Abstract
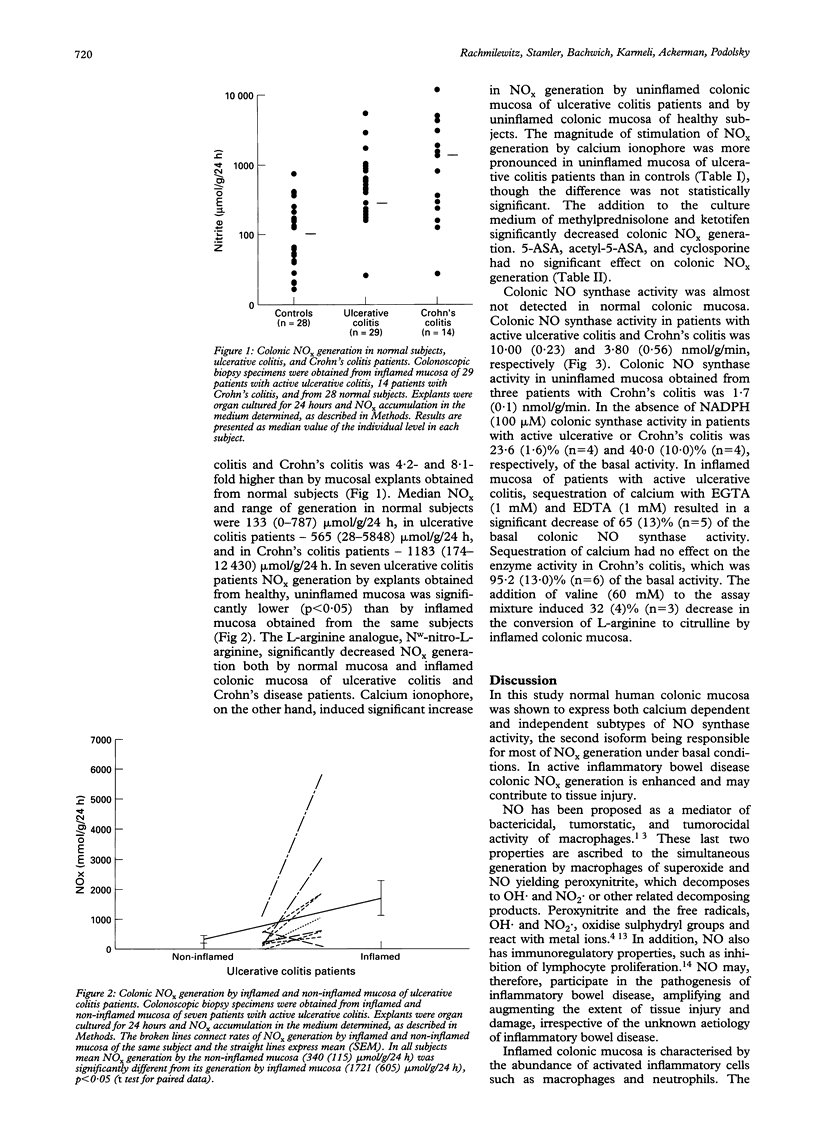
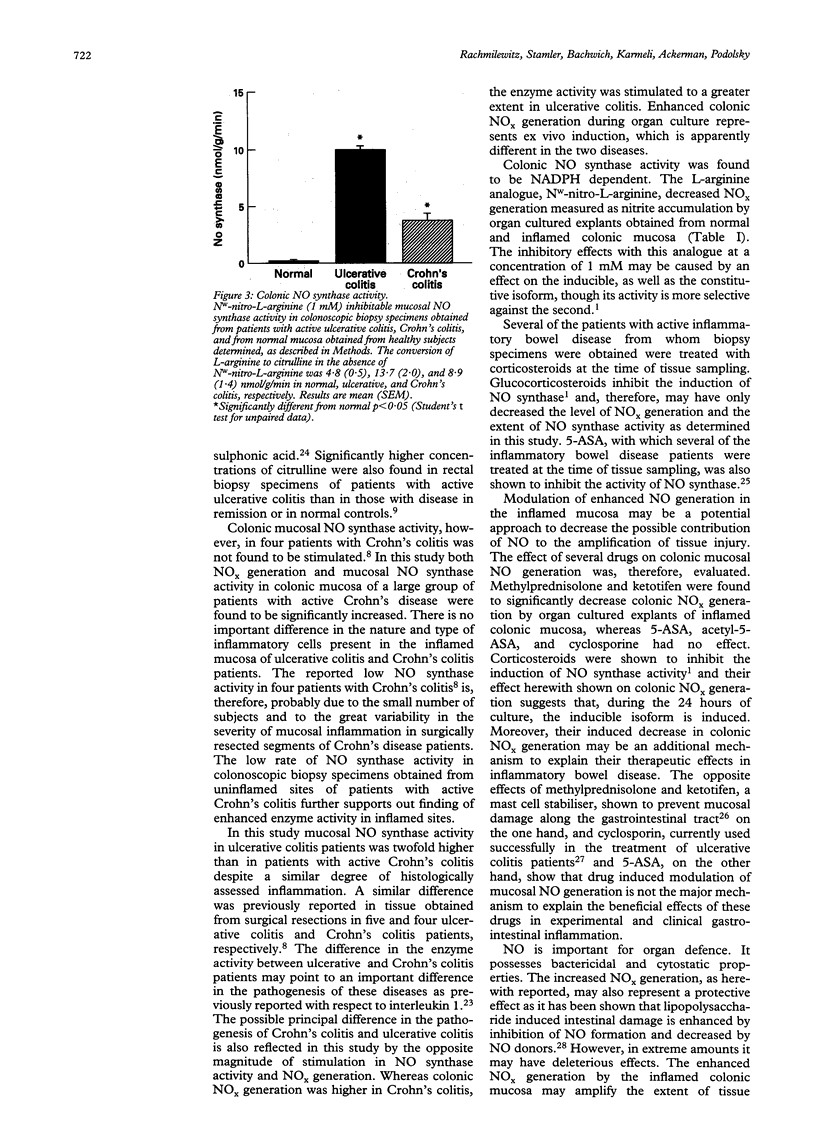
Recent studies have suggested that nitric oxide (NO.), the product of nitric oxide synthase in inflammatory cells, may play a part in tissue injury and inflammation through its oxidative metabolism. In this study the colonic generation of oxides of nitrogen (NOx) and nitric oxide synthase activity was determined in ulcerative colitis and Crohn's disease. Colonic biopsy specimens were obtained from inflammatory bowel disease patients and from normal controls. Mucosal explants were cultured in vitro for 24 hours and NOx generation was determined. Nitric oxide synthase activity was monitored by the conversion of [3H]-L-arginine to citrulline. Median NOx generation by inflamed colonic mucosa of patients with active ulcerative colitis and Crohn's colitis was 4.2- and 8.1-fold respectively higher than that by normal human colonic mucosa. In ulcerative colitis and Crohn's colitis nitric oxide synthase activity was 10.0- and 3.8-fold respectively higher than in normal subjects. Colonic NOx generation is significantly decreased by methylprednisolone and ketotifen. The decrease in NOx generation by cultured colonic mucosa induced by methylprednisolone suggests that NO synthase activity is induced during the culture and the steroid effect may contribute to its therapeutic effect. Enhanced colonic NOx generation by stimulated nitric oxide synthase activity in ulcerative colitis and Crohn's disease may contribute to tissue injury.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beckman J. S., Beckman T. W., Chen J., Marshall P. A., Freeman B. A. Apparent hydroxyl radical production by peroxynitrite: implications for endothelial injury from nitric oxide and superoxide. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Feb;87(4):1620–1624. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.4.1620. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boughton-Smith N. K., Evans S. M., Hawkey C. J., Cole A. T., Balsitis M., Whittle B. J., Moncada S. Nitric oxide synthase activity in ulcerative colitis and Crohn's disease. Lancet. 1993 Aug 7;342(8867):338–340. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(93)91476-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boughton-Smith N. K., Hutcheson I. R., Deakin A. M., Whittle B. J., Moncada S. Protective effect of S-nitroso-N-acetyl-penicillamine in endotoxin-induced acute intestinal damage in the rat. Eur J Pharmacol. 1990 Dec 4;191(3):485–488. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(90)94185-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bush P. A., Gonzalez N. E., Griscavage J. M., Ignarro L. J. Nitric oxide synthase from cerebellum catalyzes the formation of equimolar quantities of nitric oxide and citrulline from L-arginine. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1992 Jun 30;185(3):960–966. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(92)91720-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eliakim R., Karmeli F., Okon E., Rachmilewitz D. Ketotifen effectively prevents mucosal damage in experimental colitis. Gut. 1992 Nov;33(11):1498–1503. doi: 10.1136/gut.33.11.1498. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eliakim R., Karmeli F., Razin E., Rachmilewitz D. Role of platelet-activating factor in ulcerative colitis. Enhanced production during active disease and inhibition by sulfasalazine and prednisolone. Gastroenterology. 1988 Nov;95(5):1167–1172. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(88)90346-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geller D. A., Lowenstein C. J., Shapiro R. A., Nussler A. K., Di Silvio M., Wang S. C., Nakayama D. K., Simmons R. L., Snyder S. H., Billiar T. R. Molecular cloning and expression of inducible nitric oxide synthase from human hepatocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Apr 15;90(8):3491–3495. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.8.3491. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grisham M. B., Ware K., Gilleland H. E., Jr, Gilleland L. B., Abell C. L., Yamada T. Neutrophil-mediated nitrosamine formation: role of nitric oxide in rats. Gastroenterology. 1992 Oct;103(4):1260–1266. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(92)91513-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hibbs J. B., Jr, Vavrin Z., Taintor R. R. L-arginine is required for expression of the activated macrophage effector mechanism causing selective metabolic inhibition in target cells. J Immunol. 1987 Jan 15;138(2):550–565. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ignarro L. J. Biosynthesis and metabolism of endothelium-derived nitric oxide. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 1990;30:535–560. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pa.30.040190.002535. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jenkins D., Goodall A., Scott B. B. Ulcerative colitis: one disease or two? (Quantitative histological differences between distal and extensive disease). Gut. 1990 Apr;31(4):426–430. doi: 10.1136/gut.31.4.426. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ligumsky M., Simon P. L., Karmeli F., Rachmilewitz D. Role of interleukin 1 in inflammatory bowel disease--enhanced production during active disease. Gut. 1990 Jun;31(6):686–689. doi: 10.1136/gut.31.6.686. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacGlashan D., Jr, Guo C. B. Oscillations in free cytosolic calcium during IgE-mediated stimulation distinguish human basophils from human mast cells. J Immunol. 1991 Oct 1;147(7):2259–2269. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Middleton S. J., Shorthouse M., Hunter J. O. Increased nitric oxide synthesis in ulcerative colitis. Lancet. 1993 Feb 20;341(8843):465–466. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(93)90211-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller M. J., Sadowska-Krowicka H., Chotinaruemol S., Kakkis J. L., Clark D. A. Amelioration of chronic ileitis by nitric oxide synthase inhibition. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1993 Jan;264(1):11–16. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nathan C. Nitric oxide as a secretory product of mammalian cells. FASEB J. 1992 Sep;6(12):3051–3064. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rachmilewitz D., Stamler J. S., Karmeli F., Mullins M. E., Singel D. J., Loscalzo J., Xavier R. J., Podolsky D. K. Peroxynitrite-induced rat colitis--a new model of colonic inflammation. Gastroenterology. 1993 Dec;105(6):1681–1688. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(93)91063-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salter M., Knowles R. G., Moncada S. Widespread tissue distribution, species distribution and changes in activity of Ca(2+)-dependent and Ca(2+)-independent nitric oxide synthases. FEBS Lett. 1991 Oct 7;291(1):145–149. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(91)81123-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharon P., Ligumsky M., Rachmilewitz D., Zor U. Role of prostaglandins in ulcerative colitis. Enhanced production during active disease and inhibition by sulfasalazine. Gastroenterology. 1978 Oct;75(4):638–640. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stuehr D. J., Marletta M. A. Mammalian nitrate biosynthesis: mouse macrophages produce nitrite and nitrate in response to Escherichia coli lipopolysaccharide. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Nov;82(22):7738–7742. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.22.7738. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xie Q. W., Cho H. J., Calaycay J., Mumford R. A., Swiderek K. M., Lee T. D., Ding A., Troso T., Nathan C. Cloning and characterization of inducible nitric oxide synthase from mouse macrophages. Science. 1992 Apr 10;256(5054):225–228. doi: 10.1126/science.1373522. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamada T., Sartor R. B., Marshall S., Specian R. D., Grisham M. B. Mucosal injury and inflammation in a model of chronic granulomatous colitis in rats. Gastroenterology. 1993 Mar;104(3):759–771. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(93)91011-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhu L., Gunn C., Beckman J. S. Bactericidal activity of peroxynitrite. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1992 Nov 1;298(2):452–457. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(92)90434-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


