Abstract
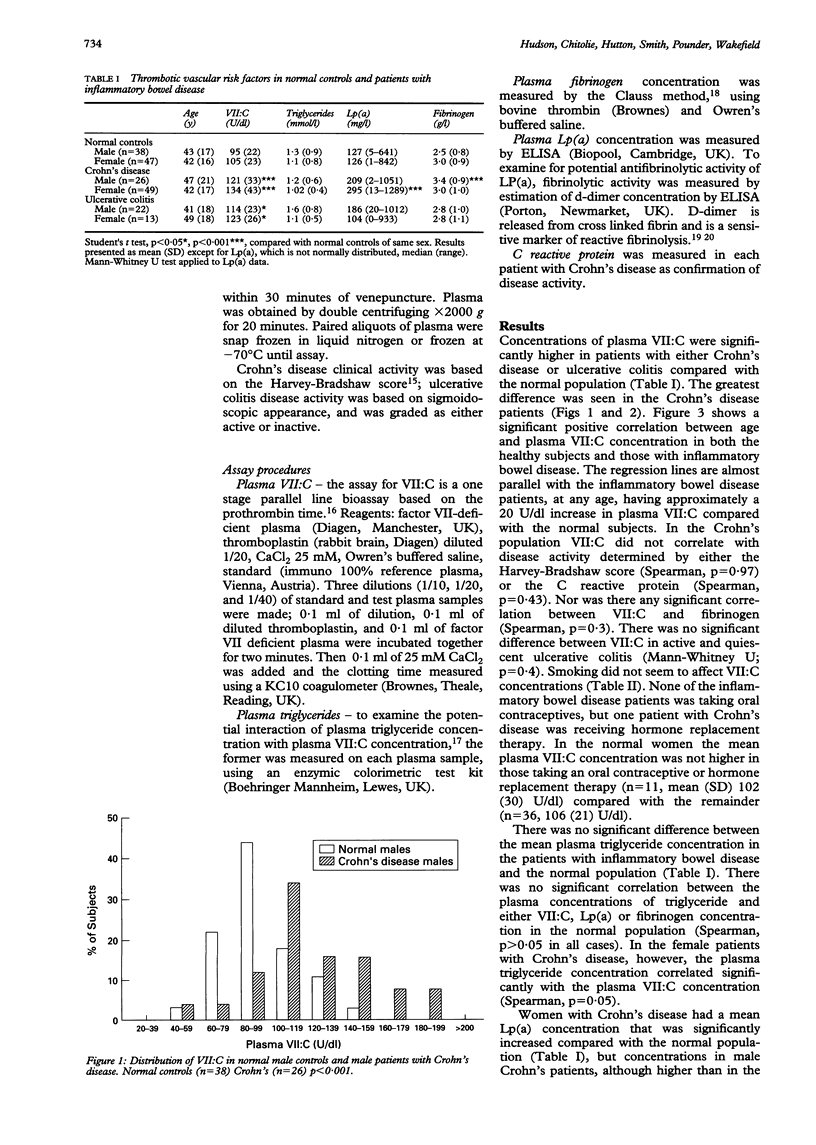
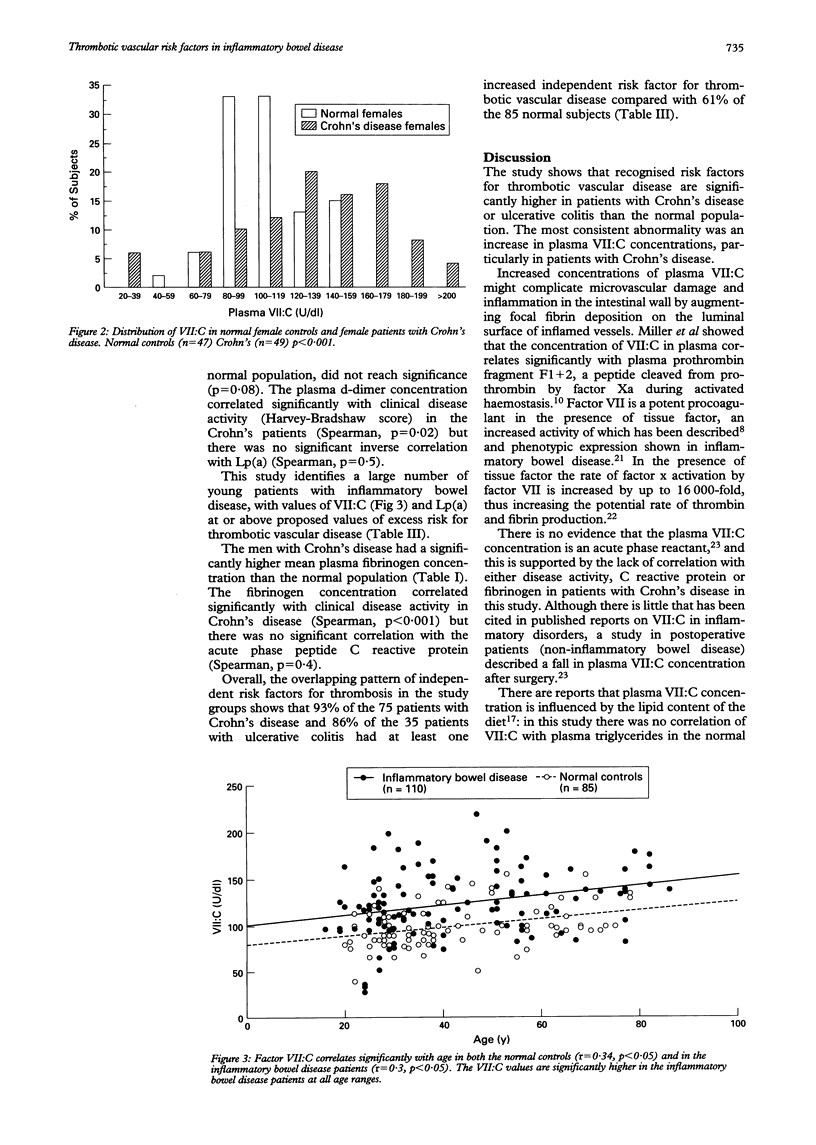
BACKGROUND--Thrombosis may be an important effector mechanism in the pathogenesis of Crohn's disease. METHODS--This study therefore investigated the prevalence of independent thrombotic risk factors (factor VII coagulant activity, lipoprotein (a), fibrinogen, plasma triglycerides, and smoking) in patients with Crohn's disease, ulcerative colitis, and normal controls. RESULTS--In Crohn's disease (n = 75), the mean plasma VII:C, lipoprotein (a) and fibrinogen concentrations were significantly greater than in the normal population (n = 85). In ulcerative colitis (n = 35), only the mean factor VII:C concentration was significantly higher than normal. Ninety three per cent of patients with Crohn's disease and 86% of those with ulcerative colitis had at least one risk factor for thrombotic vascular disease, compared with 61% of the normal population (p < 0.001). CONCLUSIONS--In many young patients with inflammatory bowel disease, plasma concentrations of these prothrombotic factors were in excess of the limits that are regarded as posing an increased risk for the development of occlusive vascular disease.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Armstrong V. W., Cremer P., Eberle E., Manke A., Schulze F., Wieland H., Kreuzer H., Seidel D. The association between serum Lp(a) concentrations and angiographically assessed coronary atherosclerosis. Dependence on serum LDL levels. Atherosclerosis. 1986 Dec;62(3):249–257. doi: 10.1016/0021-9150(86)90099-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bull H. A., Pittilo R. M., Woolf N., Machin S. J. The effect of nicotine on human endothelial cell release of prostaglandins and ultrastructure. Br J Exp Pathol. 1988 Jun;69(3):413–421. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CLAUSS A. Gerinnungsphysiologische Schnellmethode zur Bestimmung des Fibrinogens. Acta Haematol. 1957 Apr;17(4):237–246. doi: 10.1159/000205234. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conlan M. G., Haire W. D., Burnett D. A. Prothrombotic abnormalities in inflammatory bowel disease. Dig Dis Sci. 1989 Jul;34(7):1089–1093. doi: 10.1007/BF01536380. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dhillon A. P., Anthony A., Sim R., Wakefield A. J., Sankey E. A., Hudson M., Allison M. C., Pounder R. E. Mucosal capillary thrombi in rectal biopsies. Histopathology. 1992 Aug;21(2):127–133. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2559.1992.tb00360.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards R. L., Levine J. B., Green R., Duffy M., Mathews E., Brande W., Rickles F. R. Activation of blood coagulation in Crohn's disease. Increased plasma fibrinopeptide A levels and enhanced generation of monocyte tissue factor activity. Gastroenterology. 1987 Feb;92(2):329–337. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gris J. C., Schved J. F., Raffanel C., Dubois A., Aguilar-Martinez P., Arnaud A., Sanchez N., Sarlat C., Balmès J. L. Impaired fibrinolytic capacity in patients with inflammatory bowel disease. Thromb Haemost. 1990 Jun 28;63(3):472–475. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hajjar K. A., Gavish D., Breslow J. L., Nachman R. L. Lipoprotein(a) modulation of endothelial cell surface fibrinolysis and its potential role in atherosclerosis. Nature. 1989 May 25;339(6222):303–305. doi: 10.1038/339303a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harvey R. F., Bradshaw J. M. A simple index of Crohn's-disease activity. Lancet. 1980 Mar 8;1(8167):514–514. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(80)92767-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawkey C. J., Stirling Y., Chakrabarti R., Brozovic M., Cox A. G., Meade T. W. Haemostatic changes following surgery. Thromb Res. 1983 Oct 15;32(2):223–227. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(83)90033-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holdstock G., Savage D., Harman M., Wright R. Should patients with inflammatory bowel disease smoke? Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1984 Feb 4;288(6414):362–362. doi: 10.1136/bmj.288.6414.362. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hudson M., Hutton R. A., Wakefield A. J., Sawyerr A. M., Pounder R. E. Evidence for activation of coagulation in Crohn's disease. Blood Coagul Fibrinolysis. 1992 Dec;3(6):773–778. doi: 10.1097/00001721-199212000-00011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lane A., Cruickshank J. K., Mitchell J., Henderson A., Humphries S., Green F. Genetic and environmental determinants of factor VII coagulant activity in ethnic groups at differing risk of coronary heart disease. Atherosclerosis. 1992 May;94(1):43–50. doi: 10.1016/0021-9150(92)90186-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowe G. D., Drummond M. M., Lorimer A. R., Hutton I., Forbes C. D., Prentice C. R., Barbenel J. C. Relation between extent of coronary artery disease and blood viscosity. Br Med J. 1980 Mar 8;280(6215):673–674. doi: 10.1136/bmj.280.6215.673. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meade T. W., Mellows S., Brozovic M., Miller G. J., Chakrabarti R. R., North W. R., Haines A. P., Stirling Y., Imeson J. D., Thompson S. G. Haemostatic function and ischaemic heart disease: principal results of the Northwick Park Heart Study. Lancet. 1986 Sep 6;2(8506):533–537. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(86)90111-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meade T. W., Vickers M. V., Thompson S. G., Seghatchian M. J. The effect of physiological levels of fibrinogen on platelet aggregation. Thromb Res. 1985 Jun 1;38(5):527–534. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(85)90185-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miles L. A., Plow E. F. Lp(a): an interloper into the fibrinolytic system? Thromb Haemost. 1990 Jun 28;63(3):331–335. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller G. J., Martin J. C., Webster J., Wilkes H., Miller N. E., Wilkinson W. H., Meade T. W. Association between dietary fat intake and plasma factor VII coagulant activity--a predictor of cardiovascular mortality. Atherosclerosis. 1986 Jun;60(3):269–277. doi: 10.1016/0021-9150(86)90174-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- More L., Sim R., Hudson M., Dhillon A. P., Pounder R., Wakefield A. J. Immunohistochemical study of tissue factor expression in normal intestine and idiopathic inflammatory bowel disease. J Clin Pathol. 1993 Aug;46(8):703–708. doi: 10.1136/jcp.46.8.703. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orholm M., Iselius L., Sørensen T. I., Munkholm P., Langholz E., Binder V. Investigation of inheritance of chronic inflammatory bowel diseases by complex segregation analysis. BMJ. 1993 Jan 2;306(6869):20–24. doi: 10.1136/bmj.306.6869.20. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osborne M. J., Stansby G. P. Cigarette smoking and its relationship to inflammatory bowel disease: a review. J R Soc Med. 1992 Apr;85(4):214–216. doi: 10.1177/014107689208500412. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pittilo R. M., Mackie I. J., Rowles P. M., Machin S. J., Woolf N. Effects of cigarette smoking on the ultrastructure of rat thoracic aorta and its ability to produce prostacyclin. Thromb Haemost. 1982 Oct 29;48(2):173–176. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhoads G. G., Dahlen G., Berg K., Morton N. E., Dannenberg A. L. Lp(a) lipoprotein as a risk factor for myocardial infarction. JAMA. 1986 Nov 14;256(18):2540–2544. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowbotham B. J., Carroll P., Whitaker A. N., Bunce I. H., Cobcroft R. G., Elms M. J., Masci P. P., Bundesen P. G., Rylatt D. B., Webber A. J. Measurement of crosslinked fibrin derivatives--use in the diagnosis of venous thrombosis. Thromb Haemost. 1987 Feb 3;57(1):59–61. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rylatt D. B., Blake A. S., Cottis L. E., Massingham D. A., Fletcher W. A., Masci P. P., Whitaker A. N., Elms M., Bunce I., Webber A. J. An immunoassay for human D dimer using monoclonal antibodies. Thromb Res. 1983 Sep 15;31(6):767–778. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(83)90108-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scanu A. M., Fless G. M. Lipoprotein (a). Heterogeneity and biological relevance. J Clin Invest. 1990 Jun;85(6):1709–1715. doi: 10.1172/JCI114625. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stone M. C., Thorp J. M. Plasma fibrinogen--a major coronary risk factor. J R Coll Gen Pract. 1985 Dec;35(281):565–569. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Talbot R. W., Heppell J., Dozois R. R., Beart R. W., Jr Vascular complications of inflammatory bowel disease. Mayo Clin Proc. 1986 Feb;61(2):140–145. doi: 10.1016/s0025-6196(12)65200-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson N. P., Wakefield A. J., Pounder R. E. Inherited disorders of coagulation appear to protect against inflammatory bowel disease. Gastroenterology. 1995 Apr;108(4):1011–1015. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(95)90197-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Utermann G., Menzel H. J., Kraft H. G., Duba H. C., Kemmler H. G., Seitz C. Lp(a) glycoprotein phenotypes. Inheritance and relation to Lp(a)-lipoprotein concentrations in plasma. J Clin Invest. 1987 Aug;80(2):458–465. doi: 10.1172/JCI113093. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wakefield A. J., Sankey E. A., Dhillon A. P., Sawyerr A. M., More L., Sim R., Pittilo R. M., Rowles P. M., Hudson M., Lewis A. A. Granulomatous vasculitis in Crohn's disease. Gastroenterology. 1991 May;100(5 Pt 1):1279–1287. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wakefield A. J., Sawyerr A. M., Dhillon A. P., Pittilo R. M., Rowles P. M., Lewis A. A., Pounder R. E. Pathogenesis of Crohn's disease: multifocal gastrointestinal infarction. Lancet. 1989 Nov 4;2(8671):1057–1062. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(89)91078-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Bono D. P. Very early thrombolysis: the challenge and the reality. Q J Med. 1991 Jul;80(291):561–562. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


