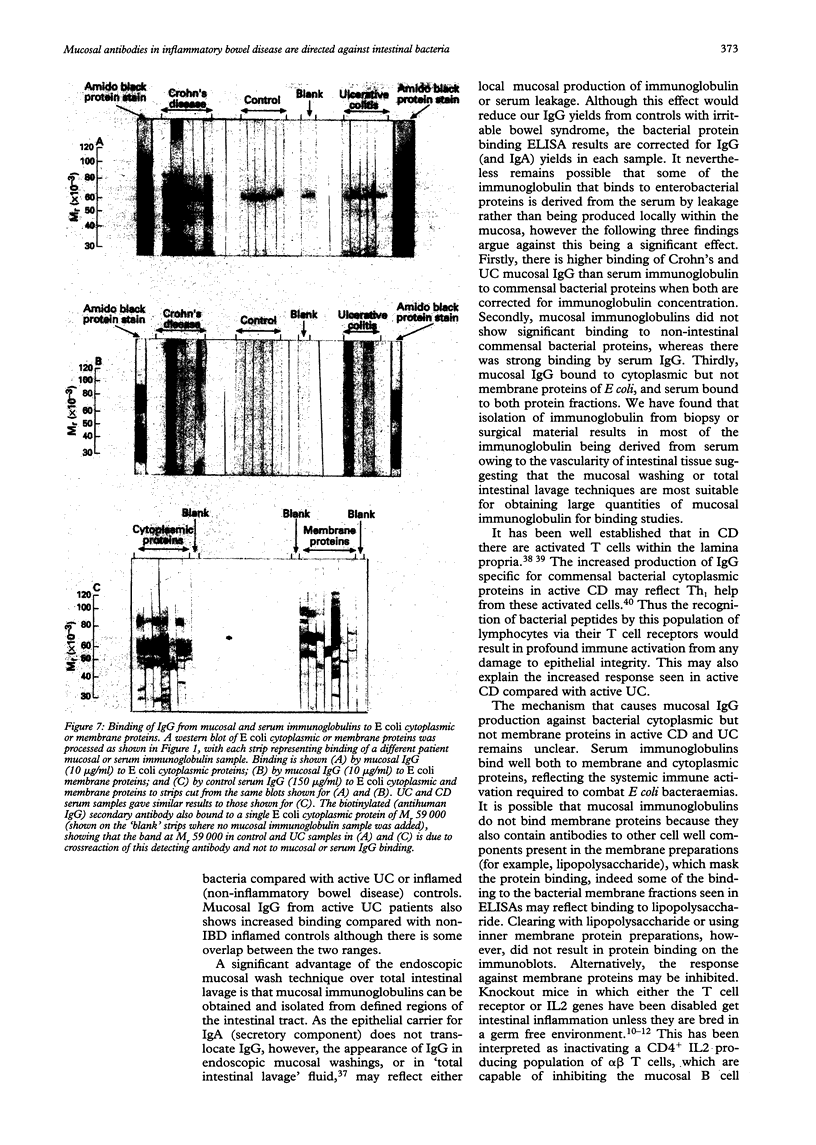
Abstract
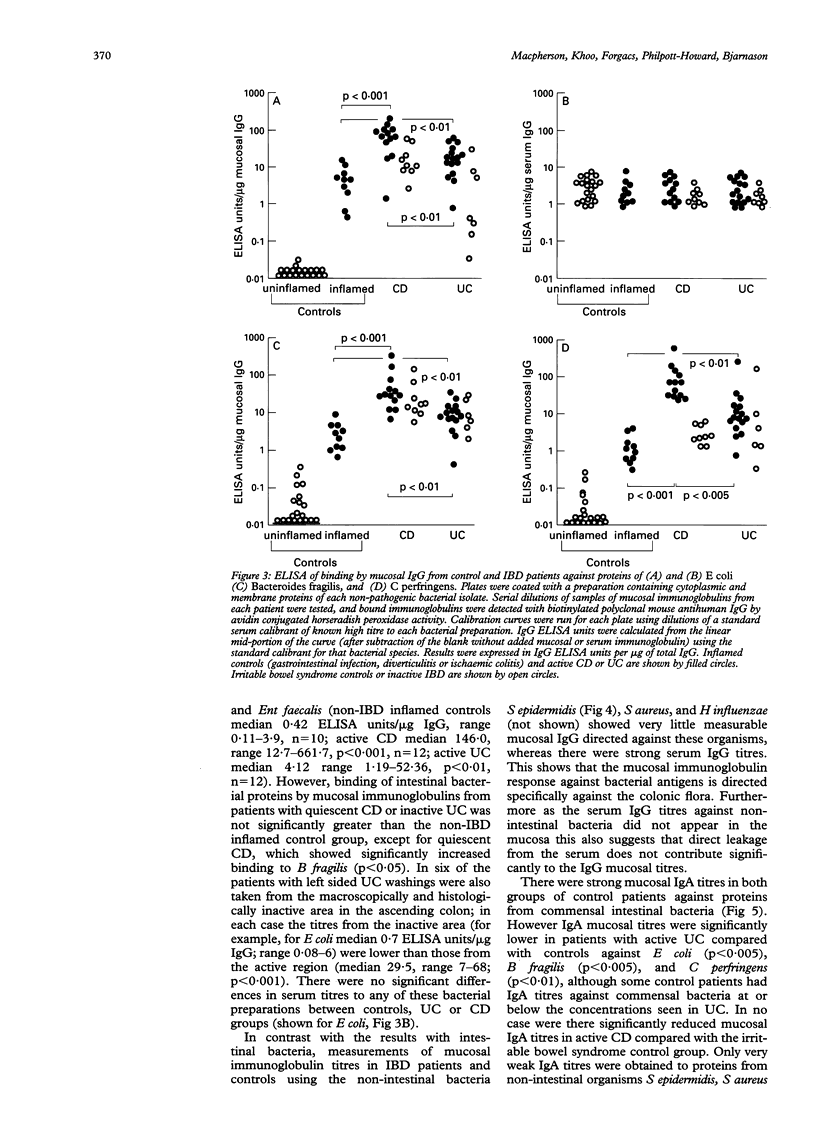
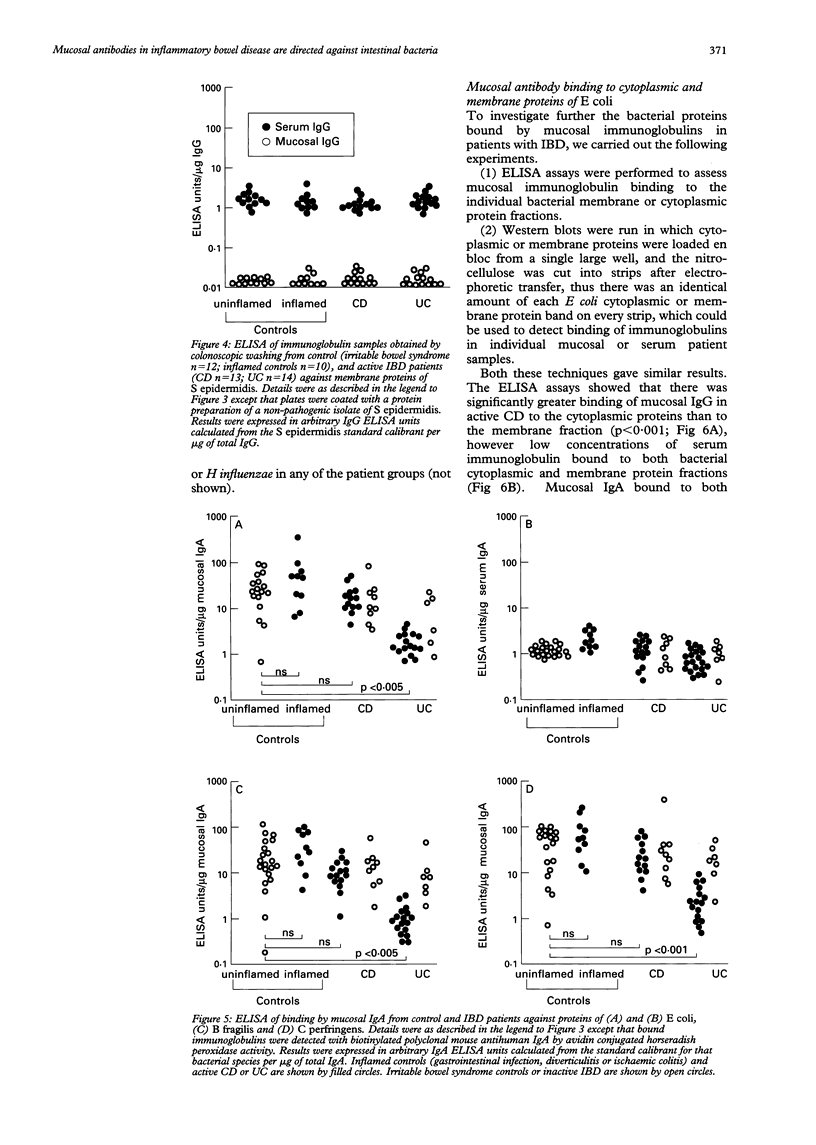
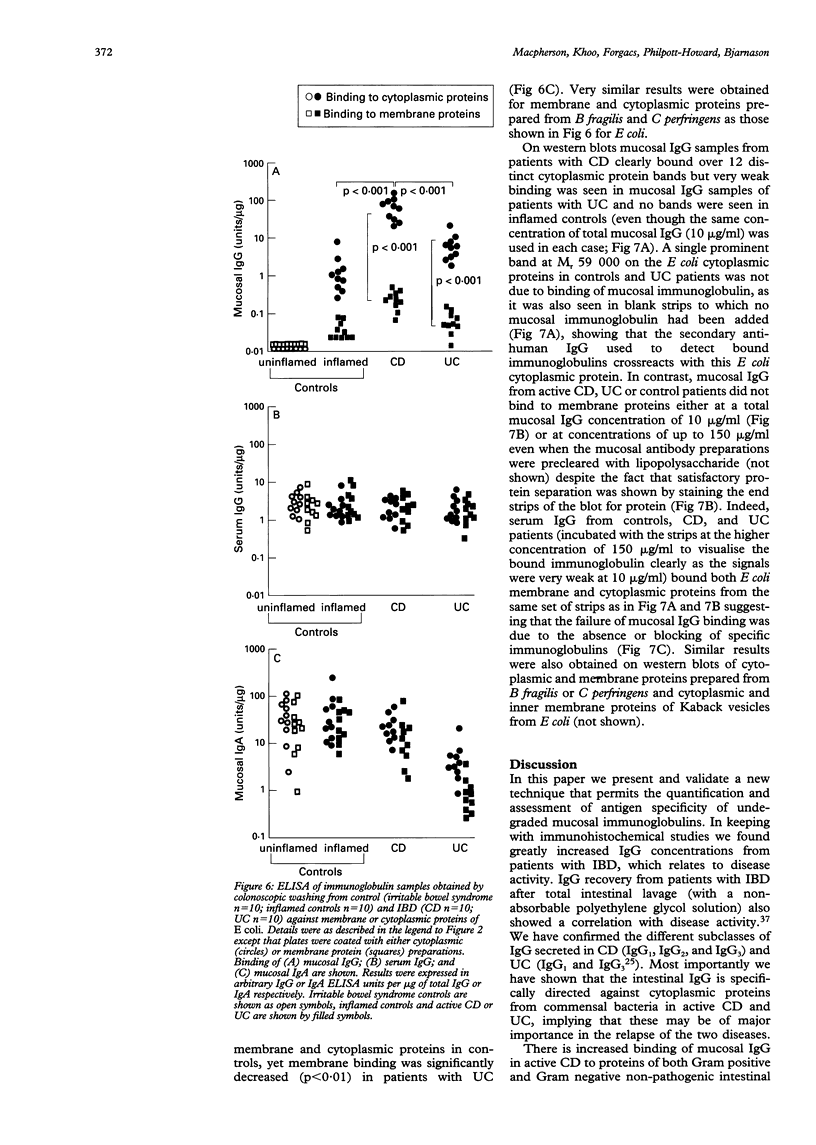
In contrast with normal subjects where IgA is the main immunoglobulin in the intestine, patients with active inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) produce high concentrations of IgG from intestinal lymphocytes, but the antigens at which these antibodies are directed are unknown. To investigate the specificities of these antibodies mucosal immunoglobulins were isolated from washings taken at endoscopy from 21 control patients with irritable bowel syndrome, 10 control patients with intestinal inflammation due to infection or ischaemia, and 51 patients with IBD: 24 Crohn's disease (CD, 15 active, nine quiescent), 27 ulcerative colitis (UC, 20 active, seven inactive). Total mucosal IgG was much higher (p < 0.001) in active UC (median 512 micrograms/ml) and active CD (256 micrograms/ml) than in irritable bowel syndrome controls (1.43 micrograms/ml), but not significantly different from controls with non-IBD intestinal inflammation (224 micrograms/ml). Mucosal IgG bound to proteins of a range of non-pathogenic commensal faecal bacteria in active CD; this was higher than in UC (p < 0.01); and both were significantly greater than controls with non-IBD intestinal inflammation (CD p < 0.001, UC p < 0.01) or IBS (p < 0.001 CD and UC). This mucosal IgG binding was shown on western blots and by enzyme linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) to be principally directed against the bacterial cytoplasmic rather than the membrane proteins. Total mucosal IgA concentrations did not differ between IBD and controls, but the IgA titres against faecal bacteria were lower in UC than controls (p < 0.01). These experiments show that there is an exaggerated mucosal immune response particularly in active CD but also in UC directed against cytoplasmic proteins of bacteria within the intestinal lumen; this implies that in relapse of IBD there is a breakdown of tolerance to the normal commensal flora of the gut.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andre C., Descos L., Landais P., Fermanian J. Assessment of appropriate laboratory measurements to supplement the Crohn's disease activity index. Gut. 1981 Jul;22(7):571–574. doi: 10.1136/gut.22.7.571. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bachmann M. F., Rohrer U. H., Kündig T. M., Bürki K., Hengartner H., Zinkernagel R. M. The influence of antigen organization on B cell responsiveness. Science. 1993 Nov 26;262(5138):1448–1451. doi: 10.1126/science.8248784. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baklien K., Brandtzaeg P. Comparative mapping of the local distribution of immunoglobulin-containing cells in ulcerative colitis and Crohn's disease of the colon. Clin Exp Immunol. 1975 Nov;22(2):197–209. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bartnik W., Swarbrick E. T., Williams C. A study of peripheral leucocyte migration in agarose medium in inflammatory bowel disease. Gut. 1974 Apr;15(4):294–300. doi: 10.1136/gut.15.4.294. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bjarnason I., MacPherson A., Hollander D. Intestinal permeability: an overview. Gastroenterology. 1995 May;108(5):1566–1581. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(95)90708-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bjarnason I., Williams P., Smethurst P., Peters T. J., Levi A. J. Effect of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and prostaglandins on the permeability of the human small intestine. Gut. 1986 Nov;27(11):1292–1297. doi: 10.1136/gut.27.11.1292. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brandtzaeg P., Baklien K., Fausa O., Hoel P. S. Immunohistochemical characterization of local immunoglobulin formation in ulcerative colitis. Gastroenterology. 1974 Jun;66(6):1123–1136. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breese E., Braegger C. P., Corrigan C. J., Walker-Smith J. A., MacDonald T. T. Interleukin-2- and interferon-gamma-secreting T cells in normal and diseased human intestinal mucosa. Immunology. 1993 Jan;78(1):127–131. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bull D. M., Ignaczak T. F. Enterobacterial common antigen-induced lymphocyte reactivity in inflammatory bowel disease. Gastroenterology. 1973 Jan;64(1):43–50. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlsson H. E., Lagercrantz R., Perlmann P. Immunological studies in ulcerative colitis. VIII. Antibodies to colon antigen in patients with ulcerative colitis, Crohn's disease, and other diseases. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1977;12(6):707–714. doi: 10.3109/00365527709181708. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chao L. P., Steele J., Rodrigues C., Lennard-Jones J., Stanford J. L., Spiliadis C., Rook G. A. Specificity of antibodies secreted by hybridomas generated from activated B cells in the mesenteric lymph nodes of patients with inflammatory bowel disease. Gut. 1988 Jan;29(1):35–40. doi: 10.1136/gut.29.1.35. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chapman R. W., Selby W. S., Jewell D. P. Controlled trial of intravenous metronidazole as an adjunct to corticosteroids in severe ulcerative colitis. Gut. 1986 Oct;27(10):1210–1212. doi: 10.1136/gut.27.10.1210. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choudari C. P., O'Mahony S., Brydon G., Mwantembe O., Ferguson A. Gut lavage fluid protein concentrations: objective measures of disease activity in inflammatory bowel disease. Gastroenterology. 1993 Apr;104(4):1064–1071. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(93)90275-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Das K. M., Erber W. F., Rubinstein A. Immunohistochemical changes in morphologically involved and uninvolved colonic mucosa of patients with idiopathic proctitis. J Clin Invest. 1977 Mar;59(3):379–385. doi: 10.1172/JCI108650. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engstrom J. F., Arvanitakis C., Sagawa A., Abdou N. I. Secretory immunoglobulin deficiency in a family with inflammatory bowel disease. Gastroenterology. 1978 Apr;74(4):747–751. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halstensen T. S., Das K. M., Brandtzaeg P. Epithelial deposits of immunoglobulin G1 and activated complement colocalise with the M(r) 40 kD putative autoantigen in ulcerative colitis. Gut. 1993 May;34(5):650–657. doi: 10.1136/gut.34.5.650. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harvey R. F., Bradshaw J. M. A simple index of Crohn's-disease activity. Lancet. 1980 Mar 8;1(8167):514–514. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(80)92767-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heddle R. J., Shearman D. J. Serum antibodies to Escherichia coli in subjects with ulcerative colitis. Clin Exp Immunol. 1979 Oct;38(1):22–30. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaback H. R. Transport across isolated bacterial cytoplasmic membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Aug 4;265(3):367–416. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(72)90014-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keren D. F., Kern S. E., Bauer D. H., Scott P. J., Porter P. Direct demonstration in intestinal secretions of an IgA memory response to orally administered Shigella flexneri antigens. J Immunol. 1982 Jan;128(1):475–479. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kühn R., Löhler J., Rennick D., Rajewsky K., Müller W. Interleukin-10-deficient mice develop chronic enterocolitis. Cell. 1993 Oct 22;75(2):263–274. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)80068-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lagercrantz R., Hammarström S., Perlmann P., Gustafsson B. E. Immunological studies in ulcerative colitis. 3. Incidence of antibodies to colon-antigen in ulcerative colitis and other gastro-intestinal diseases. Clin Exp Immunol. 1966 Jul;1(3):263–276. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liblau R. S., Singer S. M., McDevitt H. O. Th1 and Th2 CD4+ T cells in the pathogenesis of organ-specific autoimmune diseases. Immunol Today. 1995 Jan;16(1):34–38. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(95)80068-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lombardi G., Sidhu S., Batchelor R., Lechler R. Anergic T cells as suppressor cells in vitro. Science. 1994 Jun 10;264(5165):1587–1589. doi: 10.1126/science.8202711. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacDermott R. P., Stenson W. F. Alterations of the immune system in ulcerative colitis and Crohn's disease. Adv Immunol. 1988;42:285–328. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60848-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacPherson A. J., Jones-Mortimer M. C., Henderson P. J. Identification of the AraE transport protein of Escherichia coli. Biochem J. 1981 Apr 15;196(1):269–283. doi: 10.1042/bj1960269. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacQueen G., Marshall J., Perdue M., Siegel S., Bienenstock J. Pavlovian conditioning of rat mucosal mast cells to secrete rat mast cell protease II. Science. 1989 Jan 6;243(4887):83–85. doi: 10.1126/science.2911721. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malchow H., Ewe K., Brandes J. W., Goebell H., Ehms H., Sommer H., Jesdinsky H. European Cooperative Crohn's Disease Study (ECCDS): results of drug treatment. Gastroenterology. 1984 Feb;86(2):249–266. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mullin G. E., Lazenby A. J., Harris M. L., Bayless T. M., James S. P. Increased interleukin-2 messenger RNA in the intestinal mucosal lesions of Crohn's disease but not ulcerative colitis. Gastroenterology. 1992 May;102(5):1620–1627. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(92)91722-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noone C., Menzies I. S., Banatvala J. E., Scopes J. W. Intestinal permeability and lactose hydrolysis in human rotaviral gastroenteritis assessed simultaneously by non-invasive differential sugar permeation. Eur J Clin Invest. 1986 Jun;16(3):217–225. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2362.1986.tb01332.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Podolsky D. K. Inflammatory bowel disease (2) N Engl J Med. 1991 Oct 3;325(14):1008–1016. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199110033251406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reinhold R. B., Fine J. A technique for quantitative measurement of endotoxin in human plasma. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1971 May;137(1):334–340. doi: 10.3181/00379727-137-35572. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosekrans P. C., Meijer C. J., van der Wal A. M., Cornelisse C. J., Lindeman J. Immunoglobulin containing cells in inflammatory bowel disease of the colon: a morphometric and immunohistochemical study. Gut. 1980 Nov;21(11):941–947. doi: 10.1136/gut.21.11.941. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rutgeerts P., Goboes K., Peeters M., Hiele M., Penninckx F., Aerts R., Kerremans R., Vantrappen G. Effect of faecal stream diversion on recurrence of Crohn's disease in the neoterminal ileum. Lancet. 1991 Sep 28;338(8770):771–774. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(91)90663-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rüthlein J., Ibe M., Burghardt W., Mössner J., Auer I. O. Immunoglobulin G (IgG), IgG1, and IgG2 determinations from endoscopic biopsy specimens in control, Crohn's disease, and ulcerative colitis subjects. Gut. 1992 Apr;33(4):507–512. doi: 10.1136/gut.33.4.507. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sadlack B., Merz H., Schorle H., Schimpl A., Feller A. C., Horak I. Ulcerative colitis-like disease in mice with a disrupted interleukin-2 gene. Cell. 1993 Oct 22;75(2):253–261. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)80067-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott B. B., Goodall A., Stephenson P., Jenkins D. Rectal mucosal plasma cells in inflammatory bowel disease. Gut. 1983 Jun;24(6):519–524. doi: 10.1136/gut.24.6.519. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott M. G., Nahm M. H., Macke K., Nash G. S., Bertovich M. J., MacDermott R. P. Spontaneous secretion of IgG subclasses by intestinal mononuclear cells: differences between ulcerative colitis, Crohn's disease, and controls. Clin Exp Immunol. 1986 Oct;66(1):209–215. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teahon K., Smethurst P., Pearson M., Levi A. J., Bjarnason I. The effect of elemental diet on intestinal permeability and inflammation in Crohn's disease. Gastroenterology. 1991 Jul;101(1):84–89. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(91)90463-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thayer W. R., Jr, Brown M., Sangree M. H., Katz J., Hersh T. Escherichia Coli O:14 and colon hemagglutinating antibodies in inflammatory bowel disease. Gastroenterology. 1969 Sep;57(3):311–318. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wyatt J., Vogelsang H., Hübl W., Waldhöer T., Lochs H. Intestinal permeability and the prediction of relapse in Crohn's disease. Lancet. 1993 Jun 5;341(8858):1437–1439. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(93)90882-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



