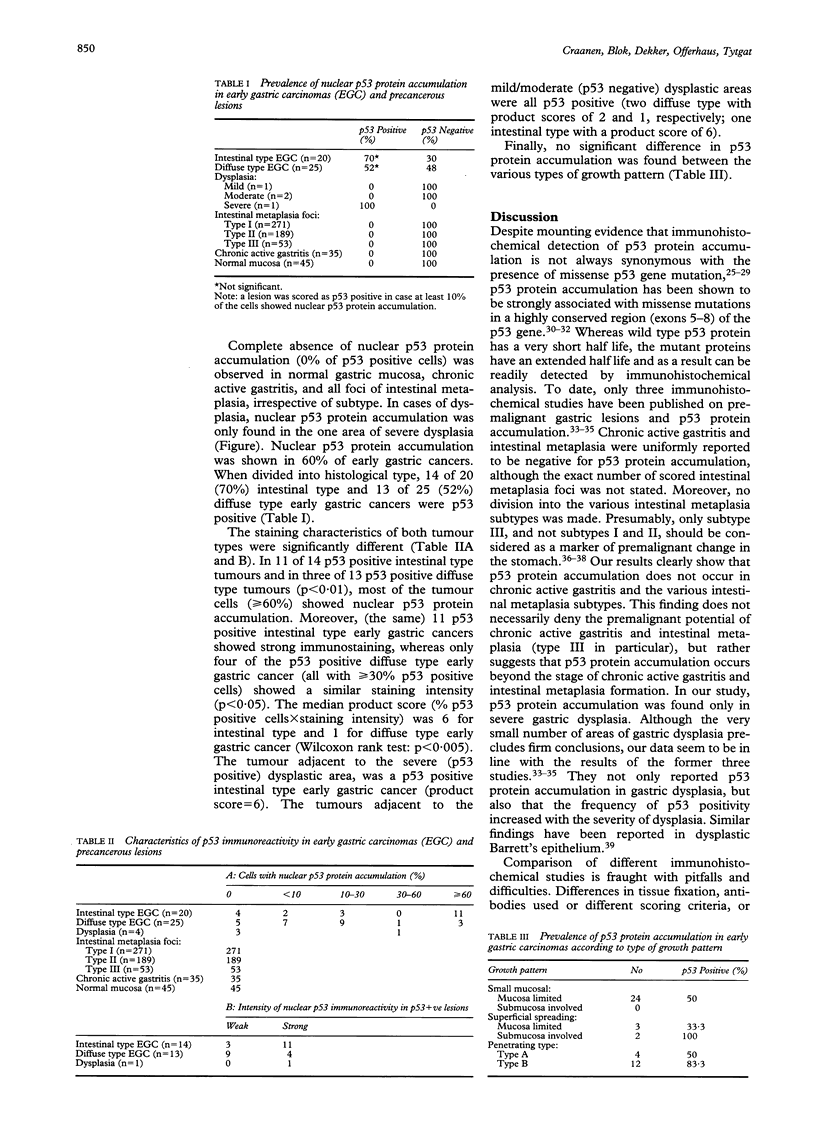
p53 Protein accumulation in early gastric carcinoma was studied in relation to the histological type (Lauren classification) and the type of growth pattern, including the chronology of p53 protein accumulation during carcinogenesis. Forty five, paraffin embedded gastrectomy specimens from early carcinomas were examined for the presence of chronic atrophic gastritis, subtypes of intestinal metaplasia, and dysplasia. The Lauren type and the type of growth pattern were reassessed for all early carcinomas. p53 Protein accumulation was examined using the monoclonal antibody DO-7. Complete absence of p53 protein accumulation was observed in normal gastric mucosa, chronic atrophic gastritis, and intestinal metaplasia, irrespective of subtype. In gastric dysplasia (one mild, two moderate, and one severe), only severe dysplasia was p53 positive. Intestinal type (n = 20) and diffuse type early gastric carcinomas (n = 25) were p53 positive in 70% and 52% of cases, respectively. Both tumour types differed significantly in the percentage of p53 positive tumour cells per tumour (p < 0.01) and in staining intensity (p < 0.05). No significant difference in p53 protein accumulation was found between early carcinomas with different types of growth pattern. It is concluded that p53 protein accumulation--usually reflecting missense p53 gene mutation--seems to be a late event in gastric carcinogenesis. Moreover, it is suggested that missense p53 gene mutation occurs in a final pathway common to both intestinal and diffuse type of early gastric carcinoma. Finally, the types of growth pattern do not seem to differ in p53 protein accumulation.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baas I. O., Mulder J. W., Offerhaus G. J., Vogelstein B., Hamilton S. R. An evaluation of six antibodies for immunohistochemistry of mutant p53 gene product in archival colorectal neoplasms. J Pathol. 1994 Jan;172(1):5–12. doi: 10.1002/path.1711720104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Banks L., Matlashewski G., Crawford L. Isolation of human-p53-specific monoclonal antibodies and their use in the studies of human p53 expression. Eur J Biochem. 1986 Sep 15;159(3):529–534. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1986.tb09919.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Battifora H. p53 immunohistochemistry: a word of caution. Hum Pathol. 1994 May;25(5):435–437. doi: 10.1016/0046-8177(94)90113-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chowdary D. R., Dermody J. J., Jha K. K., Ozer H. L. Accumulation of p53 in a mutant cell line defective in the ubiquitin pathway. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 Mar;14(3):1997–2003. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.3.1997. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarke A. R., Purdie C. A., Harrison D. J., Morris R. G., Bird C. C., Hooper M. L., Wyllie A. H. Thymocyte apoptosis induced by p53-dependent and independent pathways. Nature. 1993 Apr 29;362(6423):849–852. doi: 10.1038/362849a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Correa P. Precursors of gastric and esophageal cancer. Cancer. 1982 Dec 1;50(11 Suppl):2554–2565. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craanen M. E., Dekker W., Ferwerda J., Blok P., Tytgat G. N. Early gastric cancer: a clinicopathologic study. J Clin Gastroenterol. 1991 Jun;13(3):274–283. doi: 10.1097/00004836-199106000-00006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davessar K., Pezzullo J. C., Kessimian N., Hale J. H., Jauregui H. O. Gastric adenocarcinoma: prognostic significance of several pathologic parameters and histologic classifications. Hum Pathol. 1990 Mar;21(3):325–332. doi: 10.1016/0046-8177(90)90234-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davidoff A. M., Humphrey P. A., Iglehart J. D., Marks J. R. Genetic basis for p53 overexpression in human breast cancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jun 1;88(11):5006–5010. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.11.5006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gannon J. V., Greaves R., Iggo R., Lane D. P. Activating mutations in p53 produce a common conformational effect. A monoclonal antibody specific for the mutant form. EMBO J. 1990 May;9(5):1595–1602. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08279.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iggo R., Gatter K., Bartek J., Lane D., Harris A. L. Increased expression of mutant forms of p53 oncogene in primary lung cancer. Lancet. 1990 Mar 24;335(8691):675–679. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(90)90801-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imazeki F., Omata M., Nose H., Ohto M., Isono K. p53 gene mutations in gastric and esophageal cancers. Gastroenterology. 1992 Sep;103(3):892–896. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(92)90022-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jass J. R., Filipe M. I. Sulphomucins and precancerous lesions of the human stomach. Histopathology. 1980 May;4(3):271–279. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2559.1980.tb02921.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joypaul B. V., Newman E. L., Hopwood D., Grant A., Qureshi S., Lane D. P., Cuschieri A. Expression of p53 protein in normal, dysplastic, and malignant gastric mucosa: an immunohistochemical study. J Pathol. 1993 Jul;170(3):279–283. doi: 10.1002/path.1711700310. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kakeji Y., Korenaga D., Tsujitani S., Baba H., Anai H., Maehara Y., Sugimachi K. Gastric cancer with p53 overexpression has high potential for metastasising to lymph nodes. Br J Cancer. 1993 Mar;67(3):589–593. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1993.108. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kodama Y., Inokuchi K., Soejima K., Matsusaka T., Okamura T. Growth patterns and prognosis in early gastric carcinoma. Superficially spreading and penetrating growth types. Cancer. 1983 Jan 15;51(2):320–326. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19830115)51:2<320::aid-cncr2820510226>3.0.co;2-#. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LAUREN P. THE TWO HISTOLOGICAL MAIN TYPES OF GASTRIC CARCINOMA: DIFFUSE AND SO-CALLED INTESTINAL-TYPE CARCINOMA. AN ATTEMPT AT A HISTO-CLINICAL CLASSIFICATION. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand. 1965;64:31–49. doi: 10.1111/apm.1965.64.1.31. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lambkin H. A., Mothersill C. M., Kelehan P. Variations in immunohistochemical detection of p53 protein overexpression in cervical carcinomas with different antibodies and methods of detection. J Pathol. 1994 Jan;172(1):13–18. doi: 10.1002/path.1711720105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lauwers G. Y., Wahl S. J., Melamed J., Rojas-Corona R. R. p53 expression in precancerous gastric lesions: an immunohistochemical study of PAb 1801 monoclonal antibody on adenomatous and hyperplastic gastric polyps. Am J Gastroenterol. 1993 Nov;88(11):1916–1919. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowe S. W., Ruley H. E., Jacks T., Housman D. E. p53-dependent apoptosis modulates the cytotoxicity of anticancer agents. Cell. 1993 Sep 24;74(6):957–967. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90719-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowe S. W., Schmitt E. M., Smith S. W., Osborne B. A., Jacks T. p53 is required for radiation-induced apoptosis in mouse thymocytes. Nature. 1993 Apr 29;362(6423):847–849. doi: 10.1038/362847a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marks J. R., Davidoff A. M., Kerns B. J., Humphrey P. A., Pence J. C., Dodge R. K., Clarke-Pearson D. L., Iglehart J. D., Bast R. C., Jr, Berchuck A. Overexpression and mutation of p53 in epithelial ovarian cancer. Cancer Res. 1991 Jun 1;51(11):2979–2984. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin H. M., Filipe M. I., Morris R. W., Lane D. P., Silvestre F. p53 expression and prognosis in gastric carcinoma. Int J Cancer. 1992 Apr 1;50(6):859–862. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910500604. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKee P. H., Hobbs C., Hall P. A. Antigen retrieval by microwave irradiation lowers immunohistological detection thresholds. Histopathology. 1993 Oct;23(4):377–379. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2559.1993.tb01223.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Midgley C. A., Fisher C. J., Bártek J., Vojtesek B., Lane D., Barnes D. M. Analysis of p53 expression in human tumours: an antibody raised against human p53 expressed in Escherichia coli. J Cell Sci. 1992 Jan;101(Pt 1):183–189. doi: 10.1242/jcs.101.1.183. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Misiewicz J. J. The Sydney System: a new classification of gastritis. Introduction. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 1991 May-Jun;6(3):207–208. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1746.1991.tb01467.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muñoz N., Correa P., Cuello C., Duque E. Histologic types of gastric carcinoma in high- and low-risk areas. Int J Cancer. 1968 Nov 15;3(6):809–818. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910030614. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nomura A., Stemmermann G. N., Chyou P. H., Kato I., Perez-Perez G. I., Blaser M. J. Helicobacter pylori infection and gastric carcinoma among Japanese Americans in Hawaii. N Engl J Med. 1991 Oct 17;325(16):1132–1136. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199110173251604. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parsonnet J., Friedman G. D., Vandersteen D. P., Chang Y., Vogelman J. H., Orentreich N., Sibley R. K. Helicobacter pylori infection and the risk of gastric carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 1991 Oct 17;325(16):1127–1131. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199110173251603. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Price A. B. The Sydney System: histological division. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 1991 May-Jun;6(3):209–222. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1746.1991.tb01468.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rokkas T., Filipe M. I., Sladen G. E. Detection of an increased incidence of early gastric cancer in patients with intestinal metaplasia type III who are closely followed up. Gut. 1991 Oct;32(10):1110–1113. doi: 10.1136/gut.32.10.1110. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rugge M., Shiao Y. H., Correa P., Baffa R., DiMario F. Immunohistochemical evidence of p53 overexpression in gastric epithelial dysplasia. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 1992 Nov-Dec;1(7):551–554. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shiao Y. H., Rugge M., Correa P., Lehmann H. P., Scheer W. D. p53 alteration in gastric precancerous lesions. Am J Pathol. 1994 Mar;144(3):511–517. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sipponen P., Kosunen T. U., Valle J., Riihelä M., Seppälä K. Helicobacter pylori infection and chronic gastritis in gastric cancer. J Clin Pathol. 1992 Apr;45(4):319–323. doi: 10.1136/jcp.45.4.319. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Starzynska T., Bromley M., Ghosh A., Stern P. L. Prognostic significance of p53 overexpression in gastric and colorectal carcinoma. Br J Cancer. 1992 Sep;66(3):558–562. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1992.314. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamura G., Kihana T., Nomura K., Terada M., Sugimura T., Hirohashi S. Detection of frequent p53 gene mutations in primary gastric cancer by cell sorting and polymerase chain reaction single-strand conformation polymorphism analysis. Cancer Res. 1991 Jun 1;51(11):3056–3058. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unger C., Kress S., Buchmann A., Schwarz M. Gamma-irradiation-induced micronuclei from mouse hepatoma cells accumulate high levels of the tumor suppressor protein p53. Cancer Res. 1994 Jul 15;54(14):3651–3655. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogelstein B., Fearon E. R., Hamilton S. R., Kern S. E., Preisinger A. C., Leppert M., Nakamura Y., White R., Smits A. M., Bos J. L. Genetic alterations during colorectal-tumor development. N Engl J Med. 1988 Sep 1;319(9):525–532. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198809013190901. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vojtesek B., Bártek J., Midgley C. A., Lane D. P. An immunochemical analysis of the human nuclear phosphoprotein p53. New monoclonal antibodies and epitope mapping using recombinant p53. J Immunol Methods. 1992 Jul 6;151(1-2):237–244. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(92)90122-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wynford-Thomas D. P53 in tumour pathology: can we trust immunocytochemistry? J Pathol. 1992 Apr;166(4):329–330. doi: 10.1002/path.1711660402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamada Y., Yoshida T., Hayashi K., Sekiya T., Yokota J., Hirohashi S., Nakatani K., Nakano H., Sugimura T., Terada M. p53 gene mutations in gastric cancer metastases and in gastric cancer cell lines derived from metastases. Cancer Res. 1991 Nov 1;51(21):5800–5805. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Younes M., Lebovitz R. M., Lechago L. V., Lechago J. p53 protein accumulation in Barrett's metaplasia, dysplasia, and carcinoma: a follow-up study. Gastroenterology. 1993 Dec;105(6):1637–1642. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(93)91058-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



