Abstract
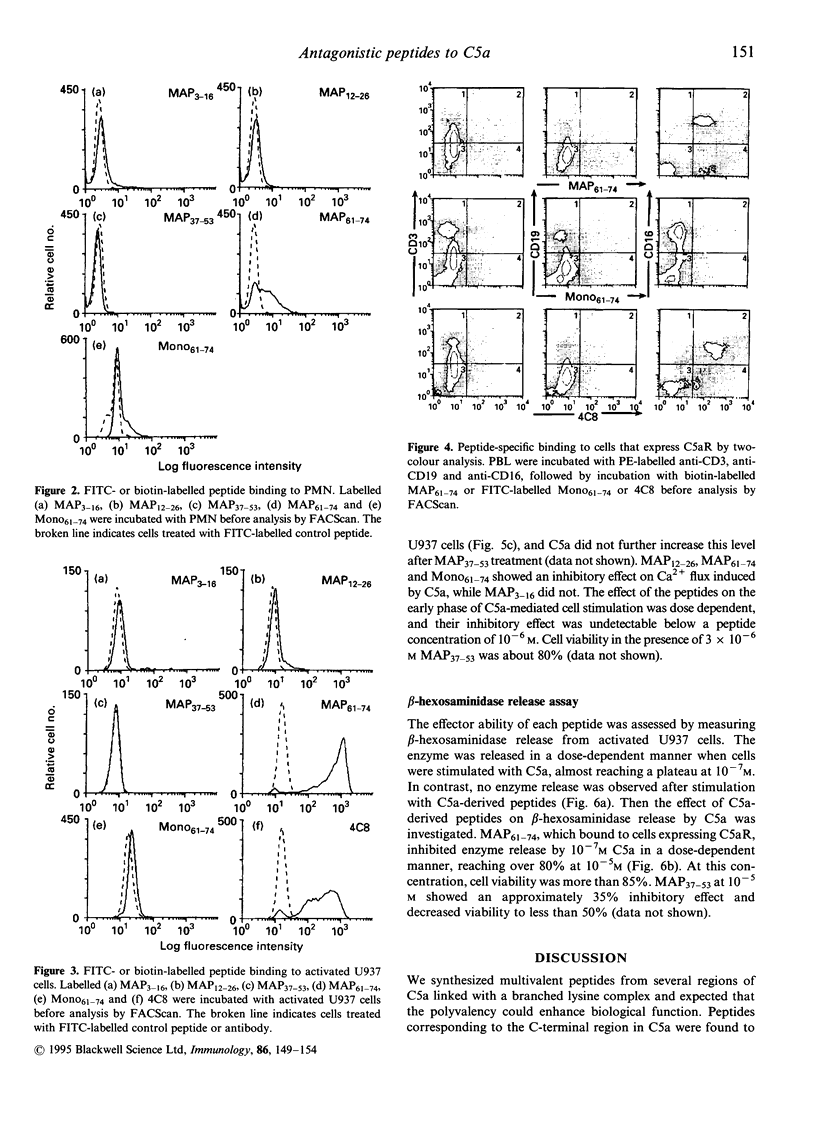
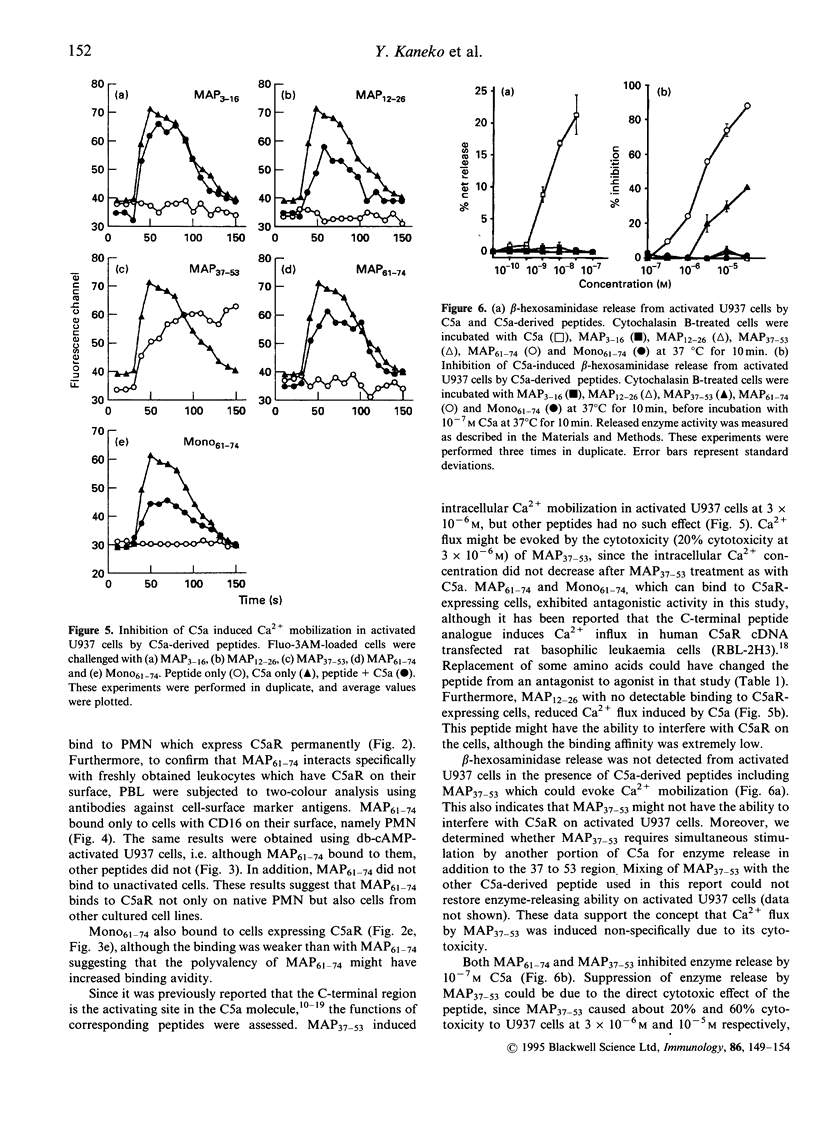
Multivalent synthetic peptides derived from C5a were prepared in order to examine their effects on the C5a receptor (C5aR). Multiple antigen peptide (MAP) of the C5a C-terminal region (MAP61-74) bound to cells expressing C5aR with high affinity. On the other hand, N-terminal peptides (MAP3-16 and MAP12-26) and one with a sequence from the mid-portion of C5a (MAP37-53) did not bind to the cells. In addition, MAP61-74 inhibited Ca2+ mobilization and release of beta-hexosaminidase by C5a from dibutyryl cAMP-activated U937 cells. This Ca2+ mobilization was also inhibited by MAP12-26 and Mono61-74, the monomeric C-terminal peptide. Taken together, these data indicate that C5a binds to the C5aR via its C-terminal region. Furthermore, MAP61-74, a 14mer peptide that has additional amino acids at the N-terminal compared with the C-terminal octapaptide, can bind to C5aR and can be considered an antagonist of C5a which may prove useful as an agent for controlling the allergic response caused by complement activation.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bubeck P., Grötzinger J., Winkler M., Köhl J., Wollmer A., Klos A., Bautsch W. Site-specific mutagenesis of residues in the human C5a anaphylatoxin which are involved in possible interaction with the C5a receptor. Eur J Biochem. 1994 Feb 1;219(3):897–904. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1994.tb18571.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carney D. F., Hugli T. E. Site-specific mutations in the N-terminal region of human C5a that affect interactions of C5a with the neutrophil C5a receptor. Protein Sci. 1993 Sep;2(9):1391–1399. doi: 10.1002/pro.5560020904. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chenoweth D. E., Erickson B. W., Hugli T. E. Human C5a-related synthetic peptides as neutrophil chemotactic factors. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1979 Jan 30;86(2):227–234. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(79)90856-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chenoweth D. E., Hugli T. E. Human C5a and C5a analogs as probes of the neutrophil C5a receptor. Mol Immunol. 1980 Feb;17(2):151–161. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(80)90067-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeMartino J. A., Van Riper G., Siciliano S. J., Molineaux C. J., Konteatis Z. D., Rosen H., Springer M. S. The amino terminus of the human C5a receptor is required for high affinity C5a binding and for receptor activation by C5a but not C5a analogs. J Biol Chem. 1994 May 20;269(20):14446–14450. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ember J. A., Sanderson S. D., Taylor S. M., Kawahara M., Hugli T. E. Biologic activity of synthetic analogues of C5a anaphylatoxin. J Immunol. 1992 May 15;148(10):3165–3173. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrante A., Thong Y. H. Optimal conditions for simultaneous purification of mononuclear and polymorphonuclear leucocytes from human blood by the Hypaque-Ficoll method. J Immunol Methods. 1980;36(2):109–117. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(80)90036-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerard C., Showell H. J., Hoeprich P. D., Jr, Hugli T. E., Stimler N. P. Evidence for a role of the amino-terminal region in the biological activity of the classical anaphylatoxin, porcine C5a des-Arg-74. J Biol Chem. 1985 Mar 10;260(5):2613–2616. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerard N. P., Gerard C. The chemotactic receptor for human C5a anaphylatoxin. Nature. 1991 Feb 14;349(6310):614–617. doi: 10.1038/349614a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hugli T. E. Structure and function of the anaphylatoxins. Springer Semin Immunopathol. 1984;7(2-3):193–219. doi: 10.1007/BF01893020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson R. J., Tamerius J. D., Chenoweth D. E. Identification of an antigenic epitope and receptor binding domain of human C5a. J Immunol. 1987 Jun 1;138(11):3856–3862. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawai M., Quincy D. A., Lane B., Mollison K. W., Luly J. R., Carter G. W. Identification and synthesis of a receptor binding site of human anaphylatoxin C5a. J Med Chem. 1991 Jul;34(7):2068–2071. doi: 10.1021/jm00111a022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Köhl J., Lübbers B., Klos A., Bautsch W., Casaretto M. Evaluation of the C-terminal C5a effector site with short synthetic C5a analog peptides. Eur J Immunol. 1993 Mar;23(3):646–652. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830230311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mollison K. W., Fey T. A., Krause R. A., Miller L., Edalji R. P., Conway R. G., Mandecki W., Shallcross M. A., Kawai M., Or Y. S. C5a structural requirements for neutrophil receptor interaction. Agents Actions Suppl. 1991;35:17–21. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mollison K. W., Mandecki W., Zuiderweg E. R., Fayer L., Fey T. A., Krause R. A., Conway R. G., Miller L., Edalji R. P., Shallcross M. A. Identification of receptor-binding residues in the inflammatory complement protein C5a by site-directed mutagenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jan;86(1):292–296. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.1.292. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan E. L., Ember J. A., Sanderson S. D., Scholz W., Buchner R., Ye R. D., Hugli T. E. Anti-C5a receptor antibodies. Characterization of neutralizing antibodies specific for a peptide, C5aR-(9-29), derived from the predicted amino-terminal sequence of the human C5a receptor. J Immunol. 1993 Jul 1;151(1):377–388. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan E. L., Sanderson S., Scholz W., Noonan D. J., Weigle W. O., Hugli T. E. Identification and characterization of the effector region within human C5a responsible for stimulation of IL-6 synthesis. J Immunol. 1992 Jun 15;148(12):3937–3942. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oppermann M., Raedt U., Hebell T., Schmidt B., Zimmermann B., Götze O. Probing the human receptor for C5a anaphylatoxin with site-directed antibodies. Identification of a potential ligand binding site on the NH2-terminal domain. J Immunol. 1993 Oct 1;151(7):3785–3794. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pease J. E., Burton D. R., Barker M. D. Generation of chimeric C5a/formyl peptide receptors: towards the identification of the human C5a receptor binding site. Eur J Immunol. 1994 Jan;24(1):211–215. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830240133. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pease J. E., Burton D. R., Barker M. D. Site directed mutagenesis of the complement C5a receptor--examination of a model for its interaction with the ligand C5a. Mol Immunol. 1994 Jul;31(10):733–737. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(94)90147-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Posnett D. N., McGrath H., Tam J. P. A novel method for producing anti-peptide antibodies. Production of site-specific antibodies to the T cell antigen receptor beta-chain. J Biol Chem. 1988 Feb 5;263(4):1719–1725. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rollins T. E., Siciliano S., Kobayashi S., Cianciarulo D. N., Bonilla-Argudo V., Collier K., Springer M. S. Purification of the active C5a receptor from human polymorphonuclear leukocytes as a receptor-Gi complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Feb 1;88(3):971–975. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.3.971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanderson S. D., Kirnarsky L., Sherman S. A., Ember J. A., Finch A. M., Taylor S. M. Decapeptide agonists of human C5a: the relationship between conformation and spasmogenic and platelet aggregatory activities. J Med Chem. 1994 Sep 16;37(19):3171–3180. doi: 10.1021/jm00045a023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz L. B., Austen K. F., Wasserman S. I. Immunologic release of beta-hexosaminidase and beta-glucuronidase from purified rat serosal mast cells. J Immunol. 1979 Oct;123(4):1445–1450. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siciliano S. J., Rollins T. E., DeMartino J., Konteatis Z., Malkowitz L., Van Riper G., Bondy S., Rosen H., Springer M. S. Two-site binding of C5a by its receptor: an alternative binding paradigm for G protein-coupled receptors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Feb 15;91(4):1214–1218. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.4.1214. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zuiderweg E. R., Henkin J., Mollison K. W., Carter G. W., Greer J. Comparison of model and nuclear magnetic resonance structures for the human inflammatory protein C5a. Proteins. 1988;3(3):139–145. doi: 10.1002/prot.340030302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zuiderweg E. R., Nettesheim D. G., Mollison K. W., Carter G. W. Tertiary structure of human complement component C5a in solution from nuclear magnetic resonance data. Biochemistry. 1989 Jan 10;28(1):172–185. doi: 10.1021/bi00427a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


