Abstract
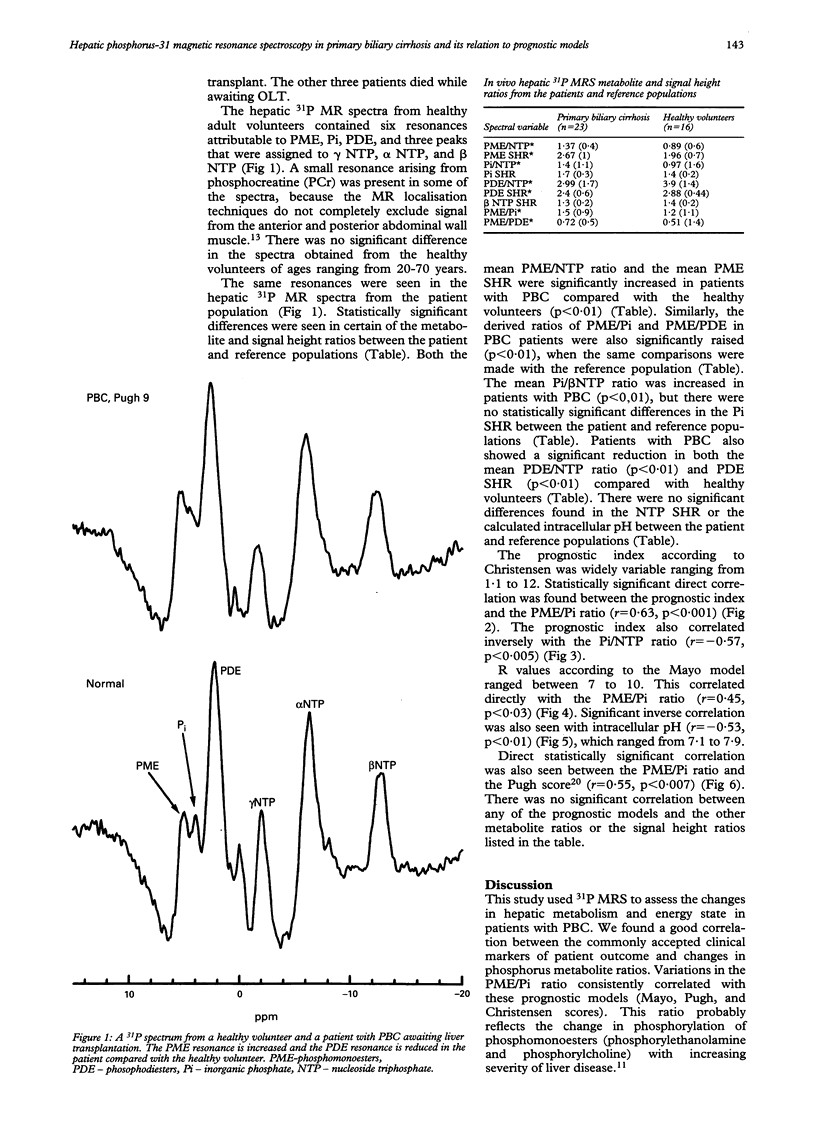
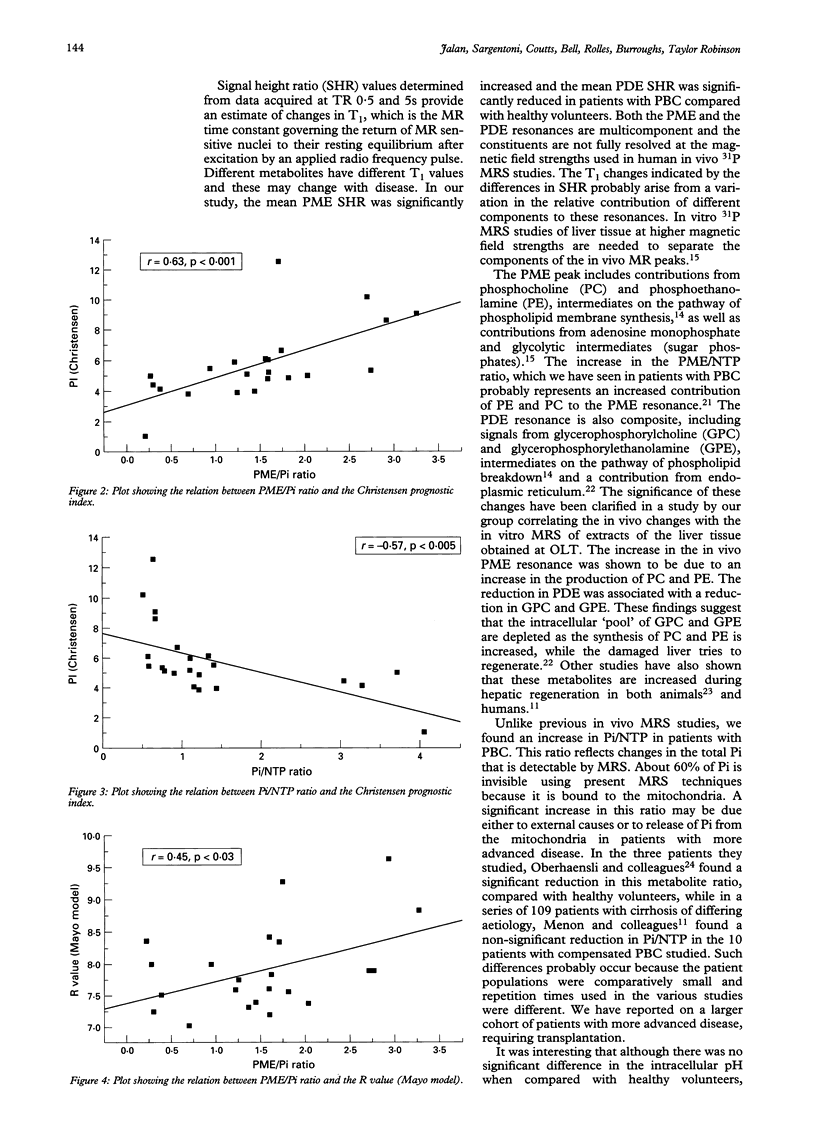
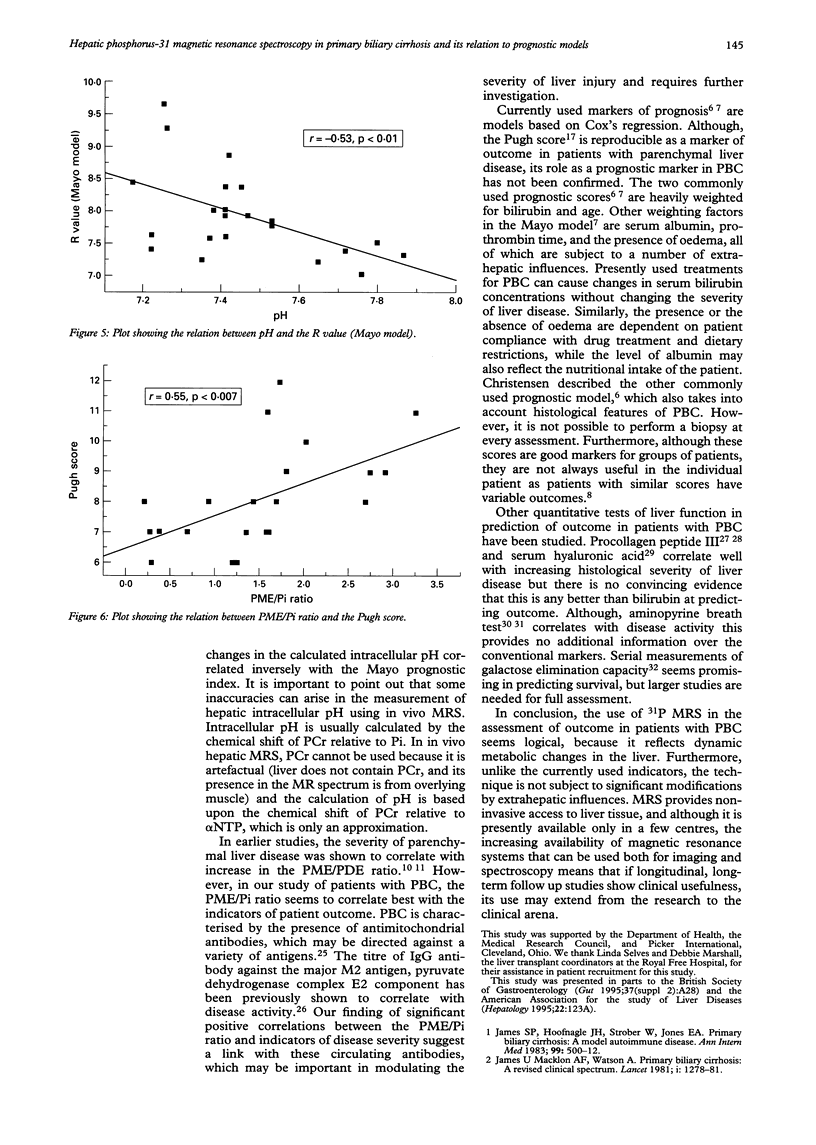
BACKGROUND: In vivo hepatic phosphorus-31 magnetic resonance spectroscopy (31P MRS) provides biochemical information about phosphorus metabolism. AIM: To assess 31P MRS as a prognostic marker in patients with primary biliary cirrhosis (PBC) in relation to the current clinical prognostic models. PATIENTS AND METHODS: Twenty three patients with PBC of varying functional severity and 16 matched healthy volunteers were studied using in vivo 31P MRS. Spectra were acquired using a 1.5 T spectroscopy system. Peak area ratios of phosphomonoesters (PME), inorganic phosphate (Pi), and phosphodiesters (PDE) and nucleotide triphosphate (NTP) were calculated. Pugh score, Christensen prognostic index, and R value according to the Mayo model were calculated from the clinical data. RESULTS: The PME/NTP, Pi/NTP, PME/PDE, and PME/Pi ratios and the PME signal height ratio (SHR) were significantly higher, while the PDE/NTP and PDE/SHR were significantly lower in PBC patients compared with healthy volunteers (p < 0.01). Significant correlations were seen between PME/Pi ratio and the prognostic index according to Christensen (r = 0.63, p < 0.001), R value according to the Mayo model (r = 0.45, p < 0.03), and with the Pugh score (r = 0.55, p < 0.007). CONCLUSIONS: This study shows that PME/Pi ratio obtained from 31P MRS correlates well with all three of the commonly used models of prognosis in patients with PBC. A longitudinal study with larger number of patients is required to confirm these findings and elucidate the biochemical changes underlying this phenomenon.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baker A. L., Krager P. S., Kotake A. N., Schoeller D. A. The aminopyrine breath test does not correlate with histologic disease severity in patients with cholestasis. Hepatology. 1987 May-Jun;7(3):464–467. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840070309. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bell J. D., Cox I. J., Sargentoni J., Peden C. J., Menon D. K., Foster C. S., Watanapa P., Iles R. A., Urenjak J. A 31P and 1H-NMR investigation in vitro of normal and abnormal human liver. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1993 Nov 25;1225(1):71–77. doi: 10.1016/0925-4439(93)90124-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beswick D. R., Klatskin G., Boyer J. L. Asymptomatic primary biliary cirrhosis. A progress report on long-term follow-up and natural history. Gastroenterology. 1985 Aug;89(2):267–271. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burroughs A. K., Biagini M., McCormick P. A., Rolles K. Liver transplantation and primary biliary cirrhosis. Postgrad Med J. 1989 Aug;65(766):553–558. doi: 10.1136/pgmj.65.766.553. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christensen E., Neuberger J., Crowe J., Altman D. G., Popper H., Portmann B., Doniach D., Ranek L., Tygstrup N., Williams R. Beneficial effect of azathioprine and prediction of prognosis in primary biliary cirrhosis. Final results of an international trial. Gastroenterology. 1985 Nov;89(5):1084–1091. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(85)90213-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dickson E. R., Grambsch P. M., Fleming T. R., Fisher L. D., Langworthy A. Prognosis in primary biliary cirrhosis: model for decision making. Hepatology. 1989 Jul;10(1):1–7. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840100102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eriksson S., Zettervall O. The N-terminal propeptide of collagen type III in serum as a prognostic indicator in primary biliary cirrhosis. J Hepatol. 1986;2(3):370–378. doi: 10.1016/s0168-8278(86)80048-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- James O., Macklon A. F., Watson A. J. Primary biliary cirrhosis--a revised clinical spectrum. Lancet. 1981 Jun 13;1(8233):1278–1281. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(81)92457-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- James S. P., Hoofnagle J. H., Strober W., Jones E. A. NIH conference: Primary biliary cirrhosis: a model autoimmune disease. Ann Intern Med. 1983 Oct;99(4):500–512. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-99-4-500. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeffrey G. P., Hoffman N. E., Reed W. D. Validation of prognostic models in primary biliary cirrhosis. Aust N Z J Med. 1990 Apr;20(2):107–110. doi: 10.1111/j.1445-5994.1990.tb01282.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein R., Klöppel G., Garbe W., Fintelmann V., Berg P. A. Antimitochondrial antibody profiles determined at early stages of primary biliary cirrhosis differentiate between a benign and a progressive course of the disease. A retrospective analysis of 76 patients over 6-18 years. J Hepatol. 1991 Jan;12(1):21–27. doi: 10.1016/0168-8278(91)90903-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lenkinski R. E. Clinical magnetic resonance spectroscopy: a critical evaluation. Invest Radiol. 1989 Dec;24(12):1034–1038. doi: 10.1097/00004424-198912000-00025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Menon D. K., Harris M., Sargentoni J., Taylor-Robinson S. D., Cox I. J., Morgan M. Y. In vivo hepatic 31P magnetic resonance spectroscopy in chronic alcohol abusers. Gastroenterology. 1995 Mar;108(3):776–788. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(95)90451-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Menon D. K., Sargentoni J., Taylor-Robinson S. D., Bell J. D., Cox I. J., Bryant D. J., Coutts G. A., Rolles K., Burroughs A. K., Morgan M. Y. Effect of functional grade and etiology on in vivo hepatic phosphorus-31 magnetic resonance spectroscopy in cirrhosis: biochemical basis of spectral appearances. Hepatology. 1995 Feb;21(2):417–427. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyerhoff D. J., Boska M. D., Thomas A. M., Weiner M. W. Alcoholic liver disease: quantitative image-guided P-31 MR spectroscopy. Radiology. 1989 Nov;173(2):393–400. doi: 10.1148/radiology.173.2.2798871. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munakata T., Griffiths R. D., Martin P. A., Jenkins S. A., Shields R., Edwards R. H. An in vivo 31P MRS study of patients with liver cirrhosis: progress towards a non-invasive assessment of disease severity. NMR Biomed. 1993 Mar-Apr;6(2):168–172. doi: 10.1002/nbm.1940060211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy E. J., Brindle K. M., Rorison C. J., Dixon R. M., Rajagopalan B., Radda G. K. Changes in phosphatidylethanolamine metabolism in regenerating rat liver as measured by 31P-NMR. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1992 Apr 30;1135(1):27–34. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(92)90162-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy E. J., Rajagopalan B., Brindle K. M., Radda G. K. Phospholipid bilayer contribution to 31P NMR spectra in vivo. Magn Reson Med. 1989 Nov;12(2):282–289. doi: 10.1002/mrm.1910120218. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mutimer D. J., Bassendine M. F., Kelly P., James O. F. Is measurement of type III procollagen amino propeptide useful in primary biliary cirrhosis? J Hepatol. 1989 Sep;9(2):184–189. doi: 10.1016/0168-8278(89)90049-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mutimer D. J., Fussey S. P., Yeaman S. J., Kelly P. J., James O. F., Bassendine M. F. Frequency of IgG and IgM autoantibodies to four specific M2 mitochondrial autoantigens in primary biliary cirrhosis. Hepatology. 1989 Oct;10(4):403–407. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840100402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nyberg A., Engström-Laurent A., Löf L. Serum hyaluronate in primary biliary cirrhosis--a biochemical marker for progressive liver damage. Hepatology. 1988 Jan-Feb;8(1):142–146. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840080127. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oberhaensli R., Rajagopalan B., Galloway G. J., Taylor D. J., Radda G. K. Study of human liver disease with P-31 magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Gut. 1990 Apr;31(4):463–467. doi: 10.1136/gut.31.4.463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pugh R. N., Murray-Lyon I. M., Dawson J. L., Pietroni M. C., Williams R. Transection of the oesophagus for bleeding oesophageal varices. Br J Surg. 1973 Aug;60(8):646–649. doi: 10.1002/bjs.1800600817. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reichen J., Widmer T., Cotting J. Accurate prediction of death by serial determination of galactose elimination capacity in primary biliary cirrhosis: a comparison with the Mayo model. Hepatology. 1991 Sep;14(3):504–510. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruiz-Cabello J., Cohen J. S. Phospholipid metabolites as indicators of cancer cell function. NMR Biomed. 1992 Sep-Oct;5(5):226–233. doi: 10.1002/nbm.1940050506. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saeed N., Menon D. K. A knowledge-based approach to minimize baseline roll in chemical shift imaging. Magn Reson Med. 1993 May;29(5):591–598. doi: 10.1002/mrm.1910290503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor-Robinson S. D., Thomas E. L., Sargentoni J., Marcus C. D., Davidson B. R., Bell J. D. Cirrhosis of the human liver: an in vitro 31P nuclear magnetic resonance study. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1995 Oct 17;1272(2):113–118. doi: 10.1016/0925-4439(95)00074-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor D. J., Bore P. J., Styles P., Gadian D. G., Radda G. K. Bioenergetics of intact human muscle. A 31P nuclear magnetic resonance study. Mol Biol Med. 1983 Jul;1(1):77–94. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Villeneuve J. P., Infante-Rivard C., Ampelas M., Pomier-Layrargues G., Huet P. M., Marleau D. Prognostic value of the aminopyrine breath test in cirrhotic patients. Hepatology. 1986 Sep-Oct;6(5):928–931. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840060520. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


