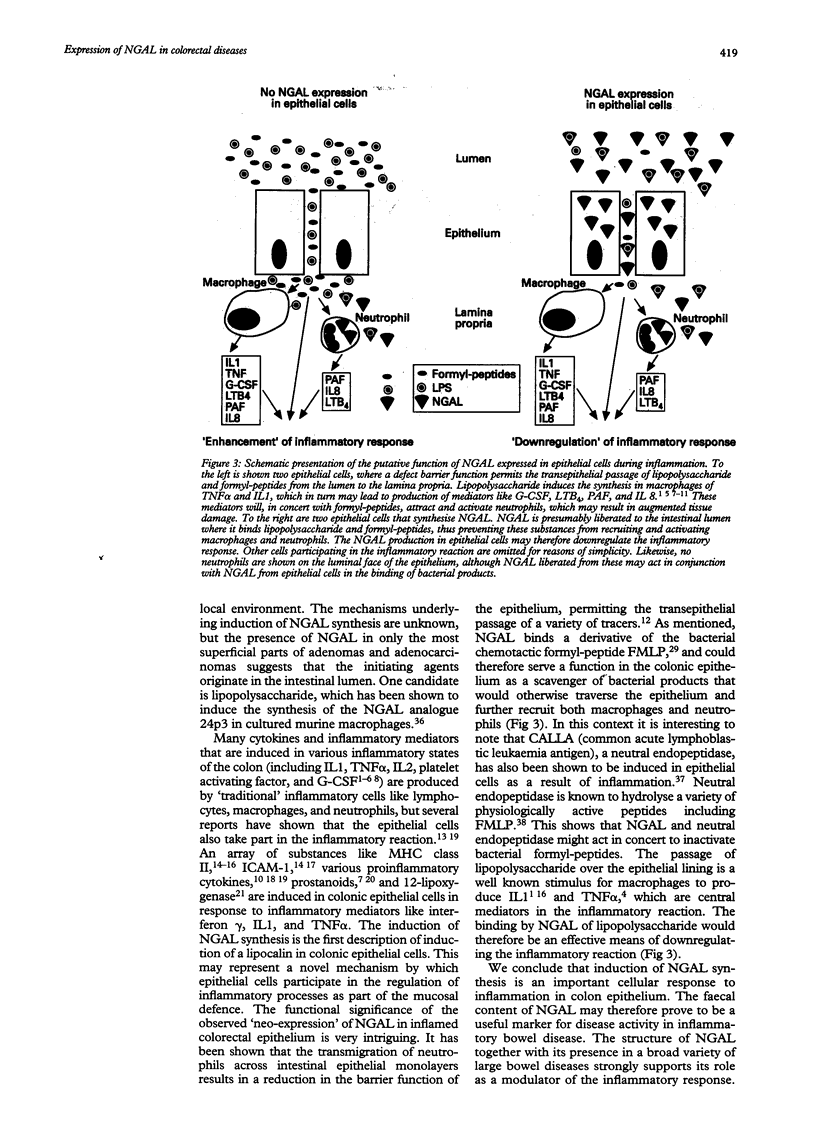
Abstract
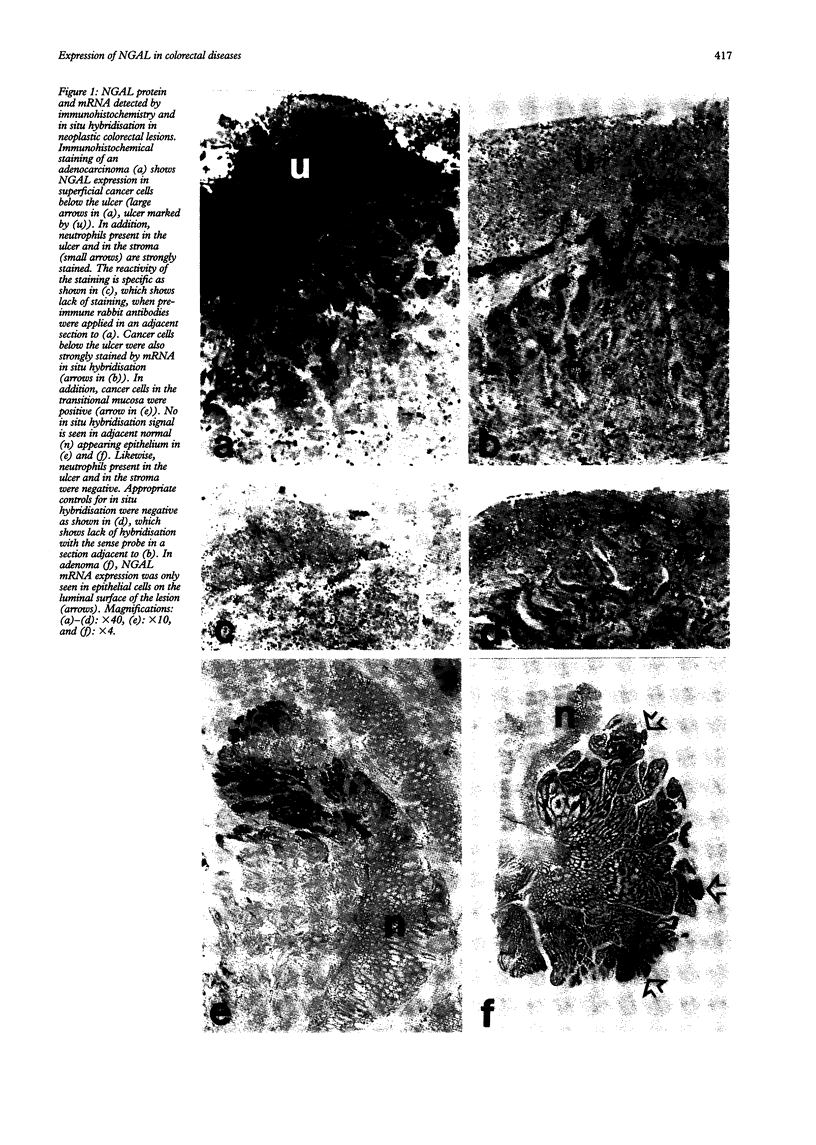
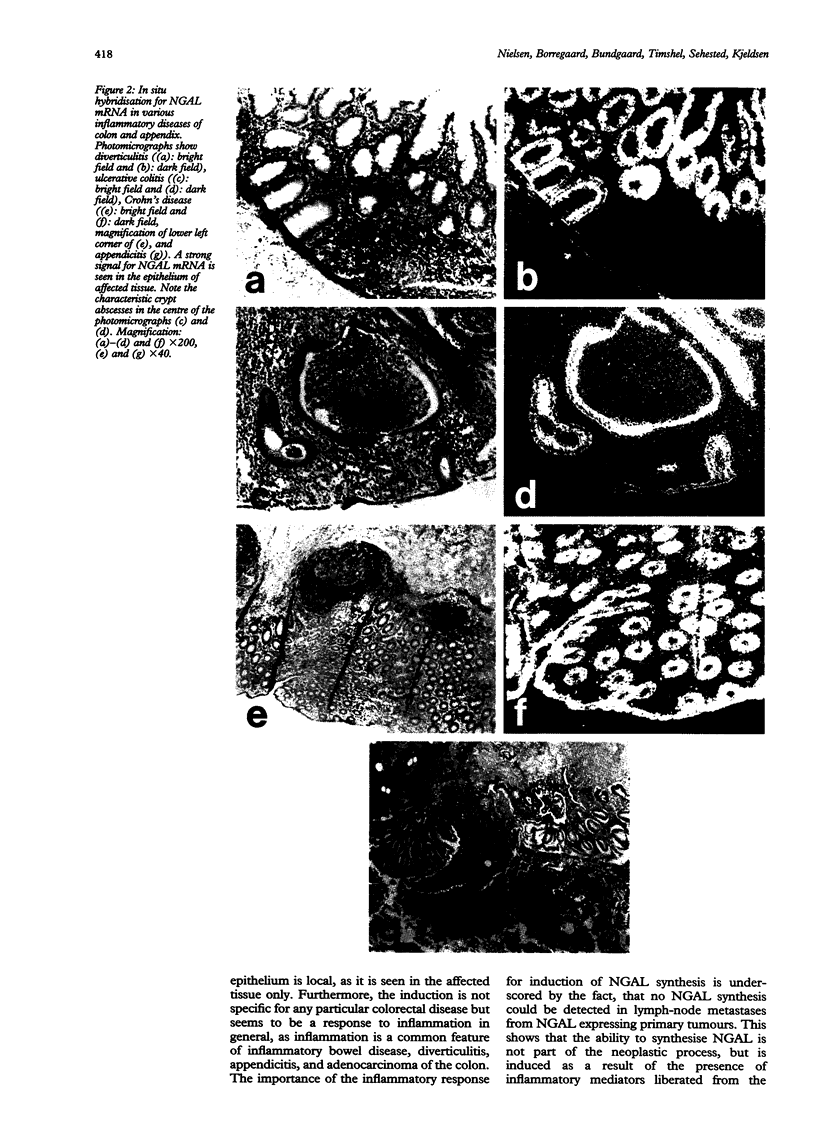
In inflammatory and neoplastic disorders of the colon a defect barrier function of the mucosa may result in absorption of bacterial products from the intestinal lumen. These products may further recruit inflammatory cells and thus augment the inflammatory response. A novel lipocalin in neutrophils, neutrophil gelatinase associated lipocalin (NGAL), with the ability to bind bacterial formylpeptides, has been described and therefore it is of interest to investigate the expression of this protein in diseases of the colon. Expression of NGAL was investigated by immunohistochemistry and by mRNA in situ hybridisation in normal colon and in neoplastic and inflammatory colorectal diseases. A very high expression of NGAL was seen in colonic epithelium in areas of inflammation, both in non-malignant epithelium (diverticulitis, inflammatory bowel disease, and appendicitis) as well as in premalignant and malignant neoplastic lesions of the colon. In adenocarcinoma, the NGAL expression was especially abundant in the transitional mucosa and in the superficial ulcerated area. On the other hand, no NGAL expression could be detected in lymph node metastases from these adenocarcinomas. A weak expression of NGAL in some epithelial cells was only occasionally seen in normal colon. In conclusion, NGAL synthesis is induced in epithelial cells in inflammatory and neoplastic, colorectal diseases. NGAL may serve an important anti-inflammatory function as a scavenger of bacterial products.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beaulieu A. D., Paquin R., Rathanaswami P., McColl S. R. Nuclear signaling in human neutrophils. Stimulation of RNA synthesis is a response to a limited number of proinflammatory agonists. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jan 5;267(1):426–432. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bland P. MHC class II expression by the gut epithelium. Immunol Today. 1988 Jun;9(6):174–178. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(88)91293-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Botto M., Lissandrini D., Sorio C., Walport M. J. Biosynthesis and secretion of complement component (C3) by activated human polymorphonuclear leukocytes. J Immunol. 1992 Aug 15;149(4):1348–1355. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brynskov J., Tvede N., Andersen C. B., Vilien M. Increased concentrations of interleukin 1 beta, interleukin-2, and soluble interleukin-2 receptors in endoscopical mucosal biopsy specimens with active inflammatory bowel disease. Gut. 1992 Jan;33(1):55–58. doi: 10.1136/gut.33.1.55. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bundgaard J. R., Sengeløv H., Borregaard N., Kjeldsen L. Molecular cloning and expression of a cDNA encoding NGAL: a lipocalin expressed in human neutrophils. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1994 Aug 15;202(3):1468–1475. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1994.2096. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cappello M., Keshav S., Prince C., Jewell D. P., Gordon S. Detection of mRNAs for macrophage products in inflammatory bowel disease by in situ hybridisation. Gut. 1992 Sep;33(9):1214–1219. doi: 10.1136/gut.33.9.1214. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cicco N. A., Lindemann A., Content J., Vandenbussche P., Lübbert M., Gauss J., Mertelsmann R., Herrmann F. Inducible production of interleukin-6 by human polymorphonuclear neutrophils: role of granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor and tumor necrosis factor-alpha. Blood. 1990 May 15;75(10):2049–2052. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cowan S. W., Newcomer M. E., Jones T. A. Crystallographic refinement of human serum retinol binding protein at 2A resolution. Proteins. 1990;8(1):44–61. doi: 10.1002/prot.340080108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Das K. M., Squillante L., Robertson F. M. Amplified expression of intercellular adhesion molecule-1 (ICAM-1) and M(r) 40K protein by DLD-1 colon tumor cells by interferon-gamma. Cell Immunol. 1993 Mar;147(1):215–221. doi: 10.1006/cimm.1993.1061. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eliakim R., Karmeli F., Razin E., Rachmilewitz D. Role of platelet-activating factor in ulcerative colitis. Enhanced production during active disease and inhibition by sulfasalazine and prednisolone. Gastroenterology. 1988 Nov;95(5):1167–1172. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(88)90346-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fais S., Pallone F. Ability of human colonic epithelium to express the 4F2 antigen, the common acute lymphoblastic leukemia antigen, and the transferrin receptor. Studies in inflammatory bowel disease and after in vitro exposure to different stimuli. Gastroenterology. 1989 Dec;97(6):1435–1441. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(89)90387-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flower D. R., North A. C., Attwood T. K. Mouse oncogene protein 24p3 is a member of the lipocalin protein family. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1991 Oct 15;180(1):69–74. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(05)81256-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Godovac-Zimmermann J. The structural motif of beta-lactoglobulin and retinol-binding protein: a basic framework for binding and transport of small hydrophobic molecules? Trends Biochem Sci. 1988 Feb;13(2):64–66. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(88)90031-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isaacs K. L., Sartor R. B., Haskill S. Cytokine messenger RNA profiles in inflammatory bowel disease mucosa detected by polymerase chain reaction amplification. Gastroenterology. 1992 Nov;103(5):1587–1595. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(92)91182-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jung H. C., Eckmann L., Yang S. K., Panja A., Fierer J., Morzycka-Wroblewska E., Kagnoff M. F. A distinct array of proinflammatory cytokines is expressed in human colon epithelial cells in response to bacterial invasion. J Clin Invest. 1995 Jan;95(1):55–65. doi: 10.1172/JCI117676. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly C. P., O'Keane J. C., Orellana J., Schroy P. C., 3rd, Yang S., LaMont J. T., Brady H. R. Human colon cancer cells express ICAM-1 in vivo and support LFA-1-dependent lymphocyte adhesion in vitro. Am J Physiol. 1992 Dec;263(6 Pt 1):G864–G870. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1992.263.6.G864. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kjeldsen L., Bainton D. F., Sengeløv H., Borregaard N. Identification of neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin as a novel matrix protein of specific granules in human neutrophils. Blood. 1994 Feb 1;83(3):799–807. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kjeldsen L., Johnsen A. H., Sengeløv H., Borregaard N. Isolation and primary structure of NGAL, a novel protein associated with human neutrophil gelatinase. J Biol Chem. 1993 May 15;268(14):10425–10432. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kvale D., Brandtzaeg P., Løvhaug D. Up-regulation of the expression of secretory component and HLA molecules in a human colonic cell line by tumour necrosis factor-alpha and gamma interferon. Scand J Immunol. 1988 Sep;28(3):351–357. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1988.tb01460.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lammers K. M., Jansen J., Bijlsma P. B., Ceska M., Tytgat G. N., Laboisse C. L., van Deventer S. J. Polarised interleukin 8 secretion by HT 29/19A cells. Gut. 1994 Mar;35(3):338–342. doi: 10.1136/gut.35.3.338. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lauritsen K., Laursen L. S., Bukhave K., Rask-Madsen J. In vivo profiles of eicosanoids in ulcerative colitis, Crohn's colitis, and Clostridium difficile colitis. Gastroenterology. 1988 Jul;95(1):11–17. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(88)90284-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ligumsky M., Simon P. L., Karmeli F., Rachmilewitz D. Role of interleukin 1 in inflammatory bowel disease--enhanced production during active disease. Gut. 1990 Jun;31(6):686–689. doi: 10.1136/gut.31.6.686. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacDonald T. T., Hutchings P., Choy M. Y., Murch S., Cooke A. Tumour necrosis factor-alpha and interferon-gamma production measured at the single cell level in normal and inflamed human intestine. Clin Exp Immunol. 1990 Aug;81(2):301–305. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.1990.tb03334.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mazzucchelli L., Hauser C., Zgraggen K., Wagner H., Hess M., Laissue J. A., Mueller C. Expression of interleukin-8 gene in inflammatory bowel disease is related to the histological grade of active inflammation. Am J Pathol. 1994 May;144(5):997–1007. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meheus L. A., Fransen L. M., Raymackers J. G., Blockx H. A., Van Beeumen J. J., Van Bun S. M., Van de Voorde A. Identification by microsequencing of lipopolysaccharide-induced proteins secreted by mouse macrophages. J Immunol. 1993 Aug 1;151(3):1535–1547. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nash S., Stafford J., Madara J. L. Effects of polymorphonuclear leukocyte transmigration on the barrier function of cultured intestinal epithelial monolayers. J Clin Invest. 1987 Oct;80(4):1104–1113. doi: 10.1172/JCI113167. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perdue M. H., McKay D. M. Integrative immunophysiology in the intestinal mucosa. Am J Physiol. 1994 Aug;267(2 Pt 1):G151–G165. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1994.267.2.G151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pervaiz S., Brew K. Homology and structure-function correlations between alpha 1-acid glycoprotein and serum retinol-binding protein and its relatives. FASEB J. 1987 Sep;1(3):209–214. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.1.3.3622999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pullman W. E., Elsbury S., Kobayashi M., Hapel A. J., Doe W. F. Enhanced mucosal cytokine production in inflammatory bowel disease. Gastroenterology. 1992 Feb;102(2):529–537. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(92)90100-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pyke C., Kristensen P., Ralfkiaer E., Grøndahl-Hansen J., Eriksen J., Blasi F., Danø K. Urokinase-type plasminogen activator is expressed in stromal cells and its receptor in cancer cells at invasive foci in human colon adenocarcinomas. Am J Pathol. 1991 May;138(5):1059–1067. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sengeløv H., Boulay F., Kjeldsen L., Borregaard N. Subcellular localization and translocation of the receptor for N-formylmethionyl-leucyl-phenylalanine in human neutrophils. Biochem J. 1994 Apr 15;299(Pt 2):473–479. doi: 10.1042/bj2990473. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shannon V. R., Stenson W. F., Holtzman M. J. Induction of epithelial arachidonate 12-lipoxygenase at active sites of inflammatory bowel disease. Am J Physiol. 1993 Jan;264(1 Pt 1):G104–G111. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1993.264.1.G104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharon P., Stenson W. F. Enhanced synthesis of leukotriene B4 by colonic mucosa in inflammatory bowel disease. Gastroenterology. 1984 Mar;86(3):453–460. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shipp M. A., Look A. T. Hematopoietic differentiation antigens that are membrane-associated enzymes: cutting is the key! Blood. 1993 Aug 15;82(4):1052–1070. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thornton A. J., Strieter R. M., Lindley I., Baggiolini M., Kunkel S. L. Cytokine-induced gene expression of a neutrophil chemotactic factor/IL-8 in human hepatocytes. J Immunol. 1990 Apr 1;144(7):2609–2613. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Triebel S., Bläser J., Reinke H., Tschesche H. A 25 kDa alpha 2-microglobulin-related protein is a component of the 125 kDa form of human gelatinase. FEBS Lett. 1992 Dec 21;314(3):386–388. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(92)81511-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Urieli-Shoval S., Meek R. L., Hanson R. H., Ferguson M., Gordon D., Benditt E. P. Preservation of RNA for in situ hybridization: Carnoy's versus formaldehyde fixation. J Histochem Cytochem. 1992 Dec;40(12):1879–1885. doi: 10.1177/40.12.1280665. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zifroni A., Treves A. J., Sachar D. B., Rachmilewitz D. Prostanoid synthesis by cultured intestinal epithelial and mononuclear cells in inflammatory bowel disease. Gut. 1983 Jul;24(7):659–664. doi: 10.1136/gut.24.7.659. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]