Abstract
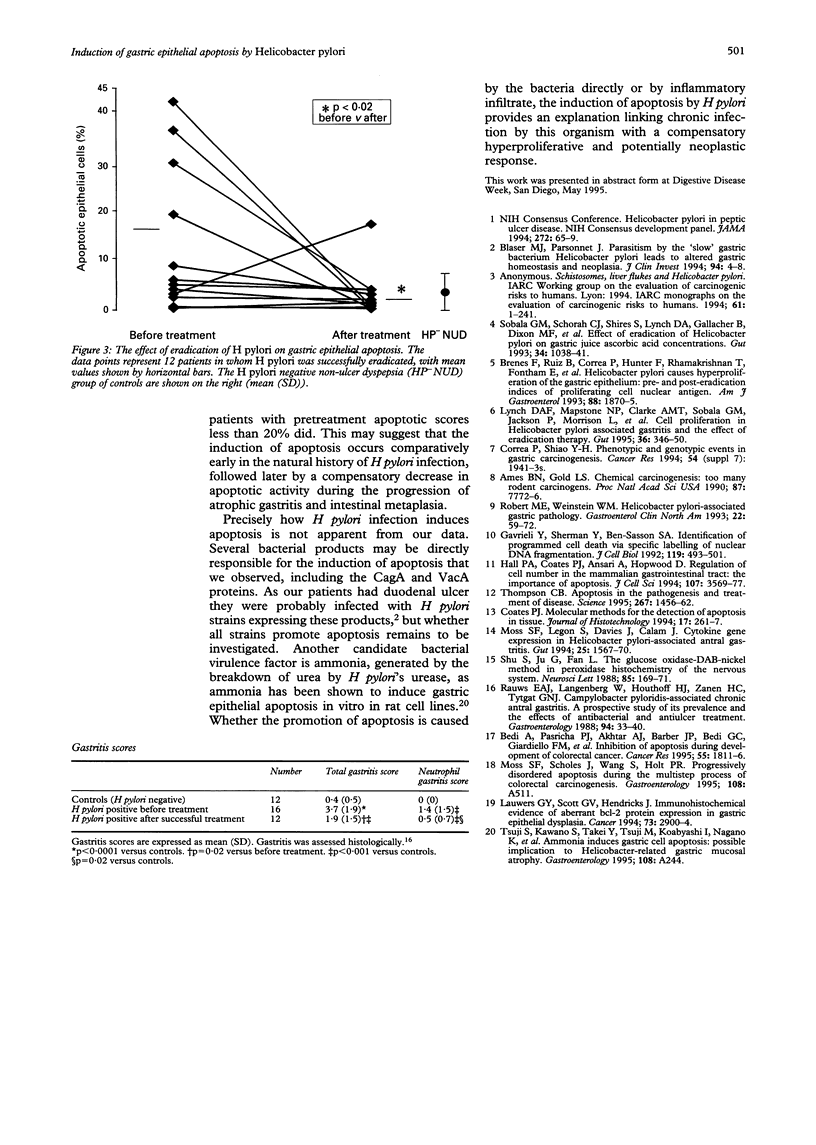
BACKGROUND--Helicobacter pylori may promote gastric carcinogenesis through increasing gastric epithelial cell proliferation. How H pylori does so is unknown. Programmed, non-necrotic, cell death (apoptosis) occurs throughout the gut and is linked to proliferation. It was hypothesised that H pylori may induce hyper-proliferation through increasing apoptosis. AIM--To measure the effect of H pylori infection on gastric epithelial apoptosis in situ. PATIENTS--Patients with duodenal ulcers treated to eradicate H pylori and patients with H pylori negative non-ulcer dyspepsia. METHODS--Retrospective quantification of apoptotic epithelial cells in situ from formalin fixed biopsy specimens, counted after staining by terminal uridine deoxynucleotidyl nick end-labelling. RESULTS--In the uninfected stomach, apoptotic cells were rare and situated in the most superficial portion of gastric glands (mean 2.9% of epithelial cells). In H pylori infection, they were more numerous and were located throughout the depth of gastric glands, comprising 16.8% of epithelial cells, falling to 3.1% after H pylori eradication, p = 0.017. Apoptotic cell number did not correlate with the degree of histological gastritis. CONCLUSIONS--These results suggest that H pylori induces epithelial apoptosis in vivo. Increased apoptosis may be the stimulus for a compensatory hyperproliferative and potentially preneoplastic response in chronic H pylori infection.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ames B. N., Gold L. S. Chemical carcinogenesis: too many rodent carcinogens. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Oct;87(19):7772–7776. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.19.7772. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bedi A., Pasricha P. J., Akhtar A. J., Barber J. P., Bedi G. C., Giardiello F. M., Zehnbauer B. A., Hamilton S. R., Jones R. J. Inhibition of apoptosis during development of colorectal cancer. Cancer Res. 1995 May 1;55(9):1811–1816. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brenes F., Ruiz B., Correa P., Hunter F., Rhamakrishnan T., Fontham E., Shi T. Y. Helicobacter pylori causes hyperproliferation of the gastric epithelium: pre- and post-eradication indices of proliferating cell nuclear antigen. Am J Gastroenterol. 1993 Nov;88(11):1870–1875. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gavrieli Y., Sherman Y., Ben-Sasson S. A. Identification of programmed cell death in situ via specific labeling of nuclear DNA fragmentation. J Cell Biol. 1992 Nov;119(3):493–501. doi: 10.1083/jcb.119.3.493. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall P. A., Coates P. J., Ansari B., Hopwood D. Regulation of cell number in the mammalian gastrointestinal tract: the importance of apoptosis. J Cell Sci. 1994 Dec;107(Pt 12):3569–3577. doi: 10.1242/jcs.107.12.3569. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lauwers G. Y., Scott G. V., Hendricks J. Immunohistochemical evidence of aberrant bcl-2 protein expression in gastric epithelial dysplasia. Cancer. 1994 Jun 15;73(12):2900–2904. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19940615)73:12<2900::aid-cncr2820731205>3.0.co;2-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lynch D. A., Mapstone N. P., Clarke A. M., Sobala G. M., Jackson P., Morrison L., Dixon M. F., Quirke P., Axon A. T. Cell proliferation in Helicobacter pylori associated gastritis and the effect of eradication therapy. Gut. 1995 Mar;36(3):346–350. doi: 10.1136/gut.36.3.346. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moss S. F., Legon S., Davies J., Calam J. Cytokine gene expression in Helicobacter pylori associated antral gastritis. Gut. 1994 Nov;35(11):1567–1570. doi: 10.1136/gut.35.11.1567. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rauws E. A., Langenberg W., Houthoff H. J., Zanen H. C., Tytgat G. N. Campylobacter pyloridis-associated chronic active antral gastritis. A prospective study of its prevalence and the effects of antibacterial and antiulcer treatment. Gastroenterology. 1988 Jan;94(1):33–40. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robert M. E., Weinstein W. M. Helicobacter pylori-associated gastric pathology. Gastroenterol Clin North Am. 1993 Mar;22(1):59–72. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shu S. Y., Ju G., Fan L. Z. The glucose oxidase-DAB-nickel method in peroxidase histochemistry of the nervous system. Neurosci Lett. 1988 Feb 29;85(2):169–171. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(88)90346-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sobala G. M., Schorah C. J., Shires S., Lynch D. A., Gallacher B., Dixon M. F., Axon A. T. Effect of eradication of Helicobacter pylori on gastric juice ascorbic acid concentrations. Gut. 1993 Aug;34(8):1038–1041. doi: 10.1136/gut.34.8.1038. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson C. B. Apoptosis in the pathogenesis and treatment of disease. Science. 1995 Mar 10;267(5203):1456–1462. doi: 10.1126/science.7878464. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]





