Abstract
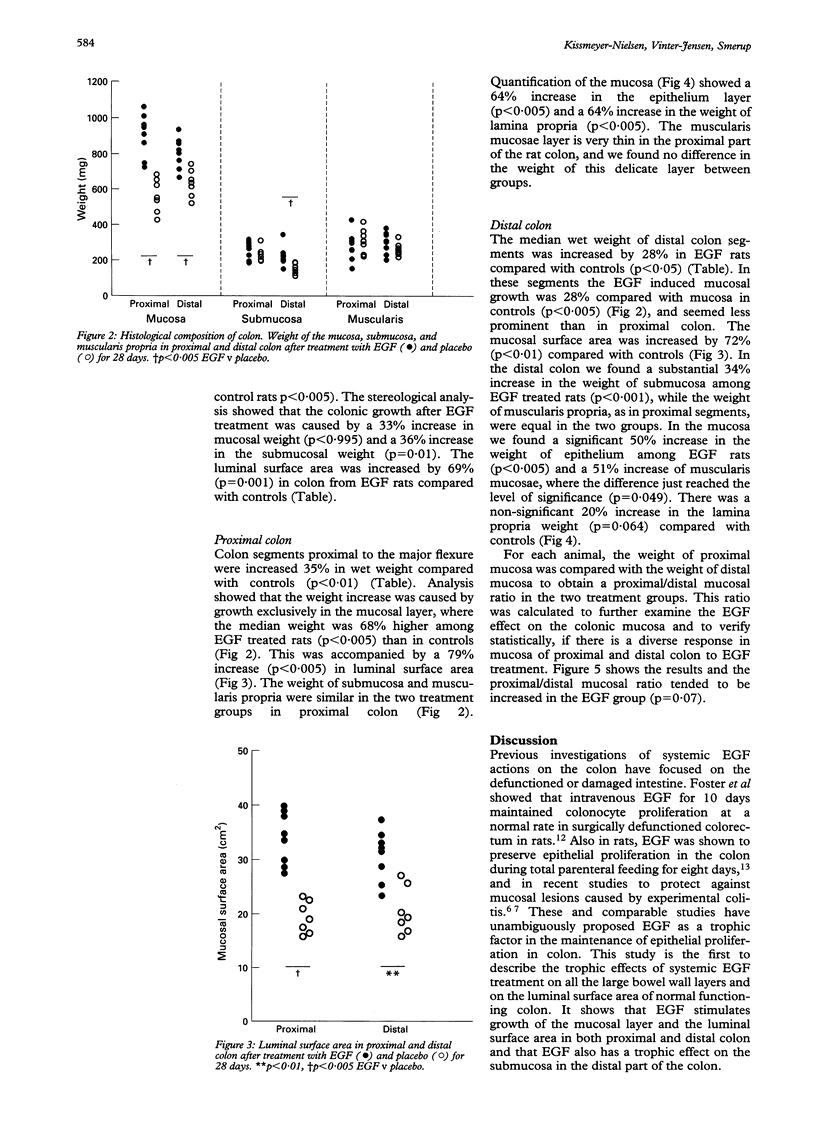
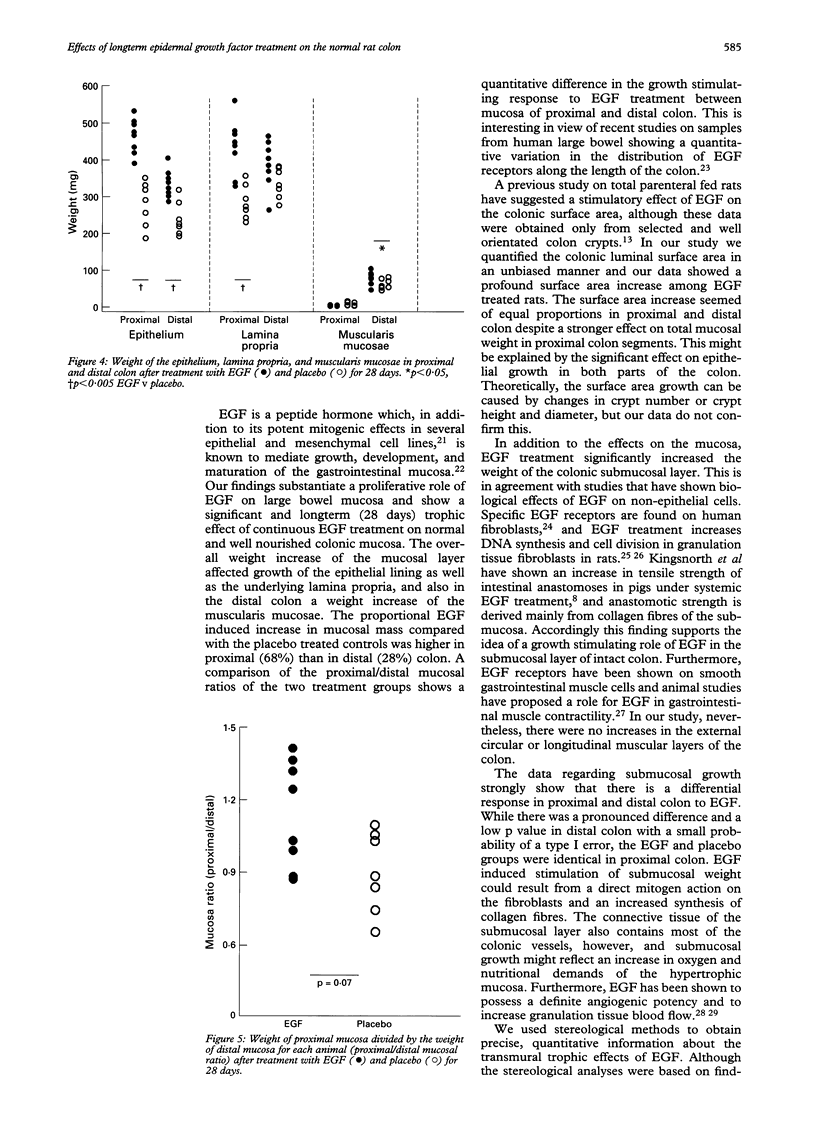
BACKGROUND--Epidermal growth factor (EGF) exerts trophic effects on the mucosa of damaged and defunctioned colon, but the effects on the normal large bowel wall are not known. AIMS--To investigate the effect of systemic EGF treatment on growth and morphology of normal rat colon. METHODS--Rats were treated with subcutaneous biosynthetic EGF injections of 150 micrograms/kg/day for 28 days. The weight of the histological colonic wall layers and the luminal surface area were measured using quantitative morphometric analysis (stereology). The colon was subdivided into proximal and distal parts. RESULTS--EGF treatment increased the total colon wet weight by 23% compared with controls (p < 0.005). The weight increase occurred in the mucosal (33%) and the submucosal layers of the bowel wall (36%) and there was a 69% increase of the total luminal surface area (p = 0.001). In the proximal part of colon of EGF rats there was a 68% increase in mucosal weight (p < 0.005) accompanied by a 79% increase in the mucosal surface area compared with controls (p < 0.005), whereas submucosal and muscularis propria weights were identical. In distal colon, the mucosal weight increased 28% in the EGF group (p < 0.005), the mucosal surface area increased by 72% after treatment (p < 0.01). Furthermore there was a 34% increase in the weight of submucosa (p < 0.001) in the distal colon among EGF rats. CONCLUSIONS--Treatment of rats with EGF has a stimulating role on the mucosa and luminal surface area of the entire functioning colon and a trophic effect on the submucosa of the distal colon.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baddeley A. J., Gundersen H. J., Cruz-Orive L. M. Estimation of surface area from vertical sections. J Microsc. 1986 Jun;142(Pt 3):259–276. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2818.1986.tb04282.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgess A. W. Epidermal growth factor and transforming growth factor alpha. Br Med Bull. 1989 Apr;45(2):401–424. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.bmb.a072331. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carpenter G., Cohen S. Human epidermal growth factor and the proliferation of human fibroblasts. J Cell Physiol. 1976 Jun;88(2):227–237. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1040880212. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drumm B., Cutz E., Tomkins K. B., Cook D., Hamilton J. R., Sherman P. Urogastrone/epidermal growth factor in treatment of congenital microvillous atrophy. Lancet. 1988 Jan 16;1(8577):111–112. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(88)90303-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foster H. M., Whitehead R. H. Intravenous but not intracolonic epidermal growth factor maintains colonocyte proliferation in defunctioned rat colorectum. Gastroenterology. 1990 Dec;99(6):1710–1714. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(90)90477-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodlad R. A., Lee C. Y., Wright N. A. Cell proliferation in the small intestine and colon of intravenously fed rats: effects of urogastrone-epidermal growth factor. Cell Prolif. 1992 Sep;25(5):393–404. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2184.1992.tb01449.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodlad R. A., Wilson T. J., Lenton W., Gregory H., McCullagh K. G., Wright N. A. Intravenous but not intragastric urogastrone-EGF is trophic to the intestine of parenterally fed rats. Gut. 1987 May;28(5):573–582. doi: 10.1136/gut.28.5.573. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gundersen H. J., Bendtsen T. F., Korbo L., Marcussen N., Møller A., Nielsen K., Nyengaard J. R., Pakkenberg B., Sørensen F. B., Vesterby A. Some new, simple and efficient stereological methods and their use in pathological research and diagnosis. APMIS. 1988 May;96(5):379–394. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1988.tb05320.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hollenberg M. D., Cuatrecasas P. Insulin and epidermal growth factor. Human fibroblast receptors related to deoxyribonucleic acid synthesis and amino acid uptake. J Biol Chem. 1975 May 25;250(10):3845–3853. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Juhl C. O., Jensen L. S., Steiniche T., Moussa E. Recombinant human epidermal growth factor prevents sclerotherapy-induced esophageal ulcer and stricture formations in pigs. Dig Dis Sci. 1994 Feb;39(2):393–401. doi: 10.1007/BF02090214. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kingsnorth A. N., Vowles R., Nash J. R. Epidermal growth factor increases tensile strength in intestinal wounds in pigs. Br J Surg. 1990 Apr;77(4):409–412. doi: 10.1002/bjs.1800770417. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kissmeyer-Nielsen P., Christensen H., Laurberg S. Diverting colostomy induces mucosal and muscular atrophy in rat distal colon. Gut. 1994 Sep;35(9):1275–1281. doi: 10.1136/gut.35.9.1275. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koenders P. G., Peters W. H., Wobbes T., Beex L. V., Nagengast F. M., Benraad T. J. Epidermal growth factor receptor levels are lower in carcinomatous than in normal colorectal tissue. Br J Cancer. 1992 Feb;65(2):189–192. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1992.39. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konturek S. J., Dembinski A., Warzecha Z., Brzozowski T., Gregory H. Role of epidermal growth factor in healing of chronic gastroduodenal ulcers in rats. Gastroenterology. 1988 Jun;94(6):1300–1307. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(88)90667-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laato M. Effect of epidermal growth factor (EGF) on blood flow and albumin extravasation in experimental granulation tissue. Acta Chir Scand. 1986 Jun-Jul;152:401–405. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laato M., Niinikoski J., Lebel L., Gerdin B. Stimulation of wound healing by epidermal growth factor. A dose-dependent effect. Ann Surg. 1986 Apr;203(4):379–381. doi: 10.1097/00000658-198604000-00007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laato M., Niinikoski J., Lundberg C., Arfors K. E. Effect of epidermal growth factor (EGF) on experimental granulation tissue. J Surg Res. 1986 Sep;41(3):252–255. doi: 10.1016/0022-4804(86)90032-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ladekarl M. The influence of tissue processing on quantitative histopathology in breast cancer. J Microsc. 1994 May;174(Pt 2):93–100. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2818.1994.tb03453.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindström C. G., Rosengren J. E., Fork F. T. Colon of the rat. An anatomic, histologic and radiographic investigation. Acta Radiol Diagn (Stockh) 1979;20(3):523–536. doi: 10.1177/028418517902000314. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luck M. S., Bass P. Effect of epidermal growth factor on experimental colitis in the rat. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1993 Feb;264(2):984–990. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marti U., Burwen S. J., Jones A. L. Biological effects of epidermal growth factor, with emphasis on the gastrointestinal tract and liver: an update. Hepatology. 1989 Jan;9(1):126–138. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840090122. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prigent S. A., Lemoine N. R. The type 1 (EGFR-related) family of growth factor receptors and their ligands. Prog Growth Factor Res. 1992;4(1):1–24. doi: 10.1016/0955-2235(92)90002-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Procaccino F., Reinshagen M., Hoffmann P., Zeeh J. M., Lakshmanan J., McRoberts J. A., Patel A., French S., Eysselein V. E. Protective effect of epidermal growth factor in an experimental model of colitis in rats. Gastroenterology. 1994 Jul;107(1):12–17. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(94)90055-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Savage C. R., Jr, Cohen S. Proliferation of corneal epithelium induced by epidermal growth factor. Exp Eye Res. 1973 Mar;15(3):361–366. doi: 10.1016/0014-4835(73)90151-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sullivan P. B., Brueton M. J., Tabara Z. B., Goodlad R. A., Lee C. Y., Wright N. A. Epidermal growth factor in necrotising enteritis. Lancet. 1991 Jul 6;338(8758):53–54. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(91)90042-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson J. S., Saxena S. K., Greaton C., Schultz G., Sharp J. G. The effect of the route of delivery of urogastrone on intestinal regeneration. Surgery. 1989 Jul;106(1):45–51. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker-Smith J. A., Phillips A. D., Walford N., Gregory H., Fitzgerald J. D., MacCullagh K., Wright N. A. Intravenous epidermal growth factor/urogastrone increases small-intestinal cell proliferation in congenital microvillous atrophy. Lancet. 1985 Nov 30;2(8466):1239–1240. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(85)90762-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



