Abstract
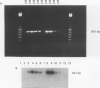
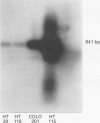
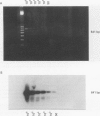
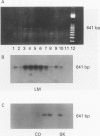
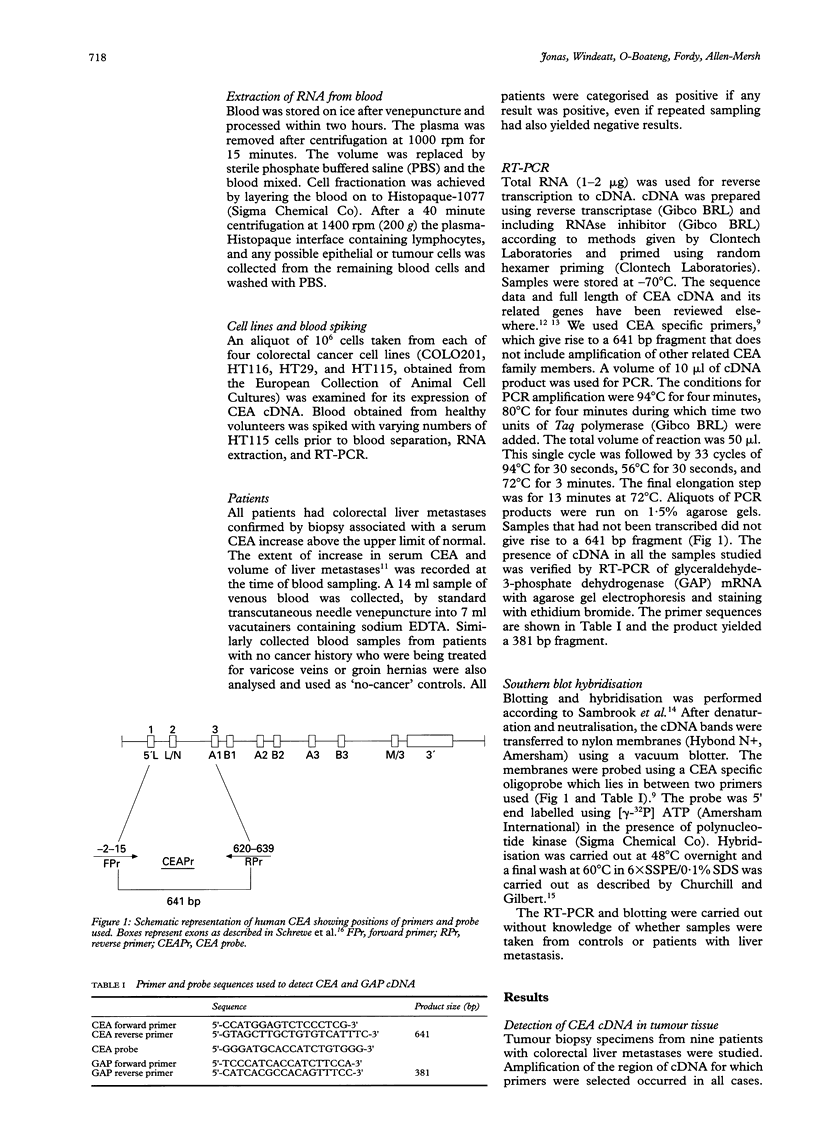
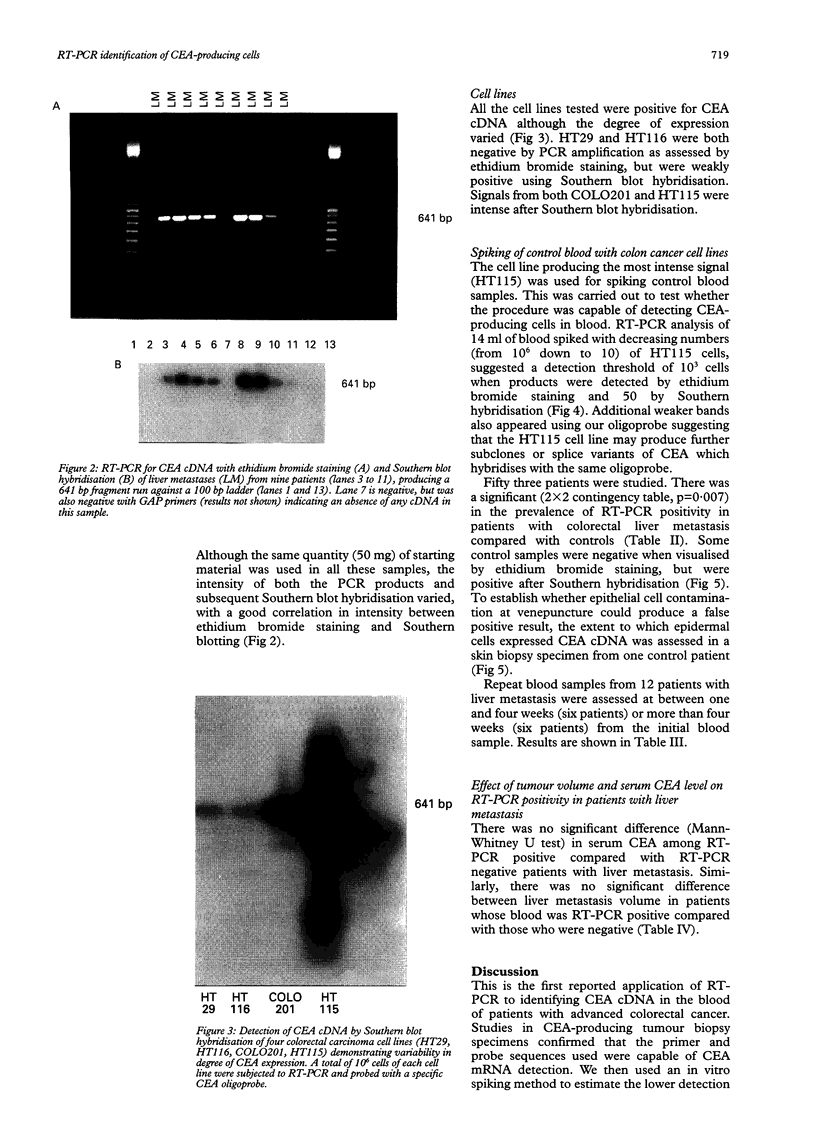
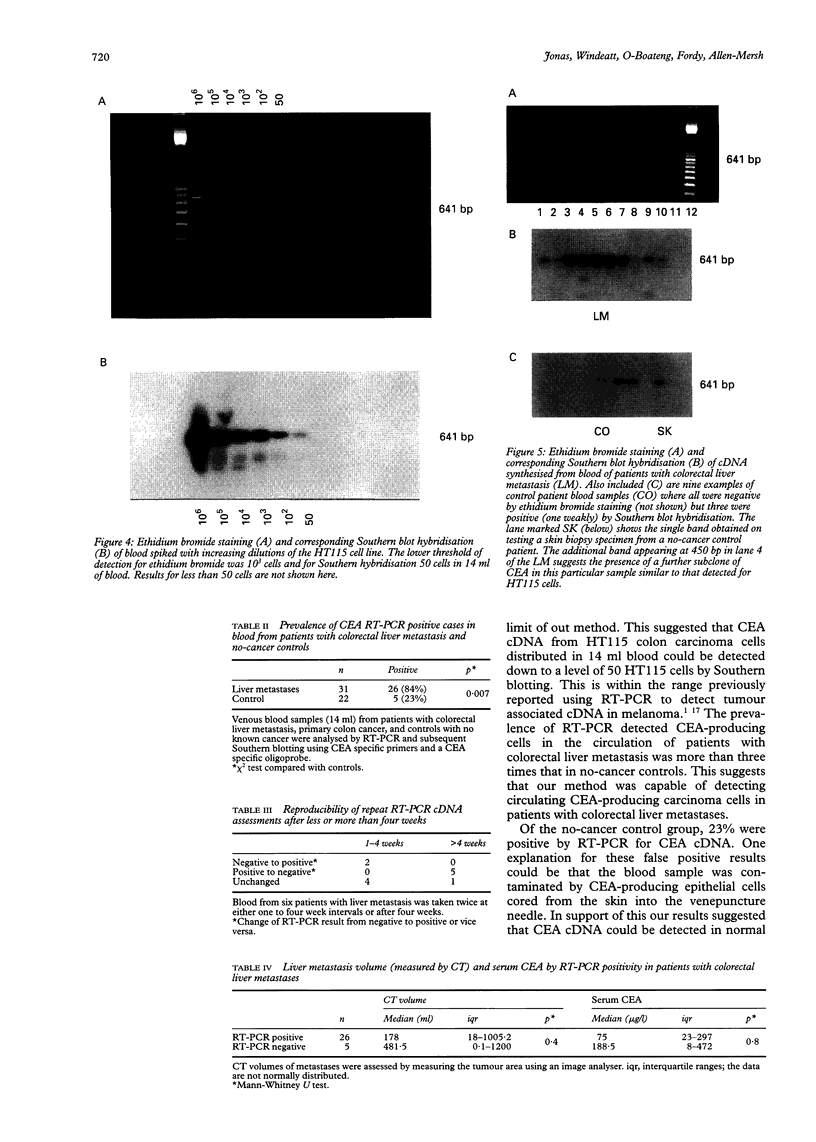
BACKGROUND: Application of the reverse transcriptase polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) to identification of circulating tumour cells in colorectal cancer. AIMS: To assess whether circulating malignant cells in patients with colorectal liver metastasis could be identified by RT-PCR recognition of mRNA coding for the tumour marker carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA). PATIENTS: A total of 31 with colorectal liver metastases and 22 no-cancer controls. METHODS: Specific cDNA primers for CEA transcripts were used to apply RT-PCR to tissue biopsy specimens, colon carcinoma cell lines, and peripheral blood samples from patients with colorectal liver metastases. A strongly CEA-expressive HT115 colorectal carcinoma cell line was used to spike blood samples from no-cancer control subjects. RESULTS: The limit for detection of CEA cDNA by Southern blotting using HT115 cells was 50 cells per 14 ml of spiked blood. There was a significant difference (p = 0.007) in RT-PCR positive expression between patients with liver metastasis (26/31) compared with controls (5/22). There was no significant relation between the prevalence of CEA cDNA amplification and serum CEA level or metastasis volume in patients with liver metastasis. CONCLUSIONS: This is the first study to suggest that identification of circulating colorectal cancer cells using RT-PCR for detection of CEA cDNA is feasible.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allen-Mersh T. G. Improving survival after large bowel cancer. BMJ. 1991 Sep 14;303(6803):595–596. doi: 10.1136/bmj.303.6803.595. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allen-Mersh T. G. Serum CEA in the follow-up of colorectal carcinoma: experience in a district general hospital. Ann R Coll Surg Engl. 1984 Jan;66(1):14–16. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beauchemin N., Benchimol S., Cournoyer D., Fuks A., Stanners C. P. Isolation and characterization of full-length functional cDNA clones for human carcinoembryonic antigen. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Sep;7(9):3221–3230. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.9.3221. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burchill S. A., Bradbury M. F., Pittman K., Southgate J., Smith B., Selby P. Detection of epithelial cancer cells in peripheral blood by reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction. Br J Cancer. 1995 Feb;71(2):278–281. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1995.56. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Church G. M., Gilbert W. Genomic sequencing. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(7):1991–1995. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.7.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dworkin M. J., Burke D., Earlam S., Fordy C., Allen-Mersh T. G. Measurement of response to treatment in colorectal liver metastases. Br J Cancer. 1995 Apr;71(4):873–876. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1995.168. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dworkin M. J., Earlam S., Fordy C., Allen-Mersh T. G. Importance of hepatic artery node involvement in patients with colorectal liver metastases. J Clin Pathol. 1995 Mar;48(3):270–272. doi: 10.1136/jcp.48.3.270. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foss A. J., Guille M. J., Occleston N. L., Hykin P. G., Hungerford J. L., Lightman S. The detection of melanoma cells in peripheral blood by reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction. Br J Cancer. 1995 Jul;72(1):155–159. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1995.293. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Israeli R. S., Miller W. H., Jr, Su S. L., Powell C. T., Fair W. R., Samadi D. S., Huryk R. F., DeBlasio A., Edwards E. T., Wise G. J. Sensitive nested reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction detection of circulating prostatic tumor cells: comparison of prostate-specific membrane antigen and prostate-specific antigen-based assays. Cancer Res. 1994 Dec 15;54(24):6306–6310. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Komeda T., Fukuda Y., Sando T., Kita R., Furukawa M., Nishida N., Amenomori M., Nakao K. Sensitive detection of circulating hepatocellular carcinoma cells in peripheral venous blood. Cancer. 1995 May 1;75(9):2214–2219. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19950501)75:9<2214::aid-cncr2820750905>3.0.co;2-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsumura M., Niwa Y., Kato N., Komatsu Y., Shiina S., Kawabe T., Kawase T., Toyoshima H., Ihori M., Shiratori Y. Detection of alpha-fetoprotein mRNA, an indicator of hematogenous spreading hepatocellular carcinoma, in the circulation: a possible predictor of metastatic hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology. 1994 Dec;20(6):1418–1425. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840200607. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mori M., Mimori K., Inoue H., Barnard G. F., Tsuji K., Nanbara S., Ueo H., Akiyoshi T. Detection of cancer micrometastases in lymph nodes by reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction. Cancer Res. 1995 Aug 1;55(15):3417–3420. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohiwa K., Harada T., Morikawa S., Nakamura T. Immunoelectron microscopic localization of carcinoembryonic antigen in gastric adenocarcinoma cell lines. Pathol Int. 1994 Aug;44(8):635–644. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1827.1994.tb01724.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schrewe H., Thompson J., Bona M., Hefta L. J., Maruya A., Hassauer M., Shively J. E., von Kleist S., Zimmermann W. Cloning of the complete gene for carcinoembryonic antigen: analysis of its promoter indicates a region conveying cell type-specific expression. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Jun;10(6):2738–2748. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.6.2738. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seiden M. V., Kantoff P. W., Krithivas K., Propert K., Bryant M., Haltom E., Gaynes L., Kaplan I., Bubley G., DeWolf W. Detection of circulating tumor cells in men with localized prostate cancer. J Clin Oncol. 1994 Dec;12(12):2634–2639. doi: 10.1200/JCO.1994.12.12.2634. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith B., Selby P., Southgate J., Pittman K., Bradley C., Blair G. E. Detection of melanoma cells in peripheral blood by means of reverse transcriptase and polymerase chain reaction. Lancet. 1991 Nov 16;338(8777):1227–1229. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(91)92100-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steele G., Jr, Ravikumar T. S. Resection of hepatic metastases from colorectal cancer. Biologic perspective. Ann Surg. 1989 Aug;210(2):127–138. doi: 10.1097/00000658-198908000-00001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas P., Zamcheck N. Role of the liver in clearance and excretion of circulating carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA). Dig Dis Sci. 1983 Mar;28(3):216–224. doi: 10.1007/BF01295116. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson J., Mössinger S., Reichardt V., Engels U., Beauchemin N., Kommoss F., von Kleist S., Zimmermann W. A polymerase-chain-reaction assay for the specific identification of transcripts encoded by individual carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA)-gene-family members. Int J Cancer. 1993 Sep 9;55(2):311–319. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910550223. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Traweek S. T., Liu J., Battifora H. Keratin gene expression in non-epithelial tissues. Detection with polymerase chain reaction. Am J Pathol. 1993 Apr;142(4):1111–1118. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmermann W., Ortlieb B., Friedrich R., von Kleist S. Isolation and characterization of cDNA clones encoding the human carcinoembryonic antigen reveal a highly conserved repeating structure. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 May;84(9):2960–2964. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.9.2960. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]