Abstract
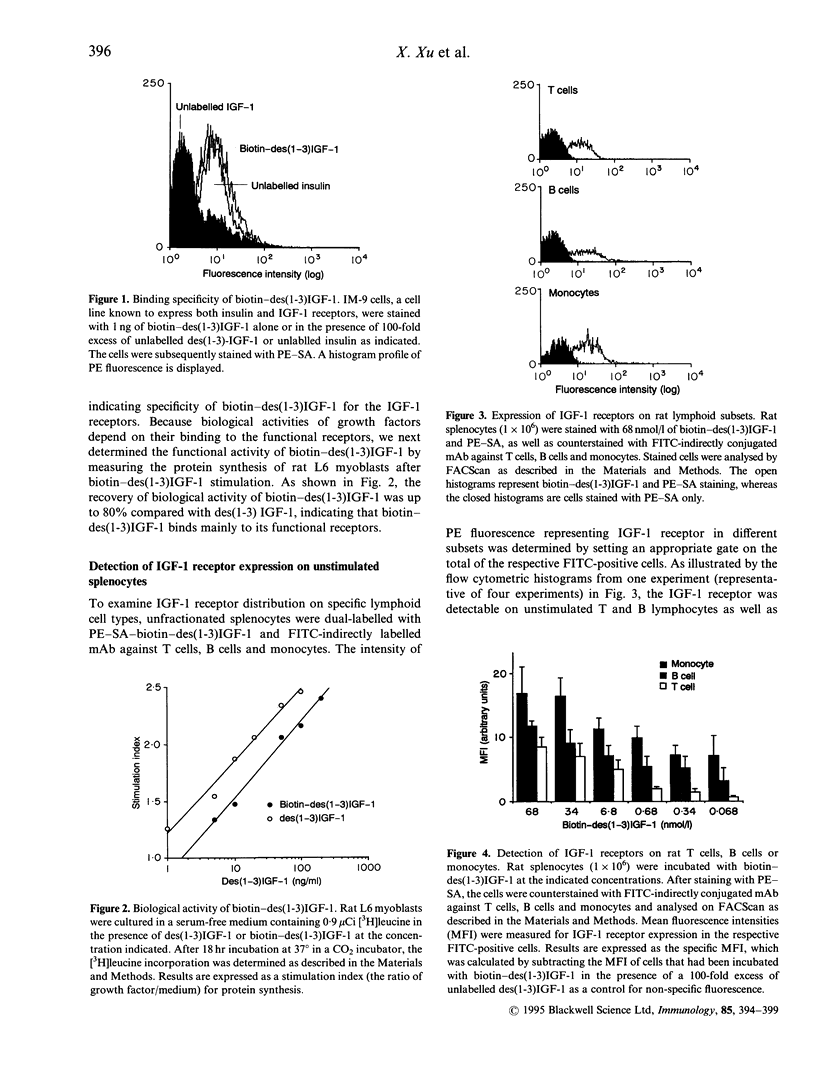
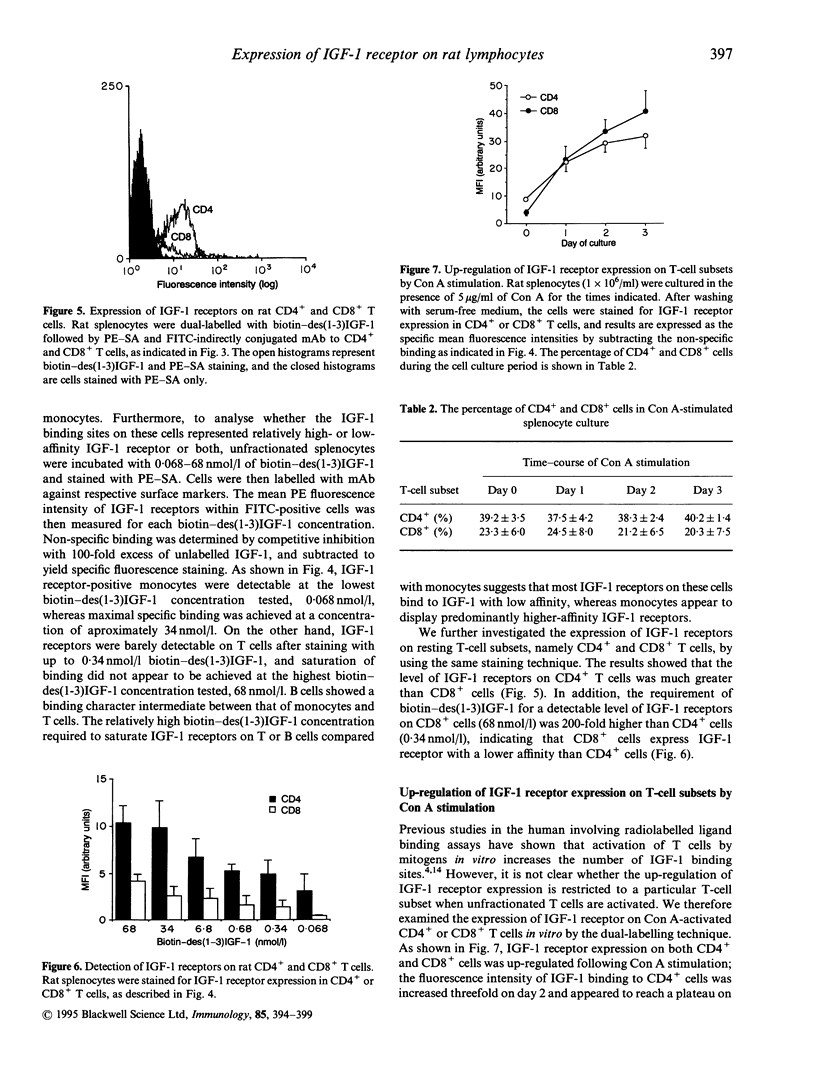
It has become evident that insulin-like growth factor-1 (IGF-1) acts as a growth factor for immune cells, yet the precise regulatory role of IGF-1 in the immune system is unknown. The aim of this study was to examine the distribution of IGF-1 receptors on rat lymphoid cells. A flow cytometric method was used, with a biotinylated and functionally active IGF-1 analogue, namely des(1-3)IGF-1, which binds well to IGF-1 receptor but poorly to IGF binding proteins, followed by phycoerythrin-conjugated streptavidin (PE-SA) staining. Our results showed that IGF-1 receptors were readily detectable on a wide variety of the immune cells, including T cells, B cells and monocytes, but the binding capacity for IGF-1 was monocytes > B cells > T cells, as determined by titration experiments. Furthermore, the level of expression on resting CD4+ T lymphocytes was greater than on CD8+ cells, and the concentration of biotin-des(1-3)IGF-1 required to demonstrate the binding to IGF-1 receptor on CD8+ cells (68 nmol/l) was 200-fold higher than for CD4+ cells (0.34 nmol/l), indicating that most of the IGF-1 receptor on CD8+ cells represented lower affinity sites. The level of IGF-1 receptor expression was increased several-fold after concanavalin A stimulation on both CD4+ and CD8+ T-cell subsets. Kinetic analysis of the expression of IGF-1 receptor and its association with interleukin-2 receptors (IL-2R) following activation showed a similar pattern, with no significant differences in the ratio of IGF-1 receptor: IL-2R per cell during the 3 days of cell culture. Our studies suggest that biological activities of IGF-1 include direct stimulation of immune cells, and that expression of IGF-1 receptor may have a role in regulation of T-cell function.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ballard F. J., Read L. C., Francis G. L., Bagley C. J., Wallace J. C. Binding properties and biological potencies of insulin-like growth factors in L6 myoblasts. Biochem J. 1986 Jan 1;233(1):223–230. doi: 10.1042/bj2330223. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Binz K., Joller P., Froesch P., Binz H., Zapf J., Froesch E. R. Repopulation of the atrophied thymus in diabetic rats by insulin-like growth factor I. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 May;87(10):3690–3694. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.10.3690. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cantrell D. A., Smith K. A. The interleukin-2 T-cell system: a new cell growth model. Science. 1984 Jun 22;224(4655):1312–1316. doi: 10.1126/science.6427923. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark R., Strasser J., McCabe S., Robbins K., Jardieu P. Insulin-like growth factor-1 stimulation of lymphopoiesis. J Clin Invest. 1993 Aug;92(2):540–548. doi: 10.1172/JCI116621. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Czech M. P. Signal transmission by the insulin-like growth factors. Cell. 1989 Oct 20;59(2):235–238. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90281-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forbes B., Szabo L., Baxter R. C., Ballard F. J., Wallace J. C. Classification of the insulin-like growth factor binding proteins into three distinct categories according to their binding specificities. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Nov 30;157(1):196–202. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(88)80032-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsu D., Olefsky J. M. Effect of a major histocompatibility complex class I peptide on insulin-like growth factor-I receptor internalization and biological signaling. Endocrinology. 1993 Sep;133(3):1247–1251. doi: 10.1210/endo.133.3.8365366. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jonas H. A., Cox A. J. Insulin receptor sub-types in a human lymphoid-derived cell line (IM-9): differential regulation by insulin, dexamethasone and monensin. J Recept Res. 1991;11(5):813–829. doi: 10.3109/10799899109064681. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak R. W., Haskell J. F., Greenstein L. A., Rechler M. M., Waldmann T. A., Nissley S. P. Type I and II insulin-like growth factor receptors on human phytohemagglutinin-activated T lymphocytes. Cell Immunol. 1987 Oct 15;109(2):318–331. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(87)90315-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nyman T., Pekonen F. The expression of insulin-like growth factors and their binding proteins in normal human lymphocytes. Acta Endocrinol (Copenh) 1993 Feb;128(2):168–172. doi: 10.1530/acta.0.1280168. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Read L. C., Ballard F. J., Francis G. L., Baxter R. C., Bagley C. J., Wallace J. C. Comparative binding of bovine, human and rat insulin-like growth factors to membrane receptors and to antibodies against human insulin-like growth factor-1. Biochem J. 1986 Jan 1;233(1):215–221. doi: 10.1042/bj2330215. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reiss K., Porcu P., Sell C., Pietrzkowski Z., Baserga R. The insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor is required for the proliferation of hemopoietic cells. Oncogene. 1992 Nov;7(11):2243–2248. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roldan A., Charreau E., Schillaci R., Eugui E. M., Allison A. C. Insulin-like growth factor-1 increases the mitogenic response of human peripheral blood lymphocytes to phytohemagglutinin. Immunol Lett. 1989 Jan 15;20(1):5–8. doi: 10.1016/0165-2478(89)90060-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rutanen E. M., Pekonen F. Insulin-like growth factors and their binding proteins. Acta Endocrinol (Copenh) 1990 Jul;123(1):7–13. doi: 10.1530/acta.0.1230007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stuart C. A., Meehan R. T., Neale L. S., Cintron N. M., Furlanetto R. W. Insulin-like growth factor-I binds selectively to human peripheral blood monocytes and B-lymphocytes. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1991 May;72(5):1117–1122. doi: 10.1210/jcem-72-5-1117. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taga T., Kawanishi Y., Hardy R. R., Hirano T., Kishimoto T. Receptors for B cell stimulatory factor 2. Quantitation, specificity, distribution, and regulation of their expression. J Exp Med. 1987 Oct 1;166(4):967–981. doi: 10.1084/jem.166.4.967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taniguchi T., Minami Y. The IL-2/IL-2 receptor system: a current overview. Cell. 1993 Apr 9;73(1):5–8. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90152-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tapson V. F., Boni-Schnetzler M., Pilch P. F., Center D. M., Berman J. S. Structural and functional characterization of the human T lymphocyte receptor for insulin-like growth factor I in vitro. J Clin Invest. 1988 Sep;82(3):950–957. doi: 10.1172/JCI113703. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss A., Imboden J. B. Cell surface molecules and early events involved in human T lymphocyte activation. Adv Immunol. 1987;41:1–38. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60029-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


