Abstract
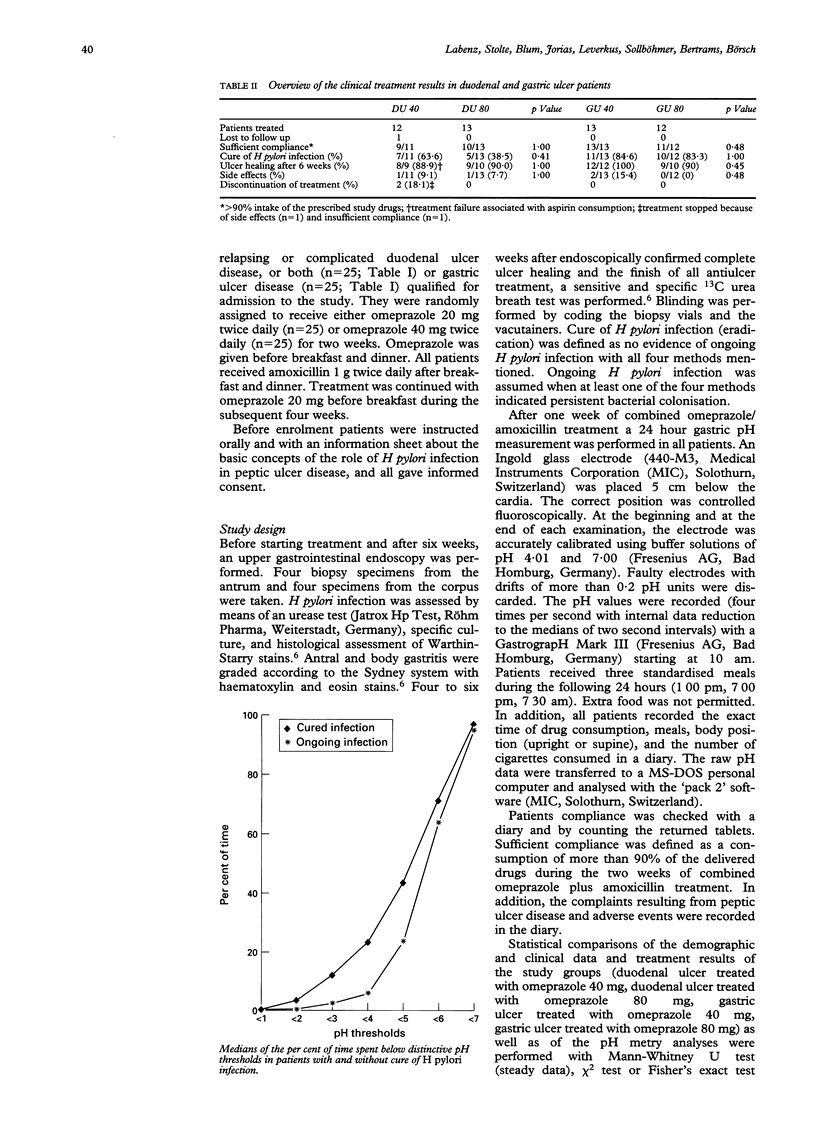
Omeprazole plus amoxicillin cures Helicobacter pylori infection. The hypothesis was tested that low acidity is a predictor of outcome. Fifty patients with relapsing or complicated, or both H pylori positive duodenal (n = 25) or gastric ulcer (n = 25) were randomly treated with either omeprazole 20 mg twice daily plus amoxicillin 1 g twice daily or with omeprazole 40 mg twice daily plus amoxicillin 1 g twice daily over two weeks. After one week of combined treatment, a 24 hour gastric pH measurement was performed in all patients. H pylori cure rate was 67%. Patients who later turned out to be cured had higher pH values during night time and after meals (p < 0.05). In an explorative analysis drug compliance, smoking, location of the ulcer (duodenum versus stomach), age, and grade of body gastritis were additional predictors of the outcome. Smoking (p = 0.006), compliance (p = 0.037), duodenal ulcer disease (p = 0.065), and young age (p = 0.021) were related to high acidity. In conclusion, the success of eradication treatment with omeprazole and amoxicillin in ulcer patients infected with H pylori depends on intragastric pH. Drug compliance, smoking habits, location of ulcer, age, and activity of body gastritis are other predictors and in part related to intragastric acidity.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Grayson M. L., Eliopoulos G. M., Ferraro M. J., Moellering R. C., Jr Effect of varying pH on the susceptibility of Campylobacter pylori to antimicrobial agents. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 1989 Oct;8(10):888–889. doi: 10.1007/BF01963775. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hosking S. W., Ling T. K., Chung S. C., Yung M. Y., Cheng A. F., Sung J. J., Li A. K. Duodenal ulcer healing by eradication of Helicobacter pylori without anti-acid treatment: randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 1994 Feb 26;343(8896):508–510. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(94)91460-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunt R. H. pH and Hp--gastric acid secretion and Helicobacter pylori: implications for ulcer healing and eradication of the organism. Am J Gastroenterol. 1993 Apr;88(4):481–483. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Labenz J., Gyenes E., Rühl G. H., Börsch G. Amoxicillin plus omeprazole versus triple therapy for eradication of Helicobacter pylori in duodenal ulcer disease: a prospective, randomized, and controlled study. Gut. 1993 Sep;34(9):1167–1170. doi: 10.1136/gut.34.9.1167. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Labenz J., Gyenes E., Rühl G. H., Börsch G. Omeprazole plus amoxicillin: efficacy of various treatment regimens to eradicate Helicobacter pylori. Am J Gastroenterol. 1993 Apr;88(4):491–495. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Labenz J., Jorias I., Sollböhmer M., Peitz U., Stolte M., Börsch G. Gastrale 24-Stunden-pH-Profile unter 2 x 20 mg und 2 x 40 mg Omeprazol bei Patienten mit Helicobacter-pylori-assoziierter gastroduodenaler Ulkuskrankheit. Z Gastroenterol. 1994 Aug;32(8):436–440. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Labenz J., Leverkus F., Börsch G. Omeprazole plus amoxicillin for cure of Helicobacter pylori infection. Factors influencing the treatment success. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1994 Dec;29(12):1070–1075. doi: 10.3109/00365529409094890. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Labenz J., Rühl G. H., Bertrams J., Börsch G. Medium- and high-dose omeprazole plus amoxicillin for eradication of Helicobacter pylori in duodenal ulcer disease. Dig Dis Sci. 1994 Jul;39(7):1483–1487. doi: 10.1007/BF02088052. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Labenz J., Rühl G. H., Bertrams J., Börsch G. Medium- or high-dose omeprazole plus amoxicillin eradicates Helicobacter pylori in gastric ulcer disease. Am J Gastroenterol. 1994 May;89(5):726–730. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Labenz J., Stolte M., Aygen S., Hennemann O., Bertrams J., Börsch G. Qualitative und semiquantitative invasive und nicht-invasive Diagnostik der Helicobacter pylori-Kolonisation der gastralen Mukosa. Z Gastroenterol. 1993 Jul-Aug;31(7-8):437–443. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Logan R. P., Gummett P. A., Hegarty B. T., Walker M. M., Baron J. H., Misiewicz J. J. Clarithromycin and omeprazole for Helicobacter pylori. Lancet. 1992 Jul 25;340(8813):239–239. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(92)90502-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mainguet P., Delmée M., Debongnie J. C. Omeprazole, campylobacter pylori, and duodenal ulcer. Lancet. 1989 Aug 12;2(8659):389–390. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(89)90569-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Penston J. G. Review article: Helicobacter pylori eradication--understandable caution but no excuse for inertia. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 1994 Aug;8(4):369–389. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2036.1994.tb00304.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tytgat G. N. Review article: treatments that impact favourably upon the eradication of Helicobacter pylori and ulcer recurrence. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 1994 Aug;8(4):359–368. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2036.1994.tb00303.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verdu E., Viani F., Armstrong D., Fraser R., Siegrist H. H., Pignatelli B., Idström J. P., Cederberg C., Blum A. L., Fried M. Effect of omeprazole on intragastric bacterial counts, nitrates, nitrites, and N-nitroso compounds. Gut. 1994 Apr;35(4):455–460. doi: 10.1136/gut.35.4.455. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yokosuka O., Omata M., Ito Y., Ohto M. Expression of HCV E2/NS1 protein as a fusion protein with maltose binding protein: detection of anti-E2/NS1 antibody in chronic liver disease. Gut. 1993;34(2 Suppl):S64–S65. doi: 10.1136/gut.34.2_suppl.s64. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zala G., Flury R., Wüst J., Meyenberger C., Ammann R., Wirth H. P. Omeprazol/Amoxicillin: verbesserte Eradikation von Helicobacter pylori bei Rauchern durch N-Acetylcystein. Schweiz Med Wochenschr. 1994 Aug 9;124(31-32):1391–1397. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


