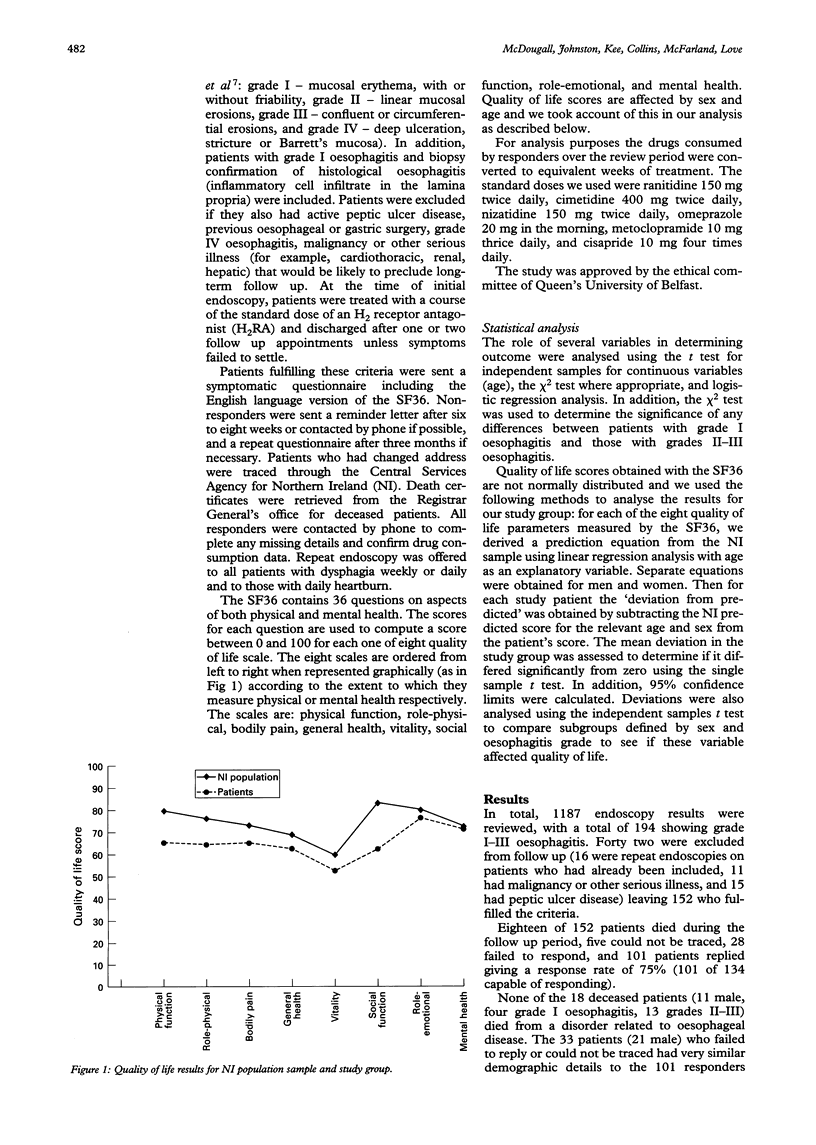
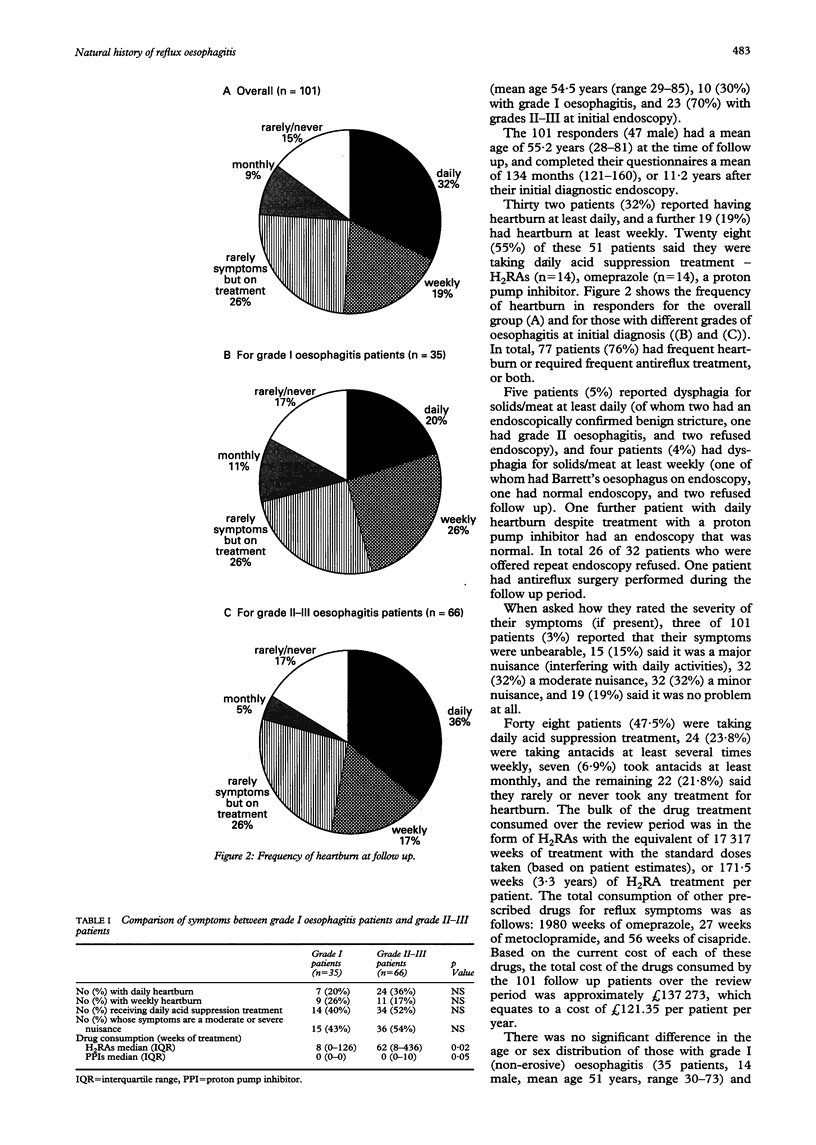
Abstract
BACKGROUND--Although oesophagitis is the most common diagnosis made at upper gastrointestinal endoscopy, data on the longterm outcome of affected patients are sparse. AIMS--This study assessed the level of reflux symptoms, quality of life, drug consumption, and complications in patients at least 10 years after diagnosis of oesophagitis at one centre. PATIENTS--One hundred and fifty two patients with typical reflux symptoms and a first time diagnosis by endoscopy of grade I-III oesophagitis between 1981 and 1984, were followed up using a postal questionnaire and telephone interview. RESULTS--Eighteen of 152 patients had died, 33 failed to respond, and 101 replied (mean follow up 11 years, range 121-160 months). Over 70% of patients still had heartburn at least daily (32%) or weekly (19%) or required daily acid suppression treatment (20%). Two patients (2%) had developed oesophageal strictures and one had Barrett's oesophagus. Two of eight quality of life scores (physical function and social function) measured by the Short Form-36 were significantly lower than Northern Ireland population scores. CONCLUSION--Nearly three quarters of patients previously diagnosed as having oesophagitis still had significant morbidity related to gastro-oesophageal reflux disease more than 10 years after diagnosis. Some quality of life scores were significantly lower than those of the general population.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Behar J., Biancani P., Sheahan D. G. Evaluation of esophageal tests in the diagnosis of reflux esophagitis. Gastroenterology. 1976 Jul;71(1):9–15. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Behar J., Sheahan D. G., Biancani P., Spiro H. M., Storer E. H. Medical and surgical management of reflux esophagitis. A 38-month report of a prospective clinical trial. N Engl J Med. 1975 Aug 7;293(6):263–268. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197508072930602. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brand D. L., Eastwood I. R., Martin D., Carter W. B., Pope C. E., 2nd Esophageal symptoms, manometry, and histology before and after antireflux surgery: a long-term follow-up study. Gastroenterology. 1979 Jun;76(6):1393–1401. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brazier J. E., Harper R., Jones N. M., O'Cathain A., Thomas K. J., Usherwood T., Westlake L. Validating the SF-36 health survey questionnaire: new outcome measure for primary care. BMJ. 1992 Jul 18;305(6846):160–164. doi: 10.1136/bmj.305.6846.160. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeMeester T. R., Bonavina L., Albertucci M. Nissen fundoplication for gastroesophageal reflux disease. Evaluation of primary repair in 100 consecutive patients. Ann Surg. 1986 Jul;204(1):9–20. doi: 10.1097/00000658-198607000-00002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dent J., Yeomans N. D., Mackinnon M., Reed W., Narielvala F. M., Hetzel D. J., Solcia E., Shearman D. J. Omeprazole v ranitidine for prevention of relapse in reflux oesophagitis. A controlled double blind trial of their efficacy and safety. Gut. 1994 May;35(5):590–598. doi: 10.1136/gut.35.5.590. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garratt A. M., Ruta D. A., Abdalla M. I., Buckingham J. K., Russell I. T. The SF36 health survey questionnaire: an outcome measure suitable for routine use within the NHS? BMJ. 1993 May 29;306(6890):1440–1444. doi: 10.1136/bmj.306.6890.1440. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hallerbäck B., Unge P., Carling L., Edwin B., Glise H., Havu N., Lyrenäs E., Lundberg K. Omeprazole or ranitidine in long-term treatment of reflux esophagitis. The Scandinavian Clinics for United Research Group. Gastroenterology. 1994 Nov;107(5):1305–1311. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(94)90531-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jenkinson C., Coulter A., Wright L. Short form 36 (SF36) health survey questionnaire: normative data for adults of working age. BMJ. 1993 May 29;306(6890):1437–1440. doi: 10.1136/bmj.306.6890.1437. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johansson K. E., Ask P., Boeryd B., Fransson S. G., Tibbling L. Oesophagitis, signs of reflux, and gastric acid secretion in patients with symptoms of gastro-oesophageal reflux disease. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1986 Sep;21(7):837–847. doi: 10.3109/00365528609011128. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klinkenberg-Knol E. C., Festen H. P., Jansen J. B., Lamers C. B., Nelis F., Snel P., Lückers A., Dekkers C. P., Havu N., Meuwissen S. G. Long-term treatment with omeprazole for refractory reflux esophagitis: efficacy and safety. Ann Intern Med. 1994 Aug 1;121(3):161–167. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-121-3-199408010-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koelz H. R., Birchler R., Bretholz A., Bron B., Capitaine Y., Delmore G., Fehr H. F., Fumagalli I., Gehrig J., Gonvers J. J. Healing and relapse of reflux esophagitis during treatment with ranitidine. Gastroenterology. 1986 Nov;91(5):1198–1205. doi: 10.1016/s0016-5085(86)80017-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuster E., Ros E., Toledo-Pimentel V., Pujol A., Bordas J. M., Grande L., Pera C. Predictive factors of the long term outcome in gastro-oesophageal reflux disease: six year follow up of 107 patients. Gut. 1994 Jan;35(1):8–14. doi: 10.1136/gut.35.1.8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lieberman D. A. Medical therapy for chronic reflux esophagitis. Long-term follow-up. Arch Intern Med. 1987 Oct;147(10):1717–1720. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Little A. G., DeMeester T. R., Kirchner P. T., O'Sullivan G. C., Skinner D. B. Pathogenesis of esophagitis in patients with gastroesophageal reflux. Surgery. 1980 Jul;88(1):101–107. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lundell L., Backman L., Ekström P., Enander L. K., Falkmer S., Fausa O., Grimelius L., Havu N., Lind T., Lönroth H. Prevention of relapse of reflux esophagitis after endoscopic healing: the efficacy and safety of omeprazole compared with ranitidine. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1991 Mar;26(3):248–256. doi: 10.3109/00365529109025038. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luostarinen M., Isolauri J., Laitinen J., Koskinen M., Keyriläinen O., Markkula H., Lehtinen E., Uusitalo A. Fate of Nissen fundoplication after 20 years. A clinical, endoscopical, and functional analysis. Gut. 1993 Aug;34(8):1015–1020. doi: 10.1136/gut.34.8.1015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martinez de Haro L. F., Ortiz A., Parrilla P., Garcia Marcilla J. A., Aguayo J. L., Morales G. Long-term results of Nissen fundoplication in reflux esophagitis without strictures. Clinical, endoscopic, and pH-metric evaluation. Dig Dis Sci. 1992 Apr;37(4):523–527. doi: 10.1007/BF01307574. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nebel O. T., Fornes M. F., Castell D. O. Symptomatic gastroesophageal reflux: incidence and precipitating factors. Am J Dig Dis. 1976 Nov;21(11):953–956. doi: 10.1007/BF01071906. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Negre J. B., Markkula H. T., Keyrilainen O., Matikainen M. Nissen fundoplication. Results at 10 year follow-up. Am J Surg. 1983 Nov;146(5):635–638. doi: 10.1016/0002-9610(83)90301-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newsholme E. A., Carrié A. L. Quantitative aspects of glucose and glutamine metabolism by intestinal cells. Gut. 1994 Jan;35(1 Suppl):S13–S17. doi: 10.1136/gut.35.1_suppl.s13. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pace F., Santalucia F., Bianchi Porro G. Natural history of gastro-oesophageal reflux disease without oesophagitis. Gut. 1991 Aug;32(8):845–848. doi: 10.1136/gut.32.8.845. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmer E. D. The hiatus hernia-esophagitis-esophageal stricture complex. Twenty-year prospective study. Am J Med. 1968 Apr;44(4):566–579. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(68)90057-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schindlbeck N. E., Klauser A. G., Berghammer G., Londong W., Müller-Lissner S. A. Three year follow up of patients with gastrooesophageal reflux disease. Gut. 1992 Aug;33(8):1016–1019. doi: 10.1136/gut.33.8.1016. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spechler S. J. Comparison of medical and surgical therapy for complicated gastroesophageal reflux disease in veterans. The Department of Veterans Affairs Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease Study Group. N Engl J Med. 1992 Mar 19;326(12):786–792. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199203193261202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spechler S. J. Epidemiology and natural history of gastro-oesophageal reflux disease. Digestion. 1992;51 (Suppl 1):24–29. doi: 10.1159/000200911. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson W. G., Heaton K. W. Heartburn and globus in apparently healthy people. Can Med Assoc J. 1982 Jan 1;126(1):46–48. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wienbeck M., Barnert J. Epidemiology of reflux disease and reflux esophagitis. Scand J Gastroenterol Suppl. 1989;156:7–13. doi: 10.3109/00365528909091032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



