Abstract
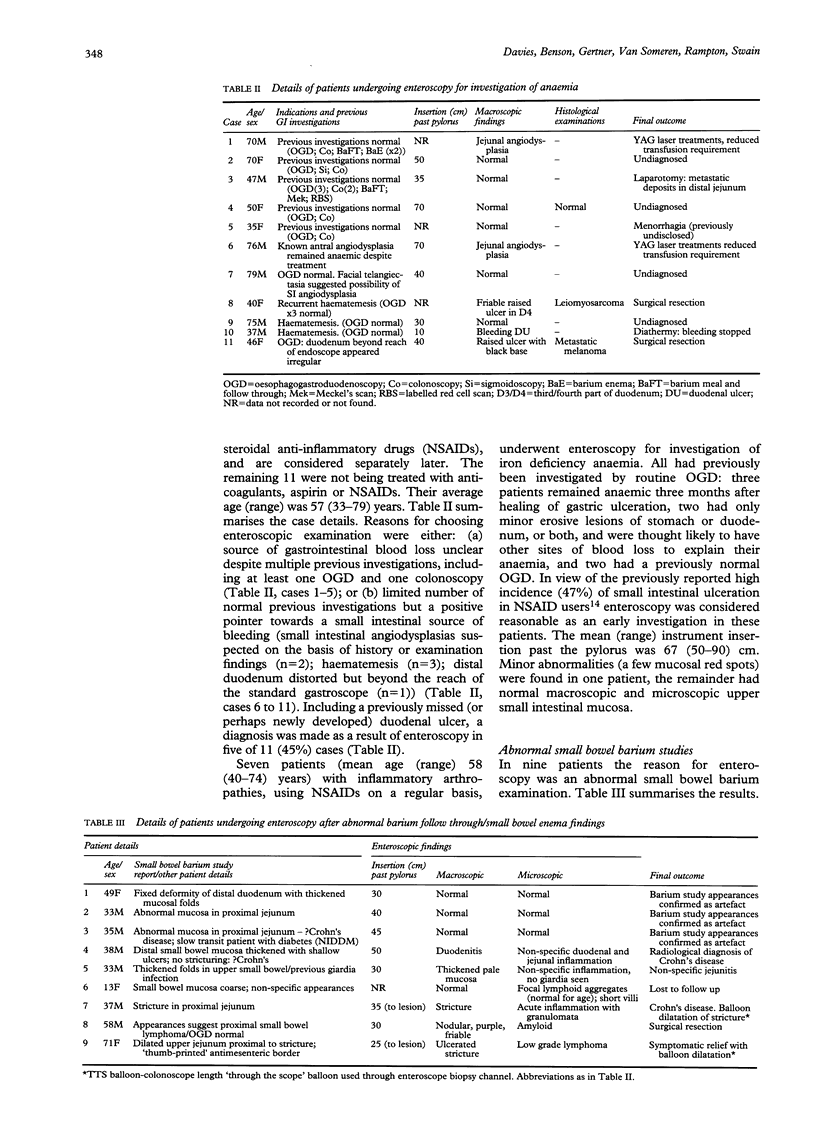
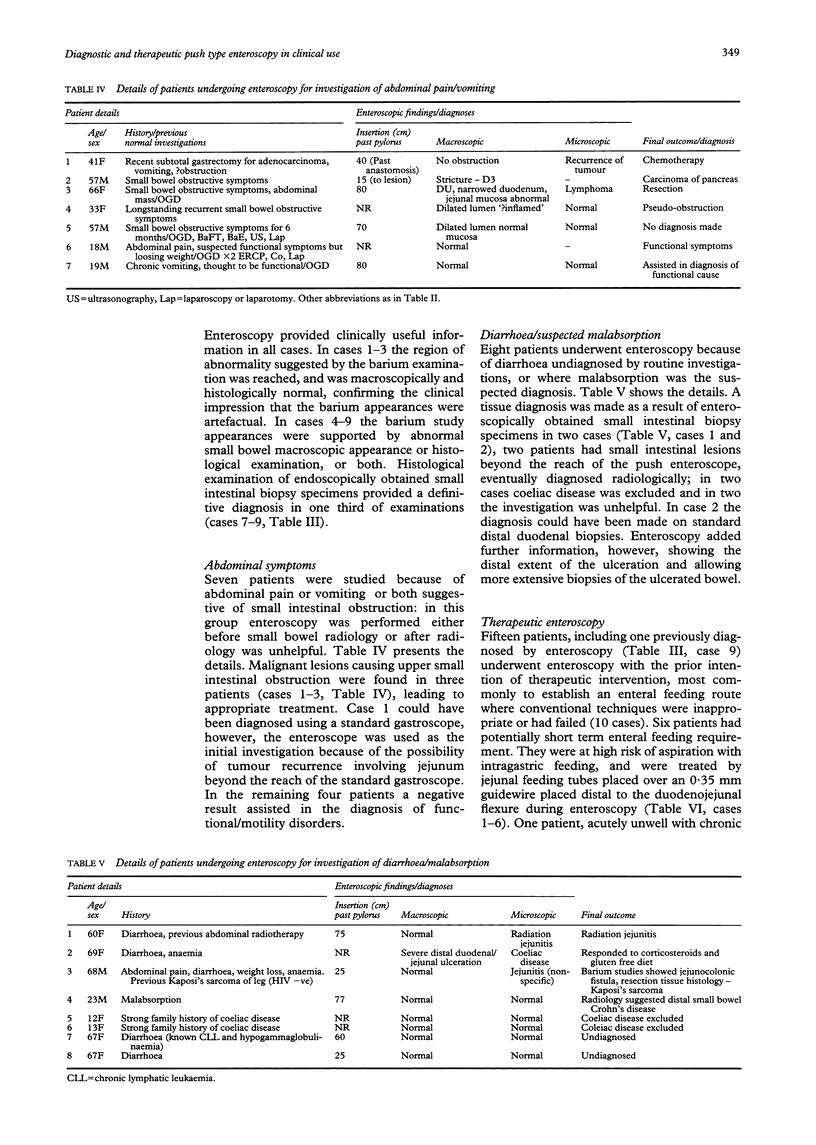
This study describes small bowel push enteroscopy in routine clinical practice, using a purpose designed instrument (Olympus SIF-10). Fifty six patients had a total of 60 procedures over a two and a half year period. The median (range) depth of small intestine intubated was 45 (15-90) cm. Procedure time varied from 10-45 minutes. Most enteroscopies were performed during routine gastroscopy lists. The technique was comparatively easy for experienced endoscopists to learn. Forty two procedures were for diagnostic purposes. Eleven patients had gastrointestinal bleeding where the source was obscure, or where early investigations had suggested a small bowel source: a specific diagnosis was made in 45% of these cases. Of seven iron deficient anaemic patients using non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), only one had a lesion detected in the upper small bowel. Nine patients had abnormal small bowel barium studies. Small bowel abnormalities were seen in six cases and were definitively diagnostic in three of these; in three patients the barium study appearances were confirmed as artefact. Fifteen patients were investigated for abdominal symptoms suggesting small bowel obstruction or malabsorption: a diagnosis was made in five cases. Fifteen patients underwent enteroscopy for therapeutic purposes, including successful treatment of difficult enteral feeding problems by nasojejunal tubes or by cutaneous endoscopic jejunostomies, polypectomy for Peutz-Jeghers syndrome, and dilatation of strictures. Additionally, bleeding lesions detected in patients during investigation of anaemia were successfully treated at the time by YAG laser or bipolar diathermy. In conclusion, push enteroscopy is a practical and valuable clinical service, which should probably become available on a subregional basis.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barkin J. S., Schonfeld W., Thomsen S., Manten H. D., Rogers A. I. Enteroscopy and small bowel biopsy--an improved technique for the diagnosis of small bowel disease. Gastrointest Endosc. 1985 Jun;31(3):215–217. doi: 10.1016/s0016-5107(85)72050-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowden T. A., Jr Endoscopy of the small intestine. Surg Clin North Am. 1989 Dec;69(6):1237–1247. doi: 10.1016/s0039-6109(16)44986-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burtch G. D., Shatney C. H. Feeding gastrostomy. Assistant or assassin? Am Surg. 1985 Apr;51(4):204–207. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen M. E., Barkin J. S. Enteroscopy and enteroclysis: the combined procedure. Am J Gastroenterol. 1989 Nov;84(11):1413–1415. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Desa L. A., Ohri S. K., Hutton K. A., Lee H., Spencer J. Role of intraoperative enteroscopy in obscure gastrointestinal bleeding of small bowel origin. Br J Surg. 1991 Feb;78(2):192–195. doi: 10.1002/bjs.1800780219. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foutch P. G., Sawyer R., Sanowski R. A. Push-enteroscopy for diagnosis of patients with gastrointestinal bleeding of obscure origin. Gastrointest Endosc. 1990 Jul-Aug;36(4):337–341. doi: 10.1016/s0016-5107(90)71060-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gostout C. J., Bender C. E. Cholangiopancreatography, sphincterotomy, and common duct stone removal via Roux-en-Y limb enteroscopy. Gastroenterology. 1988 Jul;95(1):156–163. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(88)90305-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gostout C. J. Improving the withdrawal phase of Sonde enteroscopy with the "push-away" method. Gastrointest Endosc. 1993 Jan-Feb;39(1):69–72. doi: 10.1016/s0016-5107(93)70016-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gostout C. J., Schroeder K. W., Burton D. D. Small bowel enteroscopy: an early experience in gastrointestinal bleeding of unknown origin. Gastrointest Endosc. 1991 Jan-Feb;37(1):5–8. doi: 10.1016/s0016-5107(91)70612-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hassett J. M., Sunby C., Flint L. M. No elimination of aspiration pneumonia in neurologically disabled patients with feeding gastrostomy. Surg Gynecol Obstet. 1988 Nov;167(5):383–388. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lau W. Y., Yuen W. K., Chu K. W., Poon G. P., Li A. K. Obscure bleeding in the gastrointestinal tract originating in the small intestine. Surg Gynecol Obstet. 1992 Feb;174(2):119–124. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis B. S., Kornbluth A., Waye J. D. Small bowel tumours: yield of enteroscopy. Gut. 1991 Jul;32(7):763–765. doi: 10.1136/gut.32.7.763. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis B. S. Perform PEJ, not PED. Gastrointest Endosc. 1990 May-Jun;36(3):311–313. doi: 10.1016/s0016-5107(90)71035-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis B. S., Waye J. D. Chronic gastrointestinal bleeding of obscure origin: role of small bowel enteroscopy. Gastroenterology. 1988 May;94(5 Pt 1):1117–1120. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(88)90001-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis B. S., Waye J. D. Small bowel enteroscopy in 1988: pros and cons. Am J Gastroenterol. 1988 Aug;83(8):799–802. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis B. S., Waye J. D. Total small bowel enteroscopy. Gastrointest Endosc. 1987 Dec;33(6):435–438. doi: 10.1016/s0016-5107(87)71682-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin L. F., Max M. H., Richardson J. D., Peterson G. H. Small bowel tumors: a continuing challenge. South Med J. 1980 Aug;73(8):981–985. doi: 10.1097/00007611-198008000-00010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris A. J., Madhok R., Sturrock R. D., Capell H. A., MacKenzie J. F. Enteroscopic diagnosis of small bowel ulceration in patients receiving non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Lancet. 1991 Mar 2;337(8740):520–520. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(91)91300-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris A. J., Wasson L. A., MacKenzie J. F. Small bowel enteroscopy in undiagnosed gastrointestinal blood loss. Gut. 1992 Jul;33(7):887–889. doi: 10.1136/gut.33.7.887. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker H. W., Agayoff J. D. Enteroscopy and small bowel biopsy utilizing a peroral colonoscope. Gastrointest Endosc. 1983 May;29(2):139–140. doi: 10.1016/s0016-5107(83)72558-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ress A. M., Benacci J. C., Sarr M. G. Efficacy of intraoperative enteroscopy in diagnosis and prevention of recurrent, occult gastrointestinal bleeding. Am J Surg. 1992 Jan;163(1):94–99. doi: 10.1016/0002-9610(92)90259-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott B. B., Jenkins D. Endoscopic small intestinal biopsy. Gastrointest Endosc. 1981 Aug;27(3):162–167. doi: 10.1016/s0016-5107(81)73183-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shike M., Wallach C., Likier H. Direct percutaneous endoscopic jejunostomies. Gastrointest Endosc. 1991 Jan-Feb;37(1):62–65. doi: 10.1016/s0016-5107(91)70625-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimizu S., Tada M., Kawai K. Development of a new insertion technique in push-type enteroscopy. Am J Gastroenterol. 1987 Sep;82(9):844–847. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shrake P. D., Rex D. K., Lappas J. C., Maglinte D. D. Radiographic evaluation of suspected small bowel obstruction. Am J Gastroenterol. 1991 Feb;86(2):175–178. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spigelman A. D., Thomson J. P., Phillips R. K. Towards decreasing the relaparotomy rate in the Peutz-Jeghers syndrome: the role of peroperative small bowel endoscopy. Br J Surg. 1990 Mar;77(3):301–302. doi: 10.1002/bjs.1800770320. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Status evaluation: enteroscopy. Gastrointest Endosc. 1991 Nov-Dec;37(6):673–677. doi: 10.1016/s0016-5107(91)70907-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tada M., Shimizu S., Kawai K. A new transnasal sonde type fiberscope (SSIF type VII) as a pan-enteroscope. Endoscopy. 1986 Jul;18(4):121–124. doi: 10.1055/s-2007-1018349. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


