Abstract
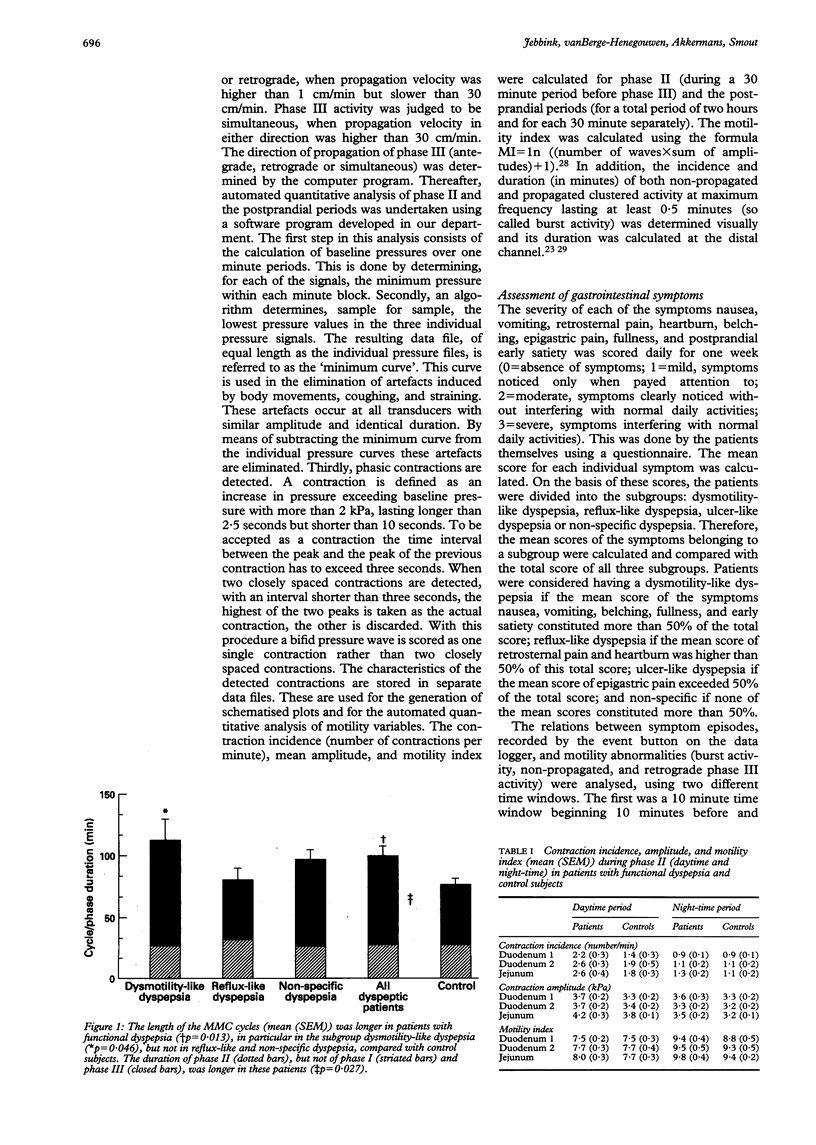
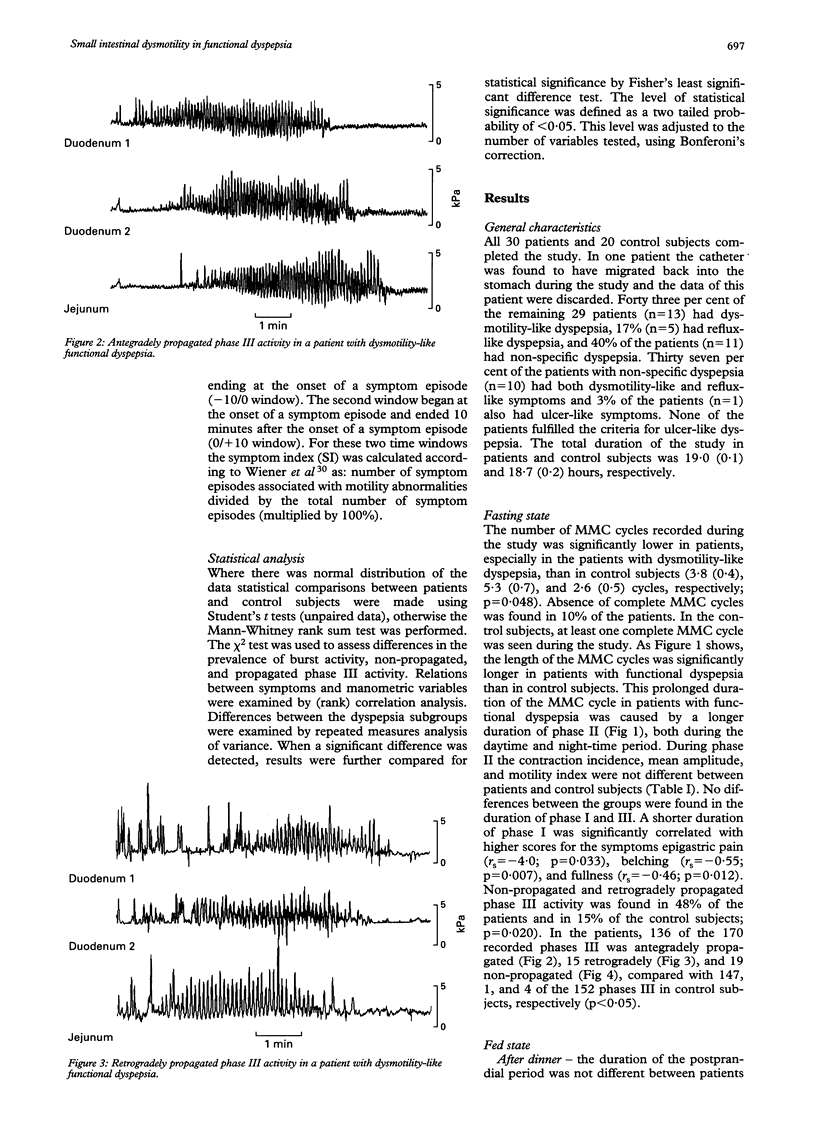
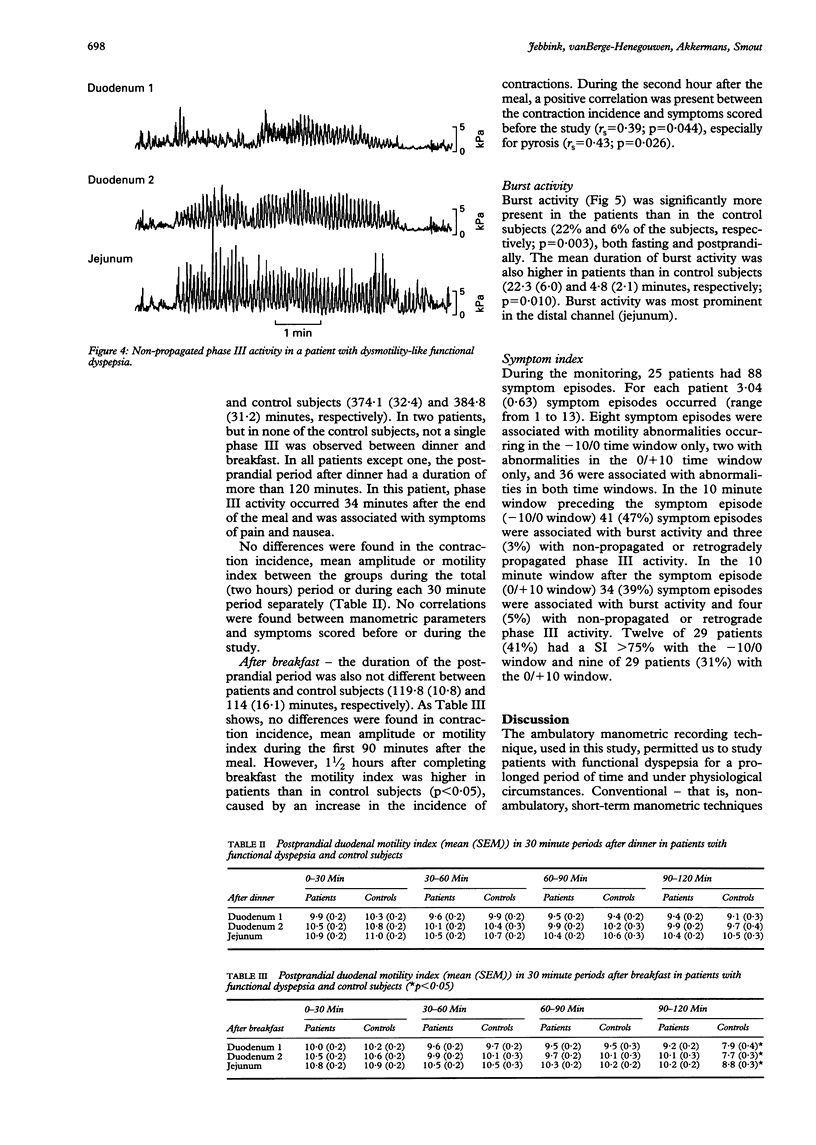
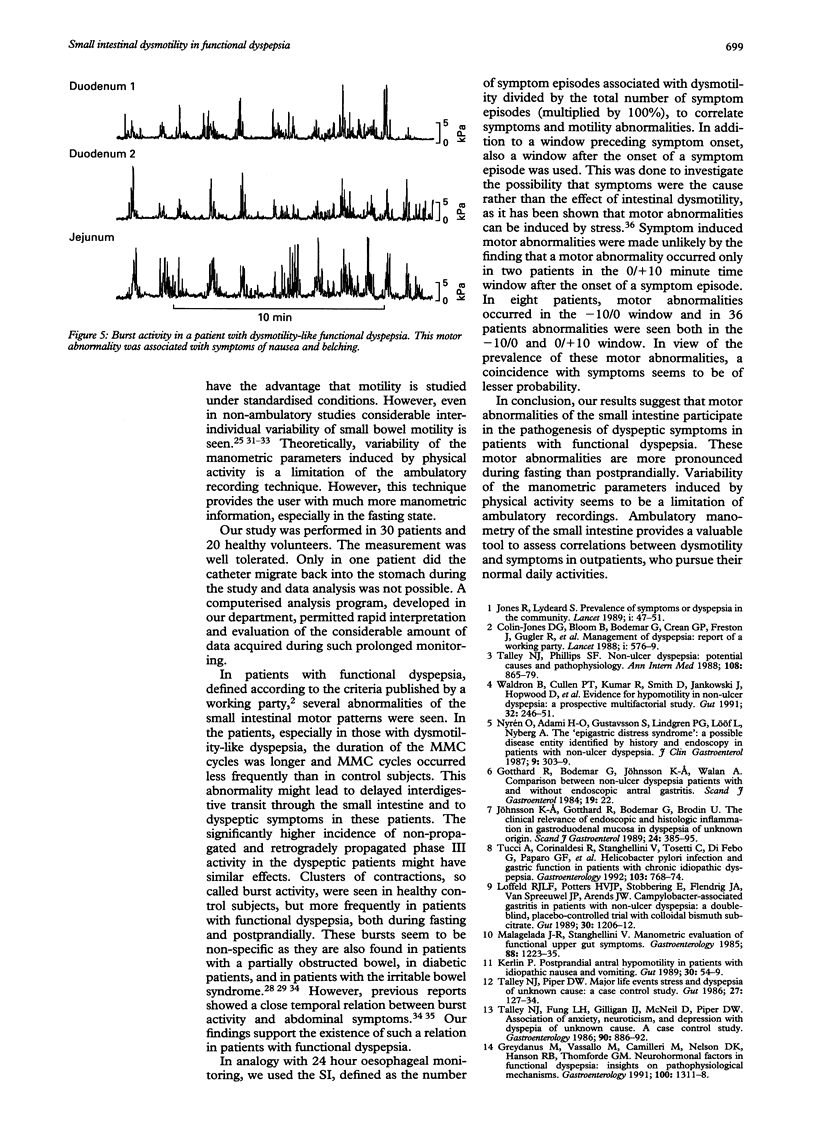
AIMS/METHODS--In 30 patients with functional dyspepsia and in 20 healthy volunteers, ambulatory duodenojejunal manometry was performed to examine the interdigestive and postprandial small intestinal motility patterns in relation to symptoms. RESULTS--In the fasting state, the number of migrating motor complex cycles mean (SEM) was significantly lower in patients, especially in patients with dysmotility-like dyspepsia, than in control subjects (3.8 (0.4), 2.6 (0.5), and 5.3 (0.7) cycles, respectively; p < 0.05), due to a longer duration of phase II. Non-propagated and retrogradely propagated phase III activity was more prevalent in patients than in control subjects (48% v 15%; p = 0.020). During phase II and after dinner no differences were found in contraction incidence, mean amplitude or motility index. However, 1 1/2 hours after completing breakfast the motility index was higher in patients at all three recording levels (p < 0.05). Burst activity was more prevalent in patients than in control subjects (22% v 6% of the subjects; p = 0.003). In 41% of the patients the symptom index was > 75%. CONCLUSIONS--These results suggest that small intestinal motor abnormalities, especially during fasting, participate in the pathogenesis of symptoms in patients with functional dyspepsia. Ambulatory manometry of the small intestine is a valuable tool to demonstrate these abnormalities in outpatients pursuing their daily activities.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bassotti G., Pelli M. A., Morelli A. Duodenojejunal motor activity in patients with chronic dyspeptic symptoms. J Clin Gastroenterol. 1990 Feb;12(1):17–21. doi: 10.1097/00004836-199002000-00006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benson M. J., Castillo F. D., Deeks J. J., Wingate D. L. Assessment by prolonged ambulatory manometry of the effect of oral cisapride on proximal small bowel inter-digestive motility. Dig Dis Sci. 1992 Oct;37(10):1569–1575. doi: 10.1007/BF01296504. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dooley C. P., Di Lorenzo C., Valenzuela J. E. Variability of migrating motor complex in humans. Dig Dis Sci. 1992 May;37(5):723–728. doi: 10.1007/BF01296429. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Husebye E., Skar V., Aalen O. O., Osnes M. Digital ambulatory manometry of the small intestine in healthy adults. Estimates of variation within and between individuals and statistical management of incomplete MMC periods. Dig Dis Sci. 1990 Sep;35(9):1057–1065. doi: 10.1007/BF01537575. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jian R., Ducrot F., Ruskone A., Chaussade S., Rambaud J. C., Modigliani R., Rain J. D., Bernier J. J. Symptomatic, radionuclide and therapeutic assessment of chronic idiopathic dyspepsia. A double-blind placebo-controlled evaluation of cisapride. Dig Dis Sci. 1989 May;34(5):657–664. doi: 10.1007/BF01540334. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jönsson K. A., Gotthard R., Bodemar G., Brodin U. The clinical relevance of endoscopic and histologic inflammation of gastroduodenal mucosa in dyspepsia of unknown origin. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1989 May;24(4):385–395. doi: 10.3109/00365528909093064. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kellow J. E., Borody T. J., Phillips S. F., Tucker R. L., Haddad A. C. Human interdigestive motility: variations in patterns from esophagus to colon. Gastroenterology. 1986 Aug;91(2):386–395. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(86)90573-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kellow J. E., Phillips S. F. Altered small bowel motility in irritable bowel syndrome is correlated with symptoms. Gastroenterology. 1987 Jun;92(6):1885–1893. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(87)90620-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerlin P., Phillips S. Variability of motility of the ileum and jejunum in healthy humans. Gastroenterology. 1982 Apr;82(4):694–700. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerlin P. Postprandial antral hypomotility in patients with idiopathic nausea and vomiting. Gut. 1989 Jan;30(1):54–59. doi: 10.1136/gut.30.1.54. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumar D., Wingate D. L. The irritable bowel syndrome: a paroxysmal motor disorder. Lancet. 1985 Nov 2;2(8462):973–977. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(85)90525-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumar D., Wingate D., Ruckebusch Y. Circadian variation in the propagation velocity of the migrating motor complex. Gastroenterology. 1986 Oct;91(4):926–930. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(86)90696-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loffeld R. J., Potters H. V., Stobberingh E., Flendrig J. A., van Spreeuwel J. P., Arends J. W. Campylobacter associated gastritis in patients with non-ulcer dyspepsia: a double blind placebo controlled trial with colloidal bismuth subcitrate. Gut. 1989 Sep;30(9):1206–1212. doi: 10.1136/gut.30.9.1206. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malagelada J. R., Stanghellini V. Manometric evaluation of functional upper gut symptoms. Gastroenterology. 1985 May;88(5 Pt 1):1223–1231. doi: 10.1016/s0016-5085(85)80083-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Management of dyspepsia: report of a working party. Lancet. 1988 Mar 12;1(8585):576–579. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nyrén O., Adami H. O., Gustavsson S., Lindgren P. G., Löf L., Nyberg A. The "epigastric distress syndrome". A possible disease entity identified by history and endoscopy in patients with nonulcer dyspepsia. J Clin Gastroenterol. 1987 Jun;9(3):303–309. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patel K., Leevers S., Abbs S., Hart K. A., Heckmatt J. Z., Bobrow M., Dubowitz V. Absence of dystrophin in Becker muscular dystrophy. Lancet. 1989 Jan 7;1(8628):47–47. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(89)91705-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quigley E. M. Intestinal manometry--technical advances, clinical limitations. Dig Dis Sci. 1992 Jan;37(1):10–13. doi: 10.1007/BF01308335. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Remington M., Malagelada J. R., Zinsmeister A., Fleming C. R. Abnormalities in gastrointestinal motor activity in patients with short bowels: effect of a synthetic opiate. Gastroenterology. 1983 Sep;85(3):629–636. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanghellini V., Camilleri M., Malagelada J. R. Chronic idiopathic intestinal pseudo-obstruction: clinical and intestinal manometric findings. Gut. 1987 Jan;28(1):5–12. doi: 10.1136/gut.28.1.5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanghellini V., Ghidini C., Maccarini M. R., Paparo G. F., Corinaldesi R., Barbara L. Fasting and postprandial gastrointestinal motility in ulcer and non-ulcer dyspepsia. Gut. 1992 Feb;33(2):184–190. doi: 10.1136/gut.33.2.184. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Summers R. W., Anuras S., Green J. Jejunal manometry patterns in health, partial intestinal obstruction, and pseudoobstruction. Gastroenterology. 1983 Dec;85(6):1290–1300. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Talley N. J., Fung L. H., Gilligan I. J., McNeil D., Piper D. W. Association of anxiety, neuroticism, and depression with dyspepsia of unknown cause. A case-control study. Gastroenterology. 1986 Apr;90(4):886–892. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(86)90864-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Talley N. J., Phillips S. F. Non-ulcer dyspepsia: potential causes and pathophysiology. Ann Intern Med. 1988 Jun;108(6):865–879. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-108-6-865. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Talley N. J., Piper D. W. Major life event stress and dyspepsia of unknown cause: a case control study. Gut. 1986 Feb;27(2):127–134. doi: 10.1136/gut.27.2.127. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tucci A., Corinaldesi R., Stanghellini V., Tosetti C., Di Febo G., Paparo G. F., Varoli O., Paganelli G. M., Labate A. M., Masci C. Helicobacter pylori infection and gastric function in patients with chronic idiopathic dyspepsia. Gastroenterology. 1992 Sep;103(3):768–774. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(92)90004-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valori R. M., Kumar D., Wingate D. L. Effects of different types of stress and of "prokinetic" drugs on the control of the fasting motor complex in humans. Gastroenterology. 1986 Jun;90(6):1890–1900. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(86)90258-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waldron B., Cullen P. T., Kumar R., Smith D., Jankowski J., Hopwood D., Sutton D., Kennedy N., Campbell F. C. Evidence for hypomotility in non-ulcer dyspepsia: a prospective multifactorial study. Gut. 1991 Mar;32(3):246–251. doi: 10.1136/gut.32.3.246. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wegener M., Börsch G., Schaffstein J., Schulz-Flake C., Mai U., Leverkus F. Are dyspeptic symptoms in patients with Campylobacter pylori-associated type B gastritis linked to delayed gastric emptying? Am J Gastroenterol. 1988 Jul;83(7):737–740. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wengrower D., Zaltzman S., Karmeli F., Goldin E. Idiopathic gastroparesis in patients with unexplained nausea and vomiting. Dig Dis Sci. 1991 Sep;36(9):1255–1258. doi: 10.1007/BF01307518. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiener G. J., Richter J. E., Copper J. B., Wu W. C., Castell D. O. The symptom index: a clinically important parameter of ambulatory 24-hour esophageal pH monitoring. Am J Gastroenterol. 1988 Apr;83(4):358–361. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


