Abstract
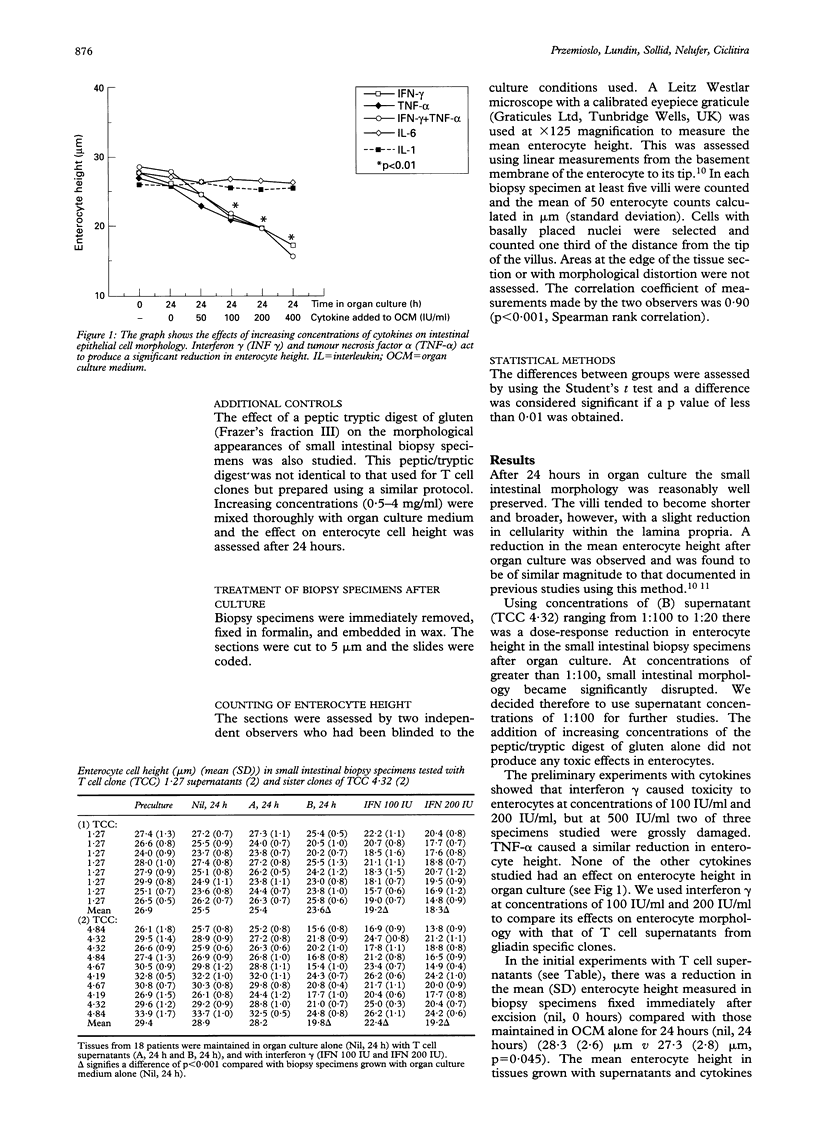
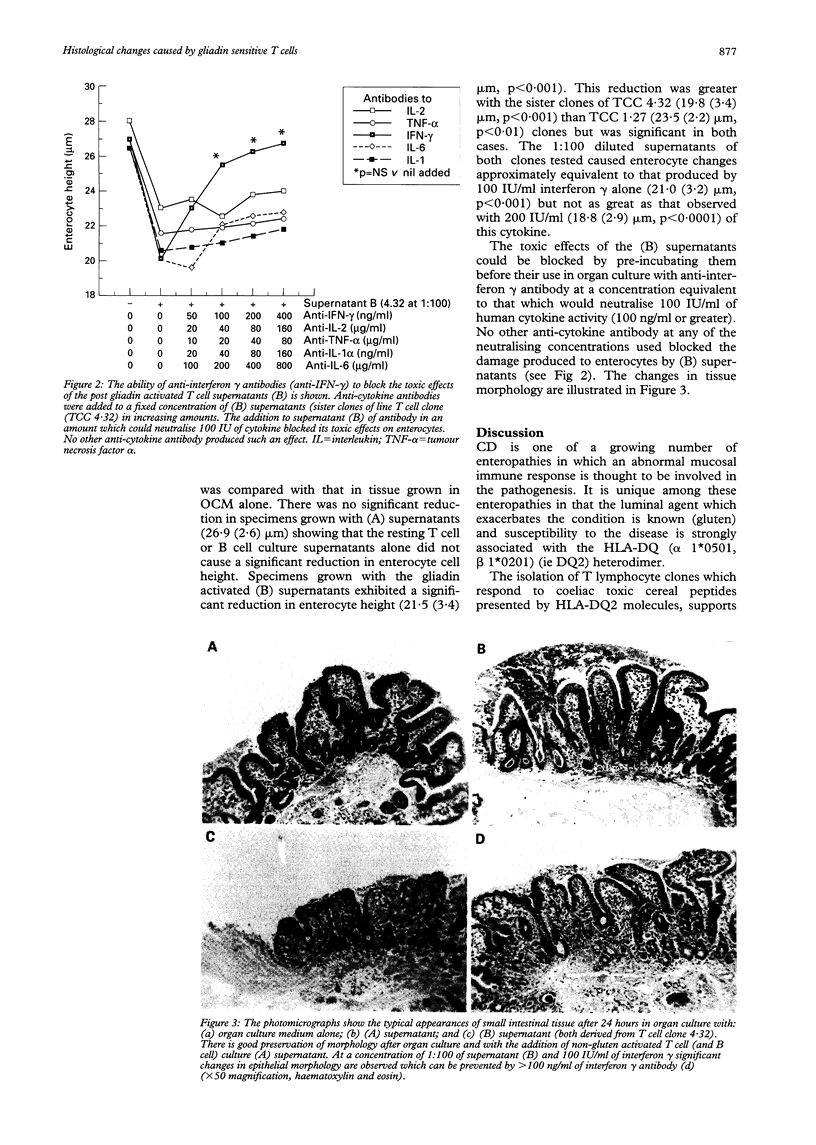
The isolation of gliadin specific HLA-DQ2 restricted T lymphocyte clones from the intestinal mucosa of patients with coeliac disease supports a role for cell mediated immunity in the pathogenesis of this condition. Whether supernatants from immune activated T cell clones could produce histological damage to duodenal mucosa in vitro was studied. Biopsy specimens were obtained from 18 patients without coeliac disease or any other demonstrable abnormality. The tissue was maintained in organ culture for 24 hours with organ culture medium alone, with supernatant from gliadin sensitive T cell clones that had (B) or had not (A) been stimulated with gluten, and compared with the effects caused by the addition of interferon gamma to the organ culture medium. Both the (B) supernatants (1:100) and interferon gamma (100 IU/ml) produced a significant reduction in the enterocyte height (21:5 (3.4) microns and 21.0 (3.2) microns respectively, each p < 0.001) compared with specimens grown in organ culture medium alone (27.3 (2.8) microns). The toxic effects of (B) supernatants could be blocked by pre-incubating them with anti-interferon gamma antibody. These findings support the role of gliadin sensitive T lymphocytes in the immune pathogenesis of coeliac disease and their secretion of interferon gamma may cause the damage to enterocytes observed in this condition.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adamson G. M., Billings R. E. Cytokine toxicity and induction of NO synthase activity in cultured mouse hepatocytes. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 1993 Mar;119(1):100–107. doi: 10.1006/taap.1993.1048. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Browning T. H., Trier J. S. Organ culture of mucosal biopsies of human small intestine. J Clin Invest. 1969 Aug;48(8):1423–1432. doi: 10.1172/JCI106108. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deem R. L., Shanahan F., Targan S. R. Triggered human mucosal T cells release tumour necrosis factor-alpha and interferon-gamma which kill human colonic epithelial cells. Clin Exp Immunol. 1991 Jan;83(1):79–84. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.1991.tb05592.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fluge G., Aksnes L. Morphological and morphometric assessment of human duodenal biopsies maintained in organ culture. In vitro influences of gluten in coeliac disease. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1981;16(4):555–567. doi: 10.3109/00365528109182012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gedde-Dahl T., 3rd, Nilsen E., Thorsby E., Gaudernack G. Growth inhibition of a colonic adenocarcinoma cell line (HT29) by T cells specific for mutant p21 ras. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 1994 Feb;38(2):127–134. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glucksberg H., Storb R., Fefer A., Buckner C. D., Neiman P. E., Clift R. A., Lerner K. G., Thomas E. D. Clinical manifestations of graft-versus-host disease in human recipients of marrow from HL-A-matched sibling donors. Transplantation. 1974 Oct;18(4):295–304. doi: 10.1097/00007890-197410000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grau G. E., Lambert P. H., Vassalli P., Piguet P. F. Tumor necrosis factor (TNF) et pathologie; ses relations avec d'autres cytokines. Schweiz Med Wochenschr. 1989 Dec 9;119(49):1756–1761. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guy-Grand D., Vassalli P. Gut injury in mouse graft-versus-host reaction. Study of its occurrence and mechanisms. J Clin Invest. 1986 May;77(5):1584–1595. doi: 10.1172/JCI112474. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halstensen T. S., Brandtzaeg P. Activated T lymphocytes in the celiac lesion: non-proliferative activation (CD25) of CD4+ alpha/beta cells in the lamina propria but proliferation (Ki-67) of alpha/beta and gamma/delta cells in the epithelium. Eur J Immunol. 1993 Feb;23(2):505–510. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830230231. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howdle P. D., Corazza G. R., Bullen A. W., Losowsky M. S. Gluten sensitivity of small intestinal mucosa in vitro: quantitative assessment of histologic change. Gastroenterology. 1981 Mar;80(3):442–450. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelsey S. M., Allen P. D., Razak K., Macey M. G., Newland A. C. Induction of surface tumor necrosis factor (TNF) expression and possible facilitation of surface TNF release from human monocytic cells by granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor or gamma interferon in combination with 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3. Exp Hematol. 1993 Jul;21(7):864–869. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kontakou M., Sturgess R. P., Przemioslo R. T., Limb G. A., Nelufer J. M., Ciclitira P. J. Detection of interferon gamma mRNA in the mucosa of patients with coeliac disease by in situ hybridisation. Gut. 1994 Aug;35(8):1037–1041. doi: 10.1136/gut.35.8.1037. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Longstreth G. F. Successful treatment of refractory sprue with cyclosporine. Ann Intern Med. 1993 Nov 15;119(10):1014–1016. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-119-10-199311150-00008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lundin K. E., Scott H., Hansen T., Paulsen G., Halstensen T. S., Fausa O., Thorsby E., Sollid L. M. Gliadin-specific, HLA-DQ(alpha 1*0501,beta 1*0201) restricted T cells isolated from the small intestinal mucosa of celiac disease patients. J Exp Med. 1993 Jul 1;178(1):187–196. doi: 10.1084/jem.178.1.187. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lundin K. E., Sollid L. M., Bosnes V., Gaudernack G., Thorsby E. T-cell recognition of HLA class II molecules induced by gamma-interferon on a colonic adenocarcinoma cell line (HT29). Scand J Immunol. 1990 Apr;31(4):469–475. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1990.tb02794.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacDonald T. T., Spencer J. Evidence that activated mucosal T cells play a role in the pathogenesis of enteropathy in human small intestine. J Exp Med. 1988 Apr 1;167(4):1341–1349. doi: 10.1084/jem.167.4.1341. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchison H. C., al Mardini H., Gillespie S., Laker M., Zaitoun A., Record C. O. A pilot study of fluticasone propionate in untreated coeliac disease. Gut. 1991 Mar;32(3):260–265. doi: 10.1136/gut.32.3.260. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piguet P. F. GVHR elicited by products of class I or class II loci of the MHC: analysis of the response of mouse T lymphocytes to products of class I and class II loci of the MHC in correlation with GVHR-induced mortality, medullary aplasia, and enteropathy. J Immunol. 1985 Sep;135(3):1637–1643. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Przemioslo R. T., Kontakou M., Nobili V., Ciclitira P. J. Raised pro-inflammatory cytokines interleukin 6 and tumour necrosis factor alpha in coeliac disease mucosa detected by immunohistochemistry. Gut. 1994 Oct;35(10):1398–1403. doi: 10.1136/gut.35.10.1398. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sollid L. M., Gaudernack G., Markussen G., Kvale D., Brandtzaeg P., Thorsby E. Induction of various HLA class II molecules in a human colonic adenocarcinoma cell line. Scand J Immunol. 1987 Feb;25(2):175–180. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1987.tb01061.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sollid L. M., Markussen G., Ek J., Gjerde H., Vartdal F., Thorsby E. Evidence for a primary association of celiac disease to a particular HLA-DQ alpha/beta heterodimer. J Exp Med. 1989 Jan 1;169(1):345–350. doi: 10.1084/jem.169.1.345. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stolpen A. H., Guinan E. C., Fiers W., Pober J. S. Recombinant tumor necrosis factor and immune interferon act singly and in combination to reorganize human vascular endothelial cell monolayers. Am J Pathol. 1986 Apr;123(1):16–24. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sturgess R. P., Hooper L. B., Spencer J., Hung C. H., Nelufer J. M., Ciclitira P. J. Effects of interferon-gamma and tumour necrosis factor-alpha on epithelial HLA class-II expression on jejunal mucosal biopsy specimens cultured in vitro. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1992 Nov;27(11):907–911. doi: 10.3109/00365529209000161. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sturgess R. P., Macartney J. C., Makgoba M. W., Hung C. H., Haskard D. O., Ciclitira P. J. Differential upregulation of intercellular adhesion molecule-1 in coeliac disease. Clin Exp Immunol. 1990 Dec;82(3):489–492. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.1990.tb05477.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Talmadge J. E., Bowersox O., Tribble H., Lee S. H., Shepard H. M., Liggitt D. Toxicity of tumor necrosis factor is synergistic with gamma-interferon and can be reduced with cyclooxygenase inhibitors. Am J Pathol. 1987 Sep;128(3):410–425. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ucer U., Bartsch H., Scheurich P., Pfizenmaier K. Biological effects of gamma-interferon on human tumor cells: quantity and affinity of cell membrane receptors for gamma-IFN in relation to growth inhibition and induction of HLA-DR expression. Int J Cancer. 1985 Jul 15;36(1):103–108. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910360116. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



