Abstract
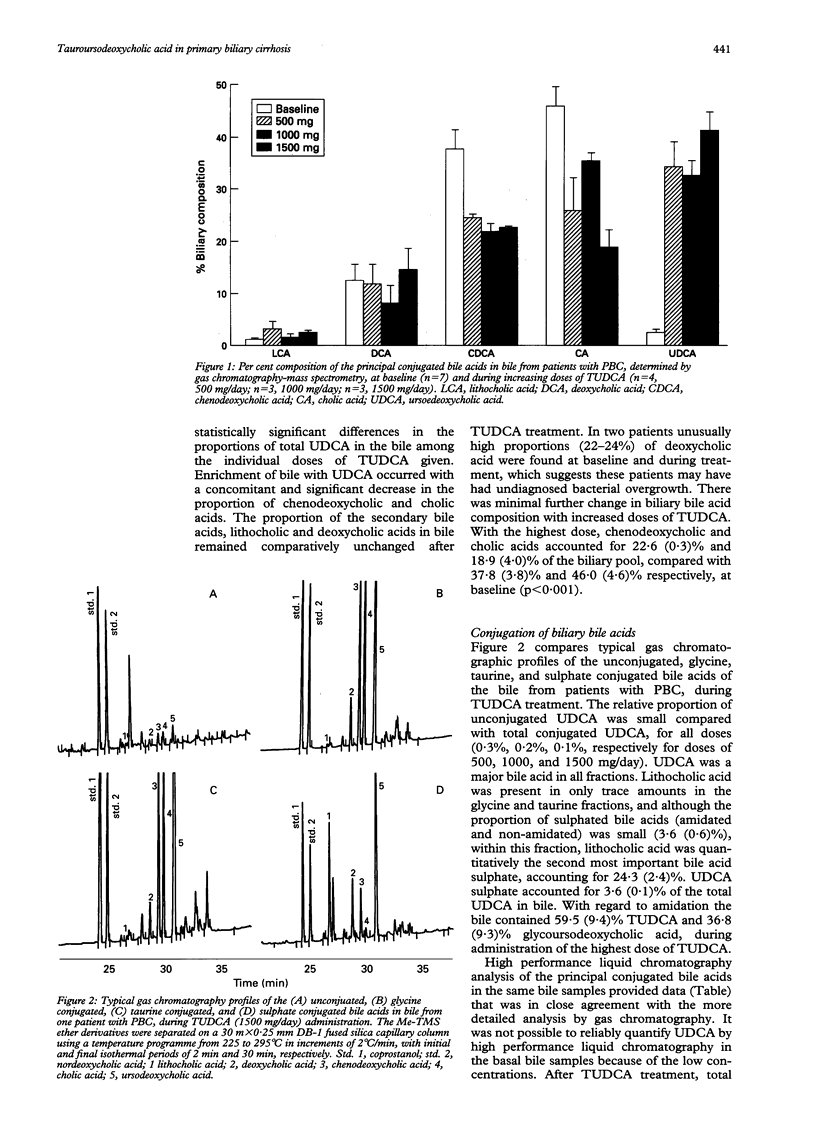
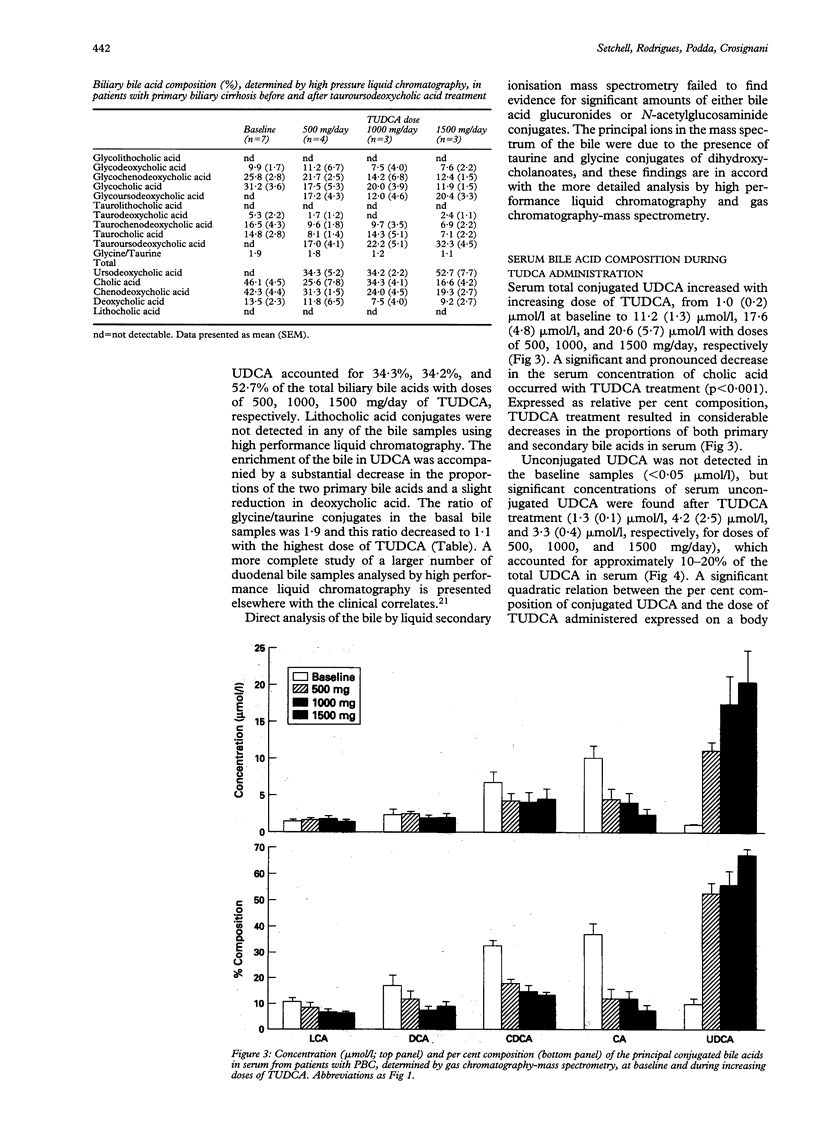
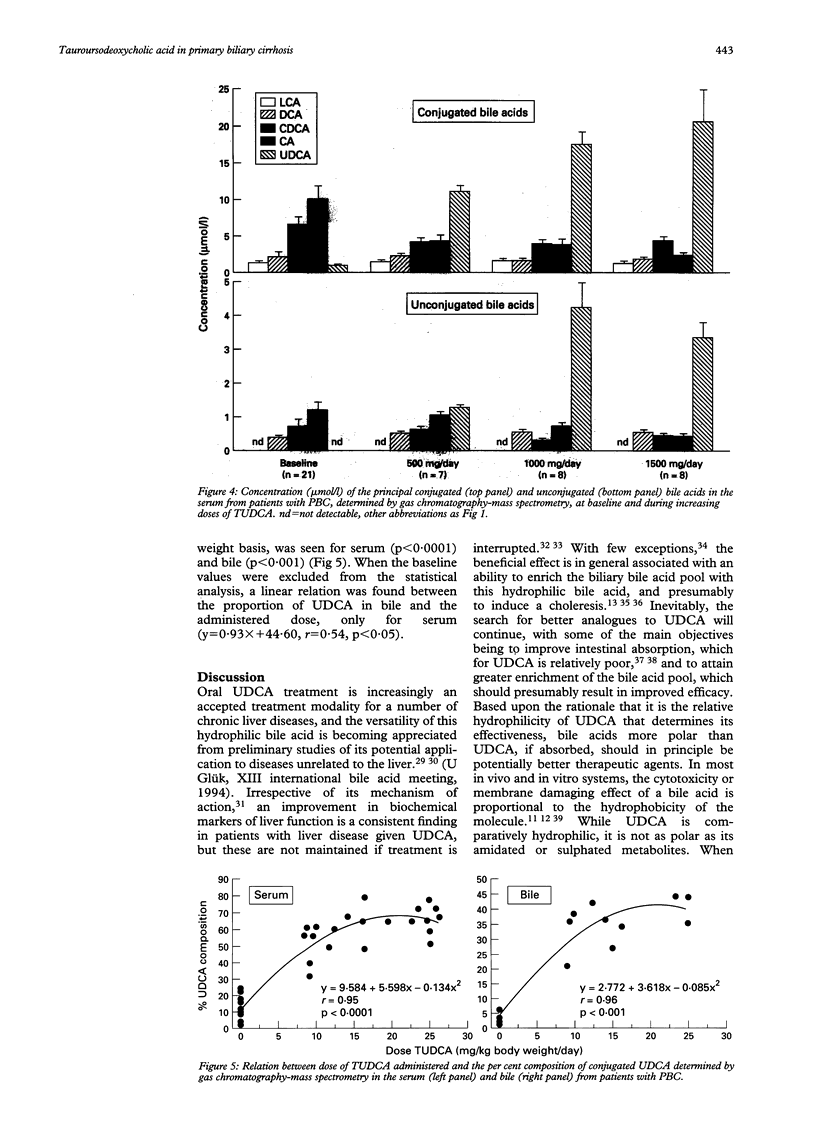
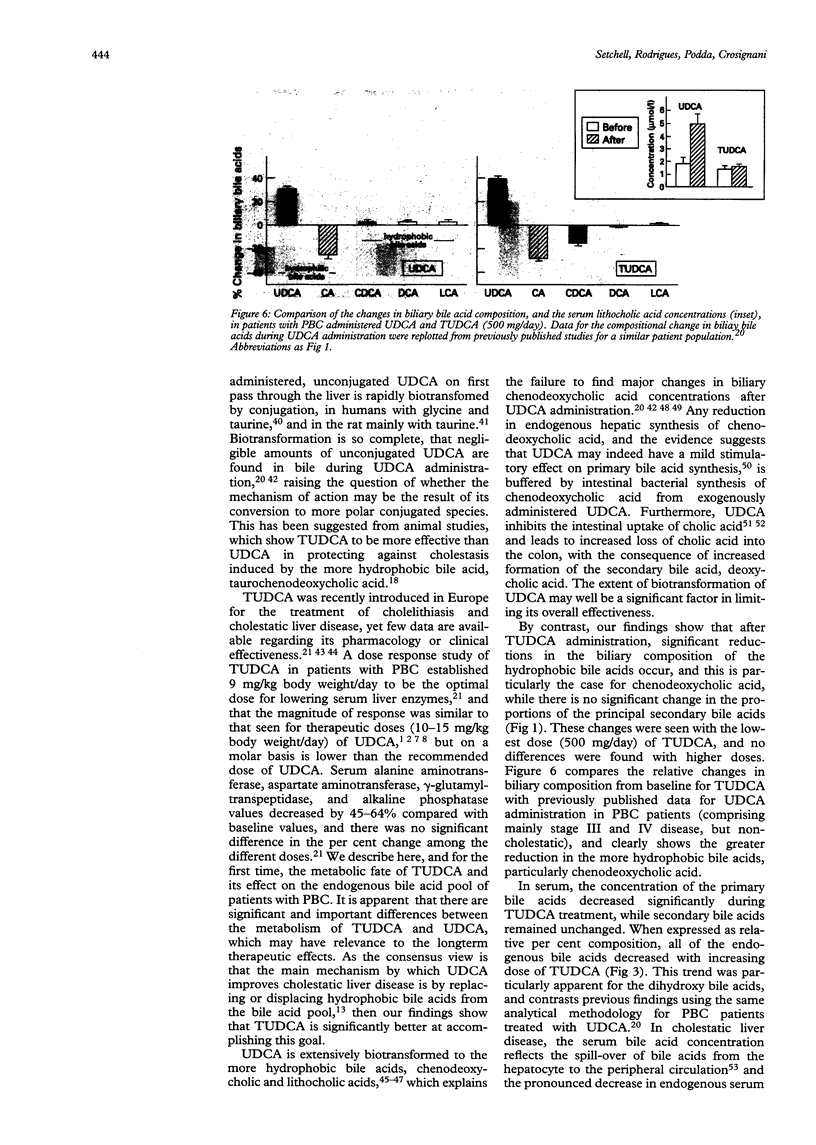
The metabolism of tauroursodeoxycholic acid orally administered and its effects on the bile acid pool of patients with asymptomatic/mildly symptomatic primary biliary cirrhosis is described. Patients were randomly assigned 500, 1000, or 1500 mg/day of tauroursodeoxycholate for six months. Biliary and serum bile acids were measured before and during treatment by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry and by high performance liquid chromatography. During tauroursodeoxycholate administration, the proportion of total ursodeoxycholate in bile reached mean (SEM) 34.4 (4.5)%, 32.8 (2.8)%, and 41.6 (3.0)% with doses of 500, 1000, and 1500 mg/day, respectively. Significant decreases in the proportions of chenodeoxycholate and cholate resulted. The glycine/taurine ratio of the biliary bile acid pool decreased from 1.9 at baseline, to 1.1 with the highest dose. Ursodeoxycholate in bile was conjugated with glycine and taurine, indicating that tauroursodeoxycholate undergoes significant deconjugation and reconjugation during its enterohepatic recycling. The proportion of lithocholate in bile remained unchanged. Fasting serum conjugated ursodeoxycholate concentration positively correlated with the tauroursodeoxycholate dose, and the increased proportion of ursodeoxycholate was accompanied by substantial decreases in the endogenous bile acids. Compared with previously published data for ursodeoxycholic acid therapy, these findings indicate that the shift toward a more hydrophilic bile acid pool is greater and potentially more favourable with tauroursodeoxycholate, and this is because of the reduced intestinal biotransformation of tauroursodeoxycholate.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Almé B., Bremmelgaard A., Sjövall J., Thomassen P. Analysis of metabolic profiles of bile acids in urine using a lipophilic anion exchanger and computerized gas-liquid chromatorgaphy-mass spectrometry. J Lipid Res. 1977 May;18(3):339–362. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Armstrong M. J., Carey M. C. The hydrophobic-hydrophilic balance of bile salts. Inverse correlation between reverse-phase high performance liquid chromatographic mobilities and micellar cholesterol-solubilizing capacities. J Lipid Res. 1982 Jan;23(1):70–80. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Attili A. F., Angelico M., Cantafora A., Alvaro D., Capocaccia L. Bile acid-induced liver toxicity: relation to the hydrophobic-hydrophilic balance of bile acids. Med Hypotheses. 1986 Jan;19(1):57–69. doi: 10.1016/0306-9877(86)90137-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bachrach W. H., Hofmann A. F. Ursodeoxycholic acid in the treatment of cholesterol cholelithiasis. Part II. Dig Dis Sci. 1982 Sep;27(9):833–856. doi: 10.1007/BF01391378. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Batta A. K., Salen G., Arora R., Shefer S., Tint G. S., Abroon J., Eskreis D., Katz S. Effect of ursodeoxycholic acid on bile acid metabolism in primary biliary cirrhosis. Hepatology. 1989 Oct;10(4):414–419. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840100404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beuers U., Spengler U., Zwiebel F. M., Pauletzki J., Fischer S., Paumgartner G. Effect of ursodeoxycholic acid on the kinetics of the major hydrophobic bile acids in health and in chronic cholestatic liver disease. Hepatology. 1992 Apr;15(4):603–608. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840150409. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calmus Y., Gane P., Rouger P., Poupon R. Hepatic expression of class I and class II major histocompatibility complex molecules in primary biliary cirrhosis: effect of ursodeoxycholic acid. Hepatology. 1990 Jan;11(1):12–15. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840110104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chazouillères O., Poupon R., Capron J. P., Metman E. H., Dhumeaux D., Amouretti M., Couzigou P., Labayle D., Trinchet J. C. Ursodeoxycholic acid for primary sclerosing cholangitis. J Hepatol. 1990 Jul;11(1):120–123. doi: 10.1016/0168-8278(90)90281-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colombo C., Setchell K. D., Podda M., Crosignani A., Roda A., Curcio L., Ronchi M., Giunta A. Effects of ursodeoxycholic acid therapy for liver disease associated with cystic fibrosis. J Pediatr. 1990 Sep;117(3):482–489. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(05)81103-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crosignani A., Podda M., Battezzati P. M., Bertolini E., Zuin M., Watson D., Setchell K. D. Changes in bile acid composition in patients with primary biliary cirrhosis induced by ursodeoxycholic acid administration. Hepatology. 1991 Dec;14(6):1000–1007. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crosignani A., Podda M., Bertolini E., Battezzati P. M., Zuin M., Setchell K. D. Failure of ursodeoxycholic acid to prevent a cholestatic episode in a patient with benign recurrent intrahepatic cholestasis: a study of bile acid metabolism. Hepatology. 1991 Jun;13(6):1076–1083. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dumont M., Erlinger S., Uchman S. Hypercholeresis induced by ursodeoxycholic acid and 7-ketolithocholic acid in the rat: possible role of bicarbonate transport. Gastroenterology. 1980 Jul;79(1):82–89. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erlinger S. Hypercholeretic bile acids: a clue to the mechanism? Hepatology. 1990 May;11(5):888–890. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840110527. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fedorowski T., Salen G., Calallilo A., Tint G. S., Mosbach E. H., Hall J. C. Metabolism of ursodeoxycholic acid in man. Gastroenterology. 1977 Nov;73(5):1131–1137. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fedorowski T., Salen G., Tint G. S., Mosbach E. Transformation of chenodeoxycholic acid and ursodeoxycholic acid by human intestinal bacteria. Gastroenterology. 1979 Nov;77(5):1068–1073. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fromm H., Carlson G. L., Hofmann A. F., Farivar S., Amin P. Metabolism in man of 7-ketolithocholic acid: precursor of cheno- and ursodeoxycholic acids. Am J Physiol. 1980 Sep;239(3):G161–G166. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1980.239.3.G161. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heuman D. M., Bajaj R. Ursodeoxycholate conjugates protect against disruption of cholesterol-rich membranes by bile salts. Gastroenterology. 1994 May;106(5):1333–1341. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(94)90027-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heuman D. M., Pandak W. M., Hylemon P. B., Vlahcevic Z. R. Conjugates of ursodeoxycholate protect against cytotoxicity of more hydrophobic bile salts: in vitro studies in rat hepatocytes and human erythrocytes. Hepatology. 1991 Nov;14(5):920–926. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840140527. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heuman D. M., Vlahcevic Z. R., Bailey M. L., Hylemon P. B. Regulation of bile acid synthesis. II. Effect of bile acid feeding on enzymes regulating hepatic cholesterol and bile acid synthesis in the rat. Hepatology. 1988 Jul-Aug;8(4):892–897. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840080431. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirano Y., Miyazaki H., Higashidate S., Nakayama F. Analysis of 3-sulfated and nonsulfated bile acids by one-step solvolysis and high performance liquid chromatography. J Lipid Res. 1987 Dec;28(12):1524–1529. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Javitt N. B. Ursodeoxycholic acid therapy: the baby and the bathwater. Hosp Pract (Off Ed) 1992 Mar 15;27(3):12, 15-6. doi: 10.1080/21548331.1992.11705373. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leuschner U., Fischer H., Kurtz W., Güldütuna S., Hübner K., Hellstern A., Gatzen M., Leuschner M. Ursodeoxycholic acid in primary biliary cirrhosis: results of a controlled double-blind trial. Gastroenterology. 1989 Nov;97(5):1268–1274. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(89)91698-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leuschner U., Güldütuna S., Imhof M., Hübner K., Benjaminov A., Leuschner M. Effects of ursodeoxycholic acid after 4 to 12 years of therapy in early and late stages of primary biliary cirrhosis. J Hepatol. 1994 Oct;21(4):624–633. doi: 10.1016/s0168-8278(94)80111-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marteau P., Chazouilléres O., Myara A., Jian R., Rambaud J. C., Poupon R. Effect of chronic administration of ursodeoxycholic acid on the ileal absorption of endogenous bile acids in man. Hepatology. 1990 Nov;12(5):1206–1208. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840120521. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nair P. P., Garcia C. A modified gas-liquid chromatographic procedure for the rapid determination of bile acids in biological fluids. Anal Biochem. 1969 Apr 11;29(1):164–166. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(69)90020-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakagawa M., Colombo C., Setchell K. D. Comprehensive study of the biliary bile acid composition of patients with cystic fibrosis and associated liver disease before and after UDCA administration. Hepatology. 1990 Aug;12(2):322–334. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840120221. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakai T., Katagiri K., Hoshino M., Hayakawa T., Ohiwa T. Microtubule-independent choleresis and anti-cholestatic action of tauroursodeoxycholate in colchicine-treated rat liver. Biochem J. 1992 Dec 1;288(Pt 2):613–617. doi: 10.1042/bj2880613. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Podda M., Ghezzi C., Battezzati P. M., Bertolini E., Crosignani A., Petroni M. L., Zuin M. Effect of different doses of ursodeoxycholic acid in chronic liver disease. Dig Dis Sci. 1989 Dec;34(12 Suppl):59S–65S. doi: 10.1007/BF01536665. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Podda M., Ghezzi C., Battezzati P. M., Crosignani A., Zuin M., Roda A. Effects of ursodeoxycholic acid and taurine on serum liver enzymes and bile acids in chronic hepatitis. Gastroenterology. 1990 Apr;98(4):1044–1050. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(90)90032-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poupon R. E., Balkau B., Eschwège E., Poupon R. A multicenter, controlled trial of ursodiol for the treatment of primary biliary cirrhosis. UDCA-PBC Study Group. N Engl J Med. 1991 May 30;324(22):1548–1554. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199105303242204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poupon R. E., Poupon R., Balkau B. Ursodiol for the long-term treatment of primary biliary cirrhosis. The UDCA-PBC Study Group. N Engl J Med. 1994 May 12;330(19):1342–1347. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199405123301903. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poupon R., Chrétien Y., Poupon R. E., Ballet F., Calmus Y., Darnis F. Is ursodeoxycholic acid an effective treatment for primary biliary cirrhosis? Lancet. 1987 Apr 11;1(8537):834–836. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(87)91610-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Renner E. L., Lake J. R., Cragoe E. J., Jr, Van Dyke R. W., Scharschmidt B. F. Ursodeoxycholic acid choleresis: relationship to biliary HCO-3 and effects of Na+-H+ exchange inhibitors. Am J Physiol. 1988 Feb;254(2 Pt 1):G232–G241. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1988.254.2.G232. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodrigues C. M., Kren B. T., Steer C. J., Setchell K. D. Tauroursodeoxycholate increases rat liver ursodeoxycholate levels and limits lithocholate formation better than ursodeoxycholate. Gastroenterology. 1995 Aug;109(2):564–572. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(95)90346-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rossi S. S., Converse J. L., Hofmann A. F. High pressure liquid chromatographic analysis of conjugated bile acids in human bile: simultaneous resolution of sulfated and unsulfated lithocholyl amidates and the common conjugated bile acids. J Lipid Res. 1987 May;28(5):589–595. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rudolph G., Endele R., Senn M., Stiehl A. Effect of ursodeoxycholic acid on the kinetics of cholic acid and chenodeoxycholic acid in patients with primary sclerosing cholangitis. Hepatology. 1993 Jun;17(6):1028–1032. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Setchell K. D., Worthington J. A rapid method for the quantitative extraction of bile acids and their conjugates from serum using commercially available reverse-phase octadecylsilane bonded silica cartridges. Clin Chim Acta. 1982 Oct 27;125(2):135–144. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(82)90190-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stefaniwsky A. B., Tint G. S., Speck J., Shefer S., Salen G. Ursodeoxycholic acid treatment of bile reflux gastritis. Gastroenterology. 1985 Nov;89(5):1000–1004. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(85)90200-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stiehl A., Raedsch R., Rudolph G. Acute effects of ursodeoxycholic and chenodeoxycholic acid on the small intestinal absorption of bile acids. Gastroenterology. 1990 Feb;98(2):424–428. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(90)90834-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsukahara K., Kanai S., Ohta M., Kitani K. Taurine conjugate of ursodeoxycholate plays a major role in the hepatoprotective effect against cholestasis induced by taurochenodeoxycholate in rats. Liver. 1993 Oct;13(5):262–269. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0676.1993.tb00642.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vonk R. J., Kneepkens C. M., Havinga R., Kuipers F., Bijleveld C. M. Enterohepatic circulation in man. A simple method for the determination of duodenal bile acids. J Lipid Res. 1986 Aug;27(8):901–904. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker S., Rudolph G., Raedsch R., Stiehl A. Intestinal absorption of ursodeoxycholic acid in patients with extrahepatic biliary obstruction and bile drainage. Gastroenterology. 1992 Mar;102(3):810–815. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(92)90162-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Berge-Henegouwen G. P., Hofmann A. F. Systemic spill-over of bile acids. Eur J Clin Invest. 1983 Dec;13(6):433–437. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2362.1983.tb00125.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


