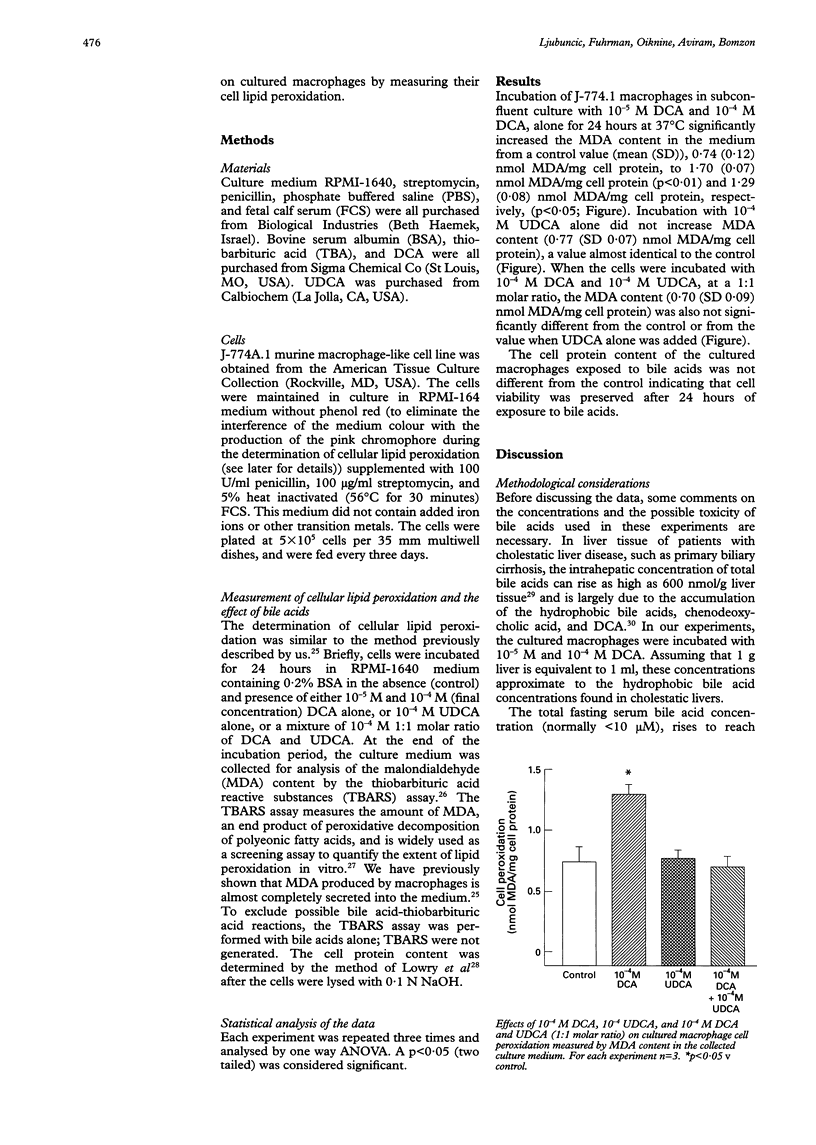
Abstract
BACKGROUND: Kupffer cells are essential for normal hepatic homeostasis and when stimulated, they secrete reactive oxygen species, nitric oxide, eicosanoids, and cytokines. Some of these products are cytotoxic and attack nucleic acids, thiol proteins, or membrane lipids causing lipid peroxidation. Hydrophobic bile acids, such as deoxycholic acid (DCA), can damage hepatocytes by solubilising membranes and impairing mitochondrial function, as well as increasing the generation of reactive oxygen species. OBJECTIVES: The hypothesis that hydrophobic bile acids could stimulate Kupffer cells to increase their capacity to generate reactive oxygen species by measuring cellular lipid peroxidation was tested. Because the hydrophilic bile acid, ursodeoxycholic acid (UDCA) can block hydrophobic bile acid induced cellular phenomena, it was also hypothesised that UDCA could antagonise macrophage activation by hydrophobic bile acids to blunt their capacity to generate reactive oxygen species. METHODS: J-774A.1 murine macrophages were incubated for 24 hours with either 10(-5) M and 10(-4) M (final concentration) DCA alone, or 10(-4) M UDCA alone, or a mixture of 10(-4) M 1:1 molar ratio of DCA and UDCA. At the end of the incubation period, the culture medium was collected for determination of cellular lipid peroxidation by measuring the malondialdehyde (MDA) content in the medium with the thiobarbituric acid reactive substances assay. RESULTS: 10(-5) M and 10(-4) M DCA increased MDA generation by cultured macrophages. 10(-4) M UDCA alone did not increase MDA generation but blocked the peroxidative actions of DCA. CONCLUSIONS: Hydrophobic bile acids, after their hepatic retention, can oxidatively activate Kupffer cells to generate reactive oxygen species. Because UDCA can block this action, the beneficial effect of UDCA is, in part, related to its ability to act as an antioxidant.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anwer M. S. Mechanism of bile acid-induced HCO3-(-)rich hypercholeresis. An analysis based on quantitative acid-base chemistry. J Hepatol. 1992 Jan;14(1):118–126. doi: 10.1016/0168-8278(92)90140-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beckman J. S., Beckman T. W., Chen J., Marshall P. A., Freeman B. A. Apparent hydroxyl radical production by peroxynitrite: implications for endothelial injury from nitric oxide and superoxide. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Feb;87(4):1620–1624. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.4.1620. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Botla R., Spivey J. R., Aguilar H., Bronk S. F., Gores G. J. Ursodeoxycholate (UDCA) inhibits the mitochondrial membrane permeability transition induced by glycochenodeoxycholate: a mechanism of UDCA cytoprotection. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1995 Feb;272(2):930–938. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chretien Y., Poupon R., Gherardt M. F., Chazouilleres O., Labbe D., Myara A., Trivin F. Bile acid glycine and taurine conjugates in serum of patients with primary biliary cirrhosis: effect of ursodeoxycholic treatment. Gut. 1989 Aug;30(8):1110–1115. doi: 10.1136/gut.30.8.1110. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crosignani A., Podda M., Battezzati P. M., Bertolini E., Zuin M., Watson D., Setchell K. D. Changes in bile acid composition in patients with primary biliary cirrhosis induced by ursodeoxycholic acid administration. Hepatology. 1991 Dec;14(6):1000–1007. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeRubertis F. R., Craven P. A. Relationship of bile salt stimulation of colonic epithelial phospholipid turnover and proliferative activity: role of activation of protein kinase C1. Prev Med. 1987 Jul;16(4):572–579. doi: 10.1016/0091-7435(87)90074-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Draper H. H., Hadley M. Malondialdehyde determination as index of lipid peroxidation. Methods Enzymol. 1990;186:421–431. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(90)86135-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elsing C., Sägesser H., Reichen J. Ursodeoxycholate-induced hypercholeresis in cirrhotic rats: further evidence for cholehepatic shunting. Hepatology. 1994 Oct;20(4 Pt 1):1048–1054. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840200438. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freeman B. A., Crapo J. D. Biology of disease: free radicals and tissue injury. Lab Invest. 1982 Nov;47(5):412–426. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuhrman B., Oiknine J., Aviram M. Iron induces lipid peroxidation in cultured macrophages, increases their ability to oxidatively modify LDL, and affects their secretory properties. Atherosclerosis. 1994 Nov;111(1):65–78. doi: 10.1016/0021-9150(94)90192-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gurantz D., Schteingart C. D., Hagey L. R., Steinbach J. H., Grotmol T., Hofmann A. F. Hypercholeresis induced by unconjugated bile acid infusion correlates with recovery in bile of unconjugated bile acids. Hepatology. 1991 Mar;13(3):540–550. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Güldütuna S., Zimmer G., Imhof M., Bhatti S., You T., Leuschner U. Molecular aspects of membrane stabilization by ursodeoxycholate [see comment]. Gastroenterology. 1993 Jun;104(6):1736–1744. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(93)90653-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heathcote E. J., Cauch-Dudek K., Walker V., Bailey R. J., Blendis L. M., Ghent C. N., Michieletti P., Minuk G. Y., Pappas S. C., Scully L. J. The Canadian Multicenter Double-blind Randomized Controlled Trial of ursodeoxycholic acid in primary biliary cirrhosis. Hepatology. 1994 May;19(5):1149–1156. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heuman D. M., Bajaj R. Ursodeoxycholate conjugates protect against disruption of cholesterol-rich membranes by bile salts. Gastroenterology. 1994 May;106(5):1333–1341. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(94)90027-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heuman D. M. Hepatoprotective properties of ursodeoxycholic acid. Gastroenterology. 1993 Jun;104(6):1865–1870. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(93)90672-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heuman D. M., Mills A. S., McCall J., Hylemon P. B., Pandak W. M., Vlahcevic Z. R. Conjugates of ursodeoxycholate protect against cholestasis and hepatocellular necrosis caused by more hydrophobic bile salts. In vivo studies in the rat. Gastroenterology. 1991 Jan;100(1):203–211. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(91)90602-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heuman D. M. Quantitative estimation of the hydrophilic-hydrophobic balance of mixed bile salt solutions. J Lipid Res. 1989 May;30(5):719–730. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hofmann A. F. Pharmacology of ursodeoxycholic acid, an enterohepatic drug. Scand J Gastroenterol Suppl. 1994;204:1–15. doi: 10.3109/00365529409103618. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holley A. E., Cheeseman K. H. Measuring free radical reactions in vivo. Br Med Bull. 1993 Jul;49(3):494–505. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.bmb.a072626. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jazrawi R. P., de Caestecker J. S., Goggin P. M., Britten A. J., Joseph A. E., Maxwell J. D., Northfield T. C. Kinetics of hepatic bile acid handling in cholestatic liver disease: effect of ursodeoxycholic acid. Gastroenterology. 1994 Jan;106(1):134–142. doi: 10.1016/s0016-5085(94)94899-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston R. B., Jr Current concepts: immunology. Monocytes and macrophages. N Engl J Med. 1988 Mar 24;318(12):747–752. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198803243181205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krähenbühl S., Fischer S., Talos C., Reichen J. Ursodeoxycholate protects oxidative mitochondrial metabolism from bile acid toxicity: dose-response study in isolated rat liver mitochondria. Hepatology. 1994 Dec;20(6):1595–1601. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840200632. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lacaille F., Paradis K. The immunosuppressive effect of ursodeoxycholic acid: a comparative in vitro study on human peripheral blood mononuclear cells. Hepatology. 1993 Jul;18(1):165–172. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leuschner U., Fischer H., Kurtz W., Güldütuna S., Hübner K., Hellstern A., Gatzen M., Leuschner M. Ursodeoxycholic acid in primary biliary cirrhosis: results of a controlled double-blind trial. Gastroenterology. 1989 Nov;97(5):1268–1274. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(89)91698-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leuschner U., Güldütuna S., Imhof M., Hübner K., Benjaminov A., Leuschner M. Effects of ursodeoxycholic acid after 4 to 12 years of therapy in early and late stages of primary biliary cirrhosis. J Hepatol. 1994 Oct;21(4):624–633. doi: 10.1016/s0168-8278(94)80111-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lim A. G., Northfield T. C. Ursodeoxycholic acid and primary biliary cirrhosis. BMJ. 1994 Aug 20;309(6953):491–492. doi: 10.1136/bmj.309.6953.491. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindor K. D., Dickson E. R., Baldus W. P., Jorgensen R. A., Ludwig J., Murtaugh P. A., Harrison J. M., Wiesner R. H., Anderson M. L., Lange S. M. Ursodeoxycholic acid in the treatment of primary biliary cirrhosis. Gastroenterology. 1994 May;106(5):1284–1290. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(94)90021-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noronha-Dutra A. A., Epperlein M. M., Woolf N. Reaction of nitric oxide with hydrogen peroxide to produce potentially cytotoxic singlet oxygen as a model for nitric oxide-mediated killing. FEBS Lett. 1993 Apr 19;321(1):59–62. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(93)80621-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oka H., Toda G., Ikeda Y., Hashimoto N., Hasumura Y., Kamimura T., Ohta Y., Tsuji T., Hattori N., Namihisa T. A multi-center double-blind controlled trial of ursodeoxycholic acid for primary biliary cirrhosis. Gastroenterol Jpn. 1990 Dec;25(6):774–780. doi: 10.1007/BF02779195. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poupon R. E., Balkau B., Eschwège E., Poupon R. A multicenter, controlled trial of ursodiol for the treatment of primary biliary cirrhosis. UDCA-PBC Study Group. N Engl J Med. 1991 May 30;324(22):1548–1554. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199105303242204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poupon R. E., Poupon R., Balkau B. Ursodiol for the long-term treatment of primary biliary cirrhosis. The UDCA-PBC Study Group. N Engl J Med. 1994 May 12;330(19):1342–1347. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199405123301903. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poupon R., Chrétien Y., Poupon R. E., Ballet F., Calmus Y., Darnis F. Is ursodeoxycholic acid an effective treatment for primary biliary cirrhosis? Lancet. 1987 Apr 11;1(8537):834–836. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(87)91610-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poupon R., Poupon R. E. Ursodeoxycholic acid therapy of chronic cholestatic conditions in adults and children. Pharmacol Ther. 1995 Apr;66(1):1–15. doi: 10.1016/0163-7258(94)00073-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosser B. G., Gores G. J. Liver cell necrosis: cellular mechanisms and clinical implications. Gastroenterology. 1995 Jan;108(1):252–275. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(95)90032-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmucker D. L., Ohta M., Kanai S., Sato Y., Kitani K. Hepatic injury induced by bile salts: correlation between biochemical and morphological events. Hepatology. 1990 Nov;12(5):1216–1221. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840120523. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sokol R. J., Devereaux M., Khandwala R., O'Brien K. Evidence for involvement of oxygen free radicals in bile acid toxicity to isolated rat hepatocytes. Hepatology. 1993 May;17(5):869–881. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spivey J. R., Bronk S. F., Gores G. J. Glycochenodeoxycholate-induced lethal hepatocellular injury in rat hepatocytes. Role of ATP depletion and cytosolic free calcium. J Clin Invest. 1993 Jul;92(1):17–24. doi: 10.1172/JCI116546. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stiehl A., Rudolph G., Raedsch R., Möller B., Hopf U., Lotterer E., Bircher J., Fölsch U., Klaus J., Endele R. Ursodeoxycholic acid-induced changes of plasma and urinary bile acids in patients with primary biliary cirrhosis. Hepatology. 1990 Sep;12(3 Pt 1):492–497. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840120308. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshikawa M., Tsujii T., Matsumura K., Yamao J., Matsumura Y., Kubo R., Fukui H., Ishizaka S. Immunomodulatory effects of ursodeoxycholic acid on immune responses. Hepatology. 1992 Aug;16(2):358–364. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840160213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


