Abstract
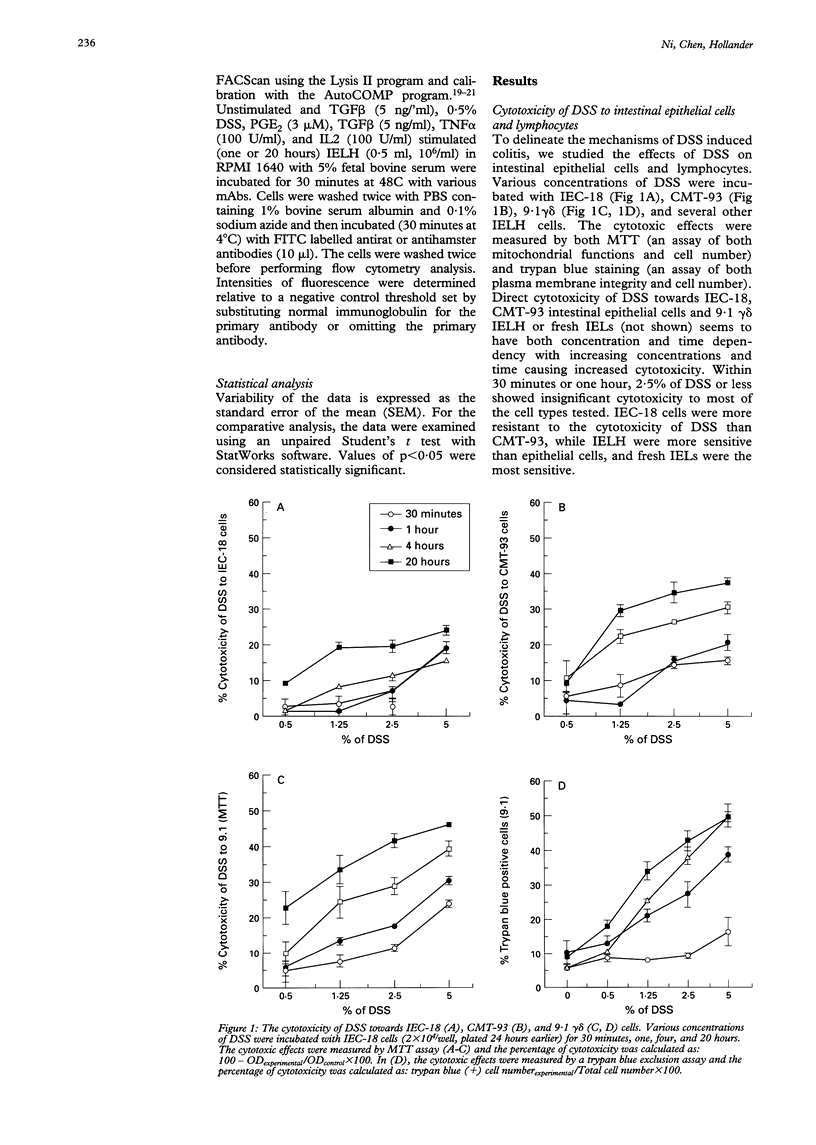
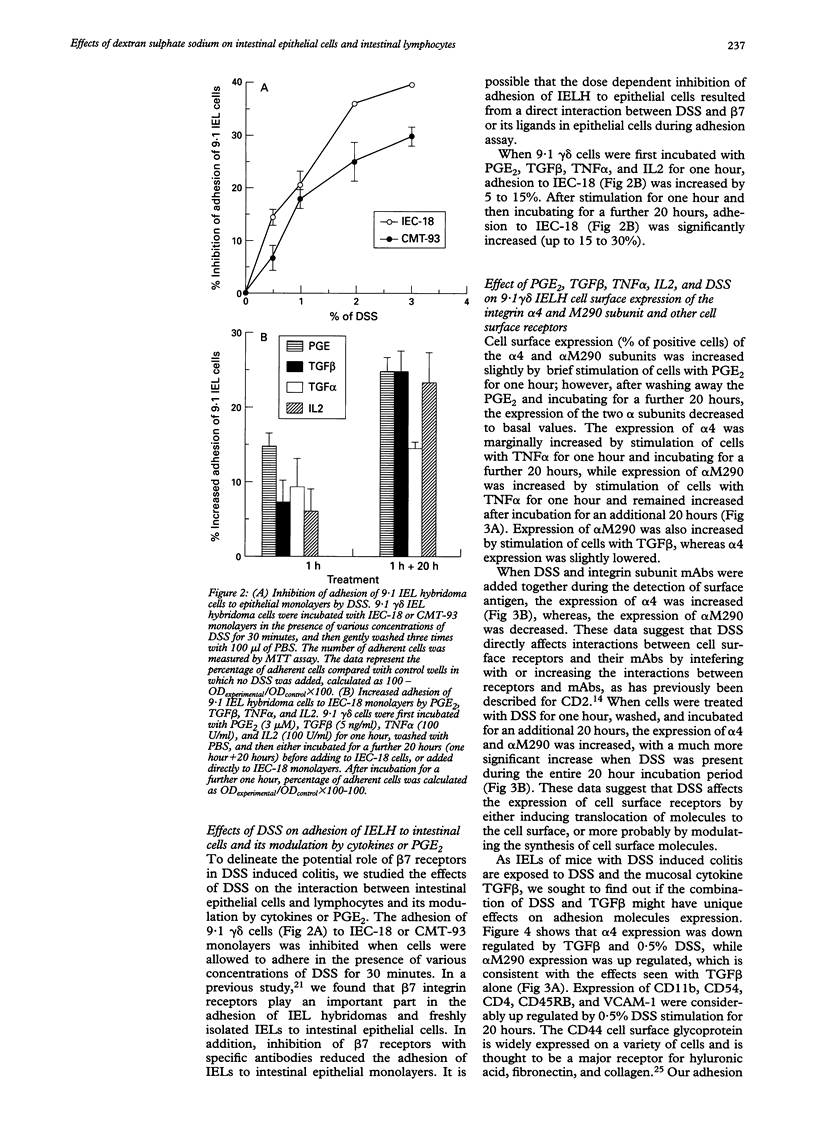
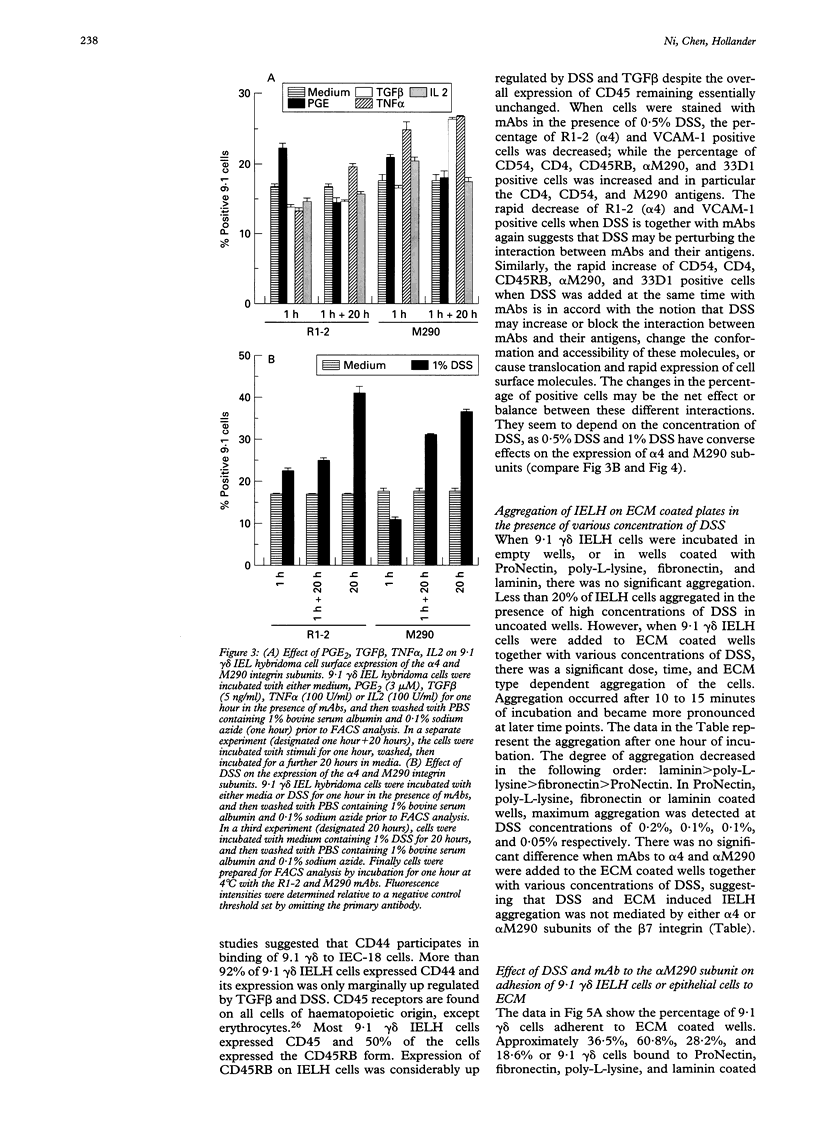
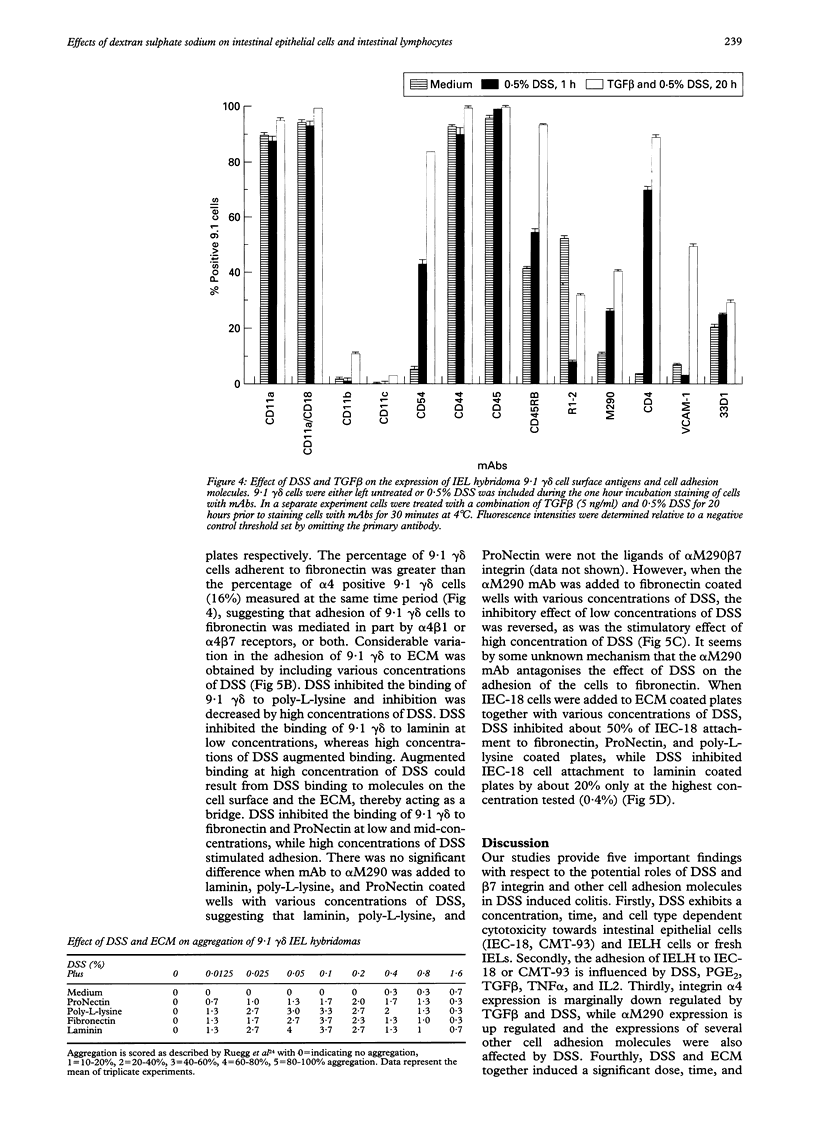
BACKGROUND AND AIMS: The effects of dextran sulphate sodium (DSS) on mouse intestinal epithelial cells and intraepithelial lymphocytes were analysed to investigate the mechanism by which DSS induces colitis and tumours in mice. Cytotoxicity of DSS towards intestinal epithelial cells and intestinal intraepithelial lymphocyte hybridomas or fresh intestinal intraepithelial lymphocytes seems to have concentration, time, and cell type dependency with increasing concentrations and time causing increased cytotoxicity. RESULTS: Integrin alpha 4 expression was marginally down regulated by 0.5% of DSS, while alpha M290 expression was up regulated. DSS inhibits the binding of 9.1 gamma delta cells to both extracellular matrix (ECM) and epithelial cells. Conversely at high concentrations it increases binding to all ECM except poly-L-lysine. Various cytokines including TGF beta, interleukin 2, and tumour necrosis factor alpha as well as prostaglandin alter the expression of the integrin alpha 4 and M290 subunits at the cell surface, and also alter the adhesion of 9.1 gamma delta cells to epithelial monolayers. The expression of a large number of cell adhesion molecules expressed on intraepithelial lymphocytes is affected by a combination of the abundant gut cytokine TGF beta and DSS, suggesting that DSS induced colitis may ultimately arise from a combination of gut cytokine and DSS. DSS also triggers intraepithelial lymphocyte aggregation on all ECM coated plate tested. CONCLUSIONS: These data suggest that the potential roles of DSS induced colitis may be: (a) direct cytotoxicity; (b) interference with the normal interaction between intestinal lymphocytes, epithelial cells, and ECMs; (c) aberrant modulation of the expression of the integrin beta 7 receptors, other cell receptors, and their functions.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cepek K. L., Shaw S. K., Parker C. M., Russell G. J., Morrow J. S., Rimm D. L., Brenner M. B. Adhesion between epithelial cells and T lymphocytes mediated by E-cadherin and the alpha E beta 7 integrin. Nature. 1994 Nov 10;372(6502):190–193. doi: 10.1038/372190a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan B. M., Elices M. J., Murphy E., Hemler M. E. Adhesion to vascular cell adhesion molecule 1 and fibronectin. Comparison of alpha 4 beta 1 (VLA-4) and alpha 4 beta 7 on the human B cell line JY. J Biol Chem. 1992 Apr 25;267(12):8366–8370. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deusch K., Pfeffer K., Reich K., Gstettenbauer M., Daum S., Lüling F., Classen M. Phenotypic and functional characterization of human TCR gamma delta+ intestinal intraepithelial lymphocytes. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1991;173:279–283. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dörries R., Schimpl A., Wecker E. Action of dextran sulfate as a direct and general B cell mitogen. Eur J Immunol. 1974 Mar;4(3):230–233. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830040315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Handa K., Nudelman E. D., Stroud M. R., Shiozawa T., Hakomori S. Selectin GMP-140 (CD62; PADGEM) binds to sialosyl-Le(a) and sialosyl-Le(x), and sulfated glycans modulate this binding. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1991 Dec 31;181(3):1223–1230. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(91)92069-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hocking D., Ferro T. J., Johnson A. Dextran sulfate and heparin sulfate inhibit platelet-activating factor-induced pulmonary edema. J Appl Physiol (1985) 1992 Jan;72(1):179–185. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1992.72.1.179. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holzmann B., McIntyre B. W., Weissman I. L. Identification of a murine Peyer's patch--specific lymphocyte homing receptor as an integrin molecule with an alpha chain homologous to human VLA-4 alpha. Cell. 1989 Jan 13;56(1):37–46. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90981-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jiang W. M., Jenkins D., Yuan Q., Leung E., Choo K. H., Watson J. D., Krissansen G. W. The gene organization of the human beta 7 subunit, the common beta subunit of the leukocyte integrins HML-1 and LPAM-1. Int Immunol. 1992 Sep;4(9):1031–1040. doi: 10.1093/intimm/4.9.1031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kilshaw P. J., Murant S. J. Expression and regulation of beta 7(beta p) integrins on mouse lymphocytes: relevance to the mucosal immune system. Eur J Immunol. 1991 Oct;21(10):2591–2597. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830211041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minchin S. A., Leitenberg D., Stunz L. L., Feldbush T. L. Polyclonal activation of rat B cells. II. Dextran sulfate as a cofactor in mitogen-induced and antigen-induced differentiation of rat B lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1990 Oct 15;145(8):2427–2433. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosmann T. Rapid colorimetric assay for cellular growth and survival: application to proliferation and cytotoxicity assays. J Immunol Methods. 1983 Dec 16;65(1-2):55–63. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(83)90303-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ni J., Hollander D. Expression of beta 7 integrins and other cell adhesion molecules on mouse lymphocytes and their modulation by a new cytokine, IL-2 receptor-inducing factor. Cell Immunol. 1995 Aug;164(1):150–155. doi: 10.1006/cimm.1995.1154. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ni J., Hollander D., Sydora B., Panwala C. Adhesion molecule expression and adhesion properties of murine intestinal intraepithelial lymphocyte hybridomas. Cell Immunol. 1995 Aug;164(1):156–160. doi: 10.1006/cimm.1995.1155. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ni J., Meager A., Karpas A. Characterization and partial purification of a novel cytotoxic lymphokine (factor 2) produced by a human B cell line (Karpas 160). Int Immunol. 1992 Apr;4(4):519–531. doi: 10.1093/intimm/4.4.519. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ni J., Porter A. G., Hollander D. Beta 7 integrins and other cell adhesion molecules are differentially expressed and modulated by TNF beta in different lymphocyte populations. Cell Immunol. 1995 Apr 1;161(2):166–172. doi: 10.1006/cimm.1995.1023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker C. M., Cepek K. L., Russell G. J., Shaw S. K., Posnett D. N., Schwarting R., Brenner M. B. A family of beta 7 integrins on human mucosal lymphocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Mar 1;89(5):1924–1928. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.5.1924. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pilarski L. M., Yacyshyn B. R., Jensen G. S., Pruski E., Pabst H. F. Beta 1 integrin (CD29) expression on human postnatal T cell subsets defined by selective CD45 isoform expression. J Immunol. 1991 Aug 1;147(3):830–837. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruoslahti E., Pekkala A., Engvall E. Effect of dextran sulfate on fibronectin-collagen interaction. FEBS Lett. 1979 Nov 1;107(1):51–54. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(79)80461-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rüegg C., Postigo A. A., Sikorski E. E., Butcher E. C., Pytela R., Erle D. J. Role of integrin alpha 4 beta 7/alpha 4 beta P in lymphocyte adherence to fibronectin and VCAM-1 and in homotypic cell clustering. J Cell Biol. 1992 Apr;117(1):179–189. doi: 10.1083/jcb.117.1.179. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schieferdecker H. L., Ullrich R., Weiss-Breckwoldt A. N., Schwarting R., Stein H., Riecken E. O., Zeitz M. The HML-1 antigen of intestinal lymphocytes is an activation antigen. J Immunol. 1990 Apr 1;144(7):2541–2549. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schieferdecker H. L., Ullrich R., Zeitz M. Phenotype of HML-1-positive T cells in the human intestinal lamina propria. Immunol Res. 1991;10(3-4):207–210. doi: 10.1007/BF02919694. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwarting R., Dienemann D., Kruschwitz M., Fritsche G., Stein H. Specificities of monoclonal antibodies B-ly7 and HML-1 are identical. Blood. 1990 Jan 1;75(1):320–321. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Screaton G. R., Bell M. V., Bell J. I., Jackson D. G. The identification of a new alternative exon with highly restricted tissue expression in transcripts encoding the mouse Pgp-1 (CD44) homing receptor. Comparison of all 10 variable exons between mouse, human, and rat. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jun 15;268(17):12235–12238. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skinner M. P., Lucas C. M., Burns G. F., Chesterman C. N., Berndt M. C. GMP-140 binding to neutrophils is inhibited by sulfated glycans. J Biol Chem. 1991 Mar 25;266(9):5371–5374. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamaru T., Kobayashi H., Kishimoto S., Kajiyama G., Shimamoto F., Brown W. R. Histochemical study of colonic cancer in experimental colitis of rats. Dig Dis Sci. 1993 Mar;38(3):529–537. doi: 10.1007/BF01316510. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warren H. S., Parish C. R. Mapping the dextran sulfate binding site on CD2. Immunol Cell Biol. 1990 Jun;68(Pt 3):199–205. doi: 10.1038/icb.1990.28. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


