Abstract
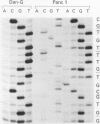
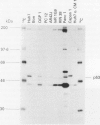
Neuroendocrine pancreatic tumours grow slower and metastasise later than ductal and acinar carcinomas. The expression of the p53 tumour suppressor gene in pancreatic neuroendocrine tumour cells is unknown. Pancreatic neuroendocrine cell lines (n = 5) and human tumour tissues (n = 19) were studied for changed p53 coding sequence, transcription, and translation. Proliferative activity of tumour cells was determined analysing Ki-67 expression. No mutation in the p53 nucleotide sequence of neuroendocrine tumour cell was found. However, an overexpression of p53 could be detected in neuroendocrine pancreatic tumour cell lines at a protein level. As no p53 mutations were seen, it is suggested that post-translational events can also lead to an overexpression of p53.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aden D. P., Fogel A., Plotkin S., Damjanov I., Knowles B. B. Controlled synthesis of HBsAg in a differentiated human liver carcinoma-derived cell line. Nature. 1979 Dec 6;282(5739):615–616. doi: 10.1038/282615a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barbareschi M., Girlando S., Mauri F. A., Arrigoni G., Laurino L., Dalla Palma P., Doglioni C. Tumour suppressor gene products, proliferation, and differentiation markers in lung neuroendocrine neoplasms. J Pathol. 1992 Apr;166(4):343–350. doi: 10.1002/path.1711660405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barton C. M., Staddon S. L., Hughes C. M., Hall P. A., O'Sullivan C., Klöppel G., Theis B., Russell R. C., Neoptolemos J., Williamson R. C. Abnormalities of the p53 tumour suppressor gene in human pancreatic cancer. Br J Cancer. 1991 Dec;64(6):1076–1082. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1991.467. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bouwmeester T., Güehmann S., el-Baradi T., Kalkbrenner F., van Wijk I., Moelling K., Pieler T. Molecular cloning, expression and in vitro functional characterization of Myb-related proteins in Xenopus. Mech Dev. 1992 Mar;37(1-2):57–68. doi: 10.1016/0925-4773(92)90015-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bressac B., Kew M., Wands J., Ozturk M. Selective G to T mutations of p53 gene in hepatocellular carcinoma from southern Africa. Nature. 1991 Apr 4;350(6317):429–431. doi: 10.1038/350429a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chaudhry A., Oberg K., Wilander E. A study of biological behavior based on the expression of a proliferating antigen in neuroendocrine tumors of the digestive system. Tumour Biol. 1992;13(1-2):27–35. doi: 10.1159/000217749. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crook T., Tidy J. A., Vousden K. H. Degradation of p53 can be targeted by HPV E6 sequences distinct from those required for p53 binding and trans-activation. Cell. 1991 Nov 1;67(3):547–556. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90529-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crook T., Wrede D., Vousden K. H. p53 point mutation in HPV negative human cervical carcinoma cell lines. Oncogene. 1991 May;6(5):873–875. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dippold W. G., Jay G., DeLeo A. B., Khoury G., Old L. J. p53 transformation-related protein: detection by monoclonal antibody in mouse and human cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Mar;78(3):1695–1699. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.3.1695. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evers B. M., Townsend C. M., Jr, Upp J. R., Allen E., Hurlbut S. C., Kim S. W., Rajaraman S., Singh P., Reubi J. C., Thompson J. C. Establishment and characterization of a human carcinoid in nude mice and effect of various agents on tumor growth. Gastroenterology. 1991 Aug;101(2):303–311. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(91)90004-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fakharzadeh S. S., Trusko S. P., George D. L. Tumorigenic potential associated with enhanced expression of a gene that is amplified in a mouse tumor cell line. EMBO J. 1991 Jun;10(6):1565–1569. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07676.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fogh J., Wright W. C., Loveless J. D. Absence of HeLa cell contamination in 169 cell lines derived from human tumors. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1977 Feb;58(2):209–214. doi: 10.1093/jnci/58.2.209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerdes J., Lemke H., Baisch H., Wacker H. H., Schwab U., Stein H. Cell cycle analysis of a cell proliferation-associated human nuclear antigen defined by the monoclonal antibody Ki-67. J Immunol. 1984 Oct;133(4):1710–1715. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greene L. A., Tischler A. S. Establishment of a noradrenergic clonal line of rat adrenal pheochromocytoma cells which respond to nerve growth factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Jul;73(7):2424–2428. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.7.2424. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gurney E. G., Harrison R. O., Fenno J. Monoclonal antibodies against simian virus 40 T antigens: evidence for distinct sublcasses of large T antigen and for similarities among nonviral T antigens. J Virol. 1980 Jun;34(3):752–763. doi: 10.1128/jvi.34.3.752-763.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heitz P. U., Klöppel G. Endokrine Tumoren des Pankreas und des Duodenum. Verh Dtsch Ges Pathol. 1987;71:202–221. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hollstein M., Sidransky D., Vogelstein B., Harris C. C. p53 mutations in human cancers. Science. 1991 Jul 5;253(5015):49–53. doi: 10.1126/science.1905840. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoorens A., Lemoine N. R., McLellan E., Morohoshi T., Kamisawa T., Heitz P. U., Stamm B., Rüschoff J., Wiedenmann B., Klöppel G. Pancreatic acinar cell carcinoma. An analysis of cell lineage markers, p53 expression, and Ki-ras mutation. Am J Pathol. 1993 Sep;143(3):685–698. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsu I. C., Metcalf R. A., Sun T., Welsh J. A., Wang N. J., Harris C. C. Mutational hotspot in the p53 gene in human hepatocellular carcinomas. Nature. 1991 Apr 4;350(6317):427–428. doi: 10.1038/350427a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iggo R., Gatter K., Bartek J., Lane D., Harris A. L. Increased expression of mutant forms of p53 oncogene in primary lung cancer. Lancet. 1990 Mar 24;335(8691):675–679. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(90)90801-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito T., Smith C. L., Cantor C. R. Sequence-specific DNA purification by triplex affinity capture. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jan 15;89(2):495–498. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.2.495. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaku M., Nishiyama T., Yagawa K., Abe M. Establishment of a carcinoembryonic antigen-producing cell line from human pancreatic carcinoma. Gan. 1980 Oct;71(5):596–601. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalthoff H., Schmiegel W., Roeder C., Kasche D., Schmidt A., Lauer G., Thiele H. G., Honold G., Pantel K., Riethmüller G. p53 and K-RAS alterations in pancreatic epithelial cell lesions. Oncogene. 1993 Feb;8(2):289–298. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kastan M. B., Onyekwere O., Sidransky D., Vogelstein B., Craig R. W. Participation of p53 protein in the cellular response to DNA damage. Cancer Res. 1991 Dec 1;51(23 Pt 1):6304–6311. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knudson W., Biswas C., Toole B. P. Interactions between human tumor cells and fibroblasts stimulate hyaluronate synthesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Nov;81(21):6767–6771. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.21.6767. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lieber M., Mazzetta J., Nelson-Rees W., Kaplan M., Todaro G. Establishment of a continuous tumor-cell line (panc-1) from a human carcinoma of the exocrine pancreas. Int J Cancer. 1975 May 15;15(5):741–747. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910150505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacNab G. M., Alexander J. J., Lecatsas G., Bey E. M., Urbanowicz J. M. Hepatitis B surface antigen produced by a human hepatoma cell line. Br J Cancer. 1976 Nov;34(5):509–515. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1976.205. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Midgley C. A., Fisher C. J., Bártek J., Vojtesek B., Lane D., Barnes D. M. Analysis of p53 expression in human tumours: an antibody raised against human p53 expressed in Escherichia coli. J Cell Sci. 1992 Jan;101(Pt 1):183–189. doi: 10.1242/jcs.101.1.183. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milner J., Medcalf E. A. Cotranslation of activated mutant p53 with wild type drives the wild-type p53 protein into the mutant conformation. Cell. 1991 May 31;65(5):765–774. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90384-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morohoshi T., Held G., Klöppel G. Exocrine pancreatic tumours and their histological classification. A study based on 167 autopsy and 97 surgical cases. Histopathology. 1983 Sep;7(5):645–661. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2559.1983.tb02277.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakabayashi H., Taketa K., Miyano K., Yamane T., Sato J. Growth of human hepatoma cells lines with differentiated functions in chemically defined medium. Cancer Res. 1982 Sep;42(9):3858–3863. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Philippe J., Chick W. L., Habener J. F. Multipotential phenotypic expression of genes encoding peptide hormones in rat insulinoma cell lines. J Clin Invest. 1987 Feb;79(2):351–358. doi: 10.1172/JCI112819. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruggeri B., Zhang S. Y., Caamano J., DiRado M., Flynn S. D., Klein-Szanto A. J. Human pancreatic carcinomas and cell lines reveal frequent and multiple alterations in the p53 and Rb-1 tumor-suppressor genes. Oncogene. 1992 Aug;7(8):1503–1511. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takaki R., Ono J., Nakamura M., Yokogawa Y., Kumae S., Hiraoka T., Yamaguchi K., Hamaguchi K., Uchida S. Isolation of glucagon-secreting cell lines by cloning insulinoma cells. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol. 1986 Mar;22(3 Pt 1):120–126. doi: 10.1007/BF02623498. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tan T. H., Wallis J., Levine A. J. Identification of the p53 protein domain involved in formation of the simian virus 40 large T-antigen-p53 protein complex. J Virol. 1986 Sep;59(3):574–583. doi: 10.1128/jvi.59.3.574-583.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ullrich S. J., Anderson C. W., Mercer W. E., Appella E. The p53 tumor suppressor protein, a modulator of cell proliferation. J Biol Chem. 1992 Aug 5;267(22):15259–15262. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogelstein B., Fearon E. R., Hamilton S. R., Kern S. E., Preisinger A. C., Leppert M., Nakamura Y., White R., Smits A. M., Bos J. L. Genetic alterations during colorectal-tumor development. N Engl J Med. 1988 Sep 1;319(9):525–532. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198809013190901. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vojtesek B., Bártek J., Midgley C. A., Lane D. P. An immunochemical analysis of the human nuclear phosphoprotein p53. New monoclonal antibodies and epitope mapping using recombinant p53. J Immunol Methods. 1992 Jul 6;151(1-2):237–244. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(92)90122-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiedenmann B., Franke W. W., Kuhn C., Moll R., Gould V. E. Synaptophysin: a marker protein for neuroendocrine cells and neoplasms. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 May;83(10):3500–3504. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.10.3500. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshimoto K., Iwahana H., Fukuda A., Sano T., Saito S., Itakura M. Role of p53 mutations in endocrine tumorigenesis: mutation detection by polymerase chain reaction-single strand conformation polymorphism. Cancer Res. 1992 Sep 15;52(18):5061–5064. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]