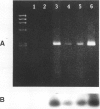
Abstract
The stable differentiated human colonic epithelial cell line, HT29-C1.16E, was used to study the effects of interleukin-1 (IL-1) on mucin exocytosis. The main findings include: (a) IL-1 stimulated a rapid release of mucin from filter grown HT29-C1.16E cells, this effect being dose related; (b) this secretory effect was abolished in the presence of the blocking monoclonal antibody M4 specific for IL-1 receptors type I, showing that IL-1 receptors type I mediated IL-1 action; (c) experiments based on chamber cultures showed that these receptors were located on the basolateral membranes of HT29-C1.16E cells; (d) finally, mRNA for IL-1 receptors type I were detected by reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction in these cells. To extend these findings to the in vivo situation, the rapid stimulatory effect of IL-1 on mucin exocytosis may contribute to the wash out of noxious agents during mucosal inflammation.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Augeron C., Laboisse C. L. Emergence of permanently differentiated cell clones in a human colonic cancer cell line in culture after treatment with sodium butyrate. Cancer Res. 1984 Sep;44(9):3961–3969. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Augeron C., Voisin T., Maoret J. J., Berthon B., Laburthe M., Laboisse C. L. Neurotensin and neuromedin N stimulate mucin output from human goblet cells (Cl.16E) via neurotensin receptors. Am J Physiol. 1992 Mar;262(3 Pt 1):G470–G476. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1992.262.3.G470. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohan V. L., Scott A. L., Dinarello C. A., Prendergast R. A. Interleukin-1 is a mucus secretagogue. Cell Immunol. 1991 Sep;136(2):425–434. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(91)90364-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lal R., John S. A. Biological applications of atomic force microscopy. Am J Physiol. 1994 Jan;266(1 Pt 1):C1–21. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1994.266.1.C1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merlin D., Augeron C., Tien X. Y., Guo X., Laboisse C. L., Hopfer U. ATP-stimulated electrolyte and mucin secretion in the human intestinal goblet cell line HT29-Cl.16E. J Membr Biol. 1994 Jan;137(2):137–149. doi: 10.1007/BF00233483. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sartor R. B. Cytokines in intestinal inflammation: pathophysiological and clinical considerations. Gastroenterology. 1994 Feb;106(2):533–539. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(94)90614-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sims J. E., Gayle M. A., Slack J. L., Alderson M. R., Bird T. A., Giri J. G., Colotta F., Re F., Mantovani A., Shanebeck K. Interleukin 1 signaling occurs exclusively via the type I receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jul 1;90(13):6155–6159. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.13.6155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spriggs M. K., Lioubin P. J., Slack J., Dower S. K., Jonas U., Cosman D., Sims J. E., Bauer J. Induction of an interleukin-1 receptor (IL-1R) on monocytic cells. Evidence that the receptor is not encoded by a T cell-type IL-1R mRNA. J Biol Chem. 1990 Dec 25;265(36):22499–22505. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Theodorou V., Eutamene H., Fioramonti J., Junien J. L., Bueno L. Interleukin 1 induces a neurally mediated colonic secretion in rats: involvement of mast cells and prostaglandins. Gastroenterology. 1994 Jun;106(6):1493–1500. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(94)90402-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]