Abstract
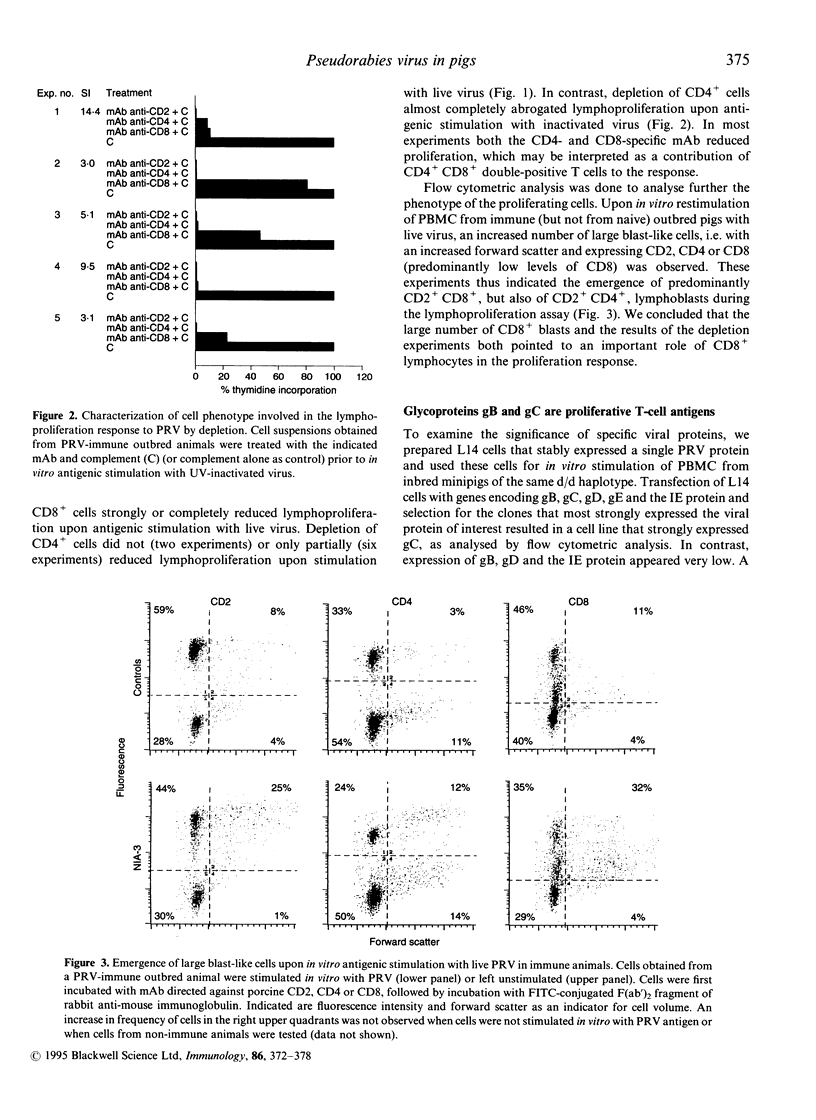
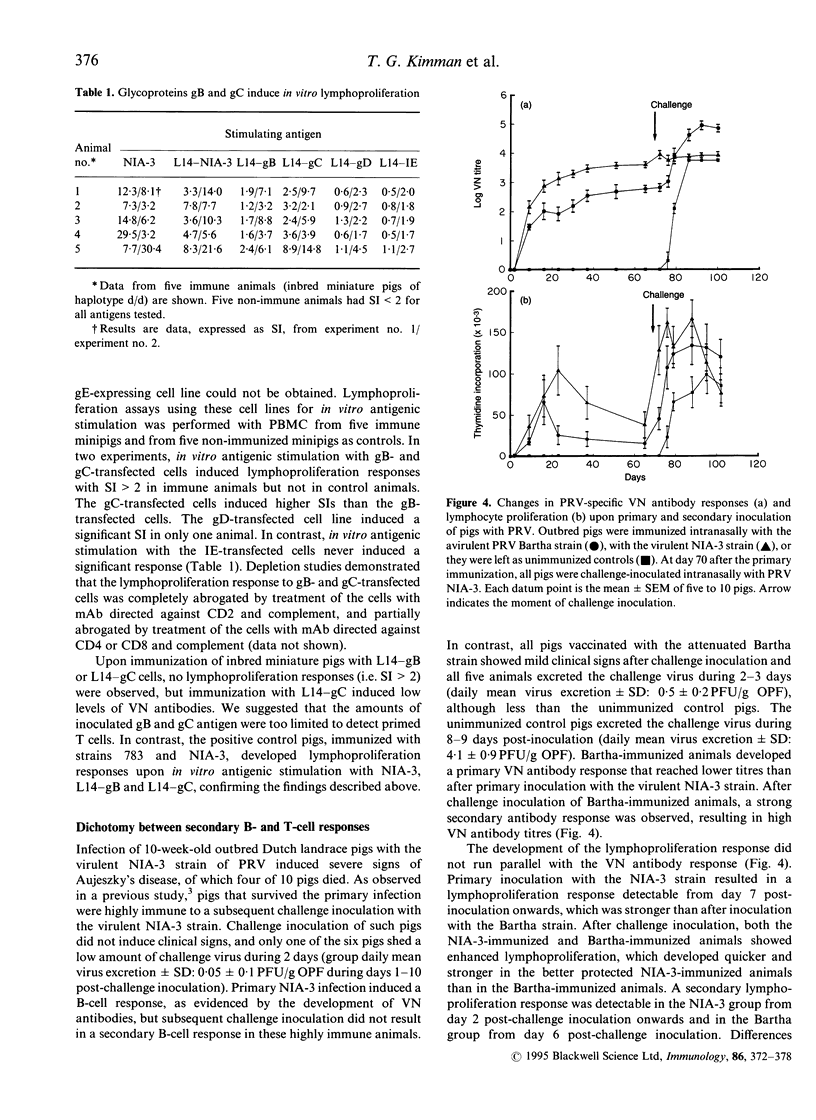
To better understand the contribution of T cells to the immunity of pigs to pseudorabies virus (PRV), we examined the lymphoproliferation response to this virus. Depletion studies demonstrated that both CD2+CD8+ and CD2+CD4+ cells contributed to lymphoproliferation, but to varying degrees upon stimulation with live and ultraviolet (UV) light-inactivated PRV. Flow cytometric analysis revealed the emergence of both CD2+CD8+ and CD2+CD4+ lymphoblastoid cells. To examine the contribution of specific viral proteins, we prepared immortalized porcine B cells of haplotype d/d that stably expressed a single PRV protein, and used these cells for in vitro stimulation of lymphocytes from PRV-immune miniature pigs of the same haplotype. Cells expressing PRV gB or gC induced proliferation. An immunization/challenge experiment showed that the lymphoproliferation response was stronger upon immunization with the virulent NIA-3 strain than with the attenuated Bartha strain. Upon challenge inoculation, the NIA-3-immunized pigs were almost completely immune, in contrast to the Bartha-immunized pigs. Such poorly protected pigs showed secondary B- and T-cell immune responses upon challenge. In contrast, the better protected NIA-3-immunized pigs did not show a secondary B-cell response. However, they developed a secondary lymphoproliferation response, which was quicker and stronger than in the Bartha-immunized pigs. This dichotomy between secondary B- and T-cell responses indicates that an effective T-cell memory response is able to quickly eliminate challenge virus in immune pigs, so preventing a secondary B-cell response.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Banks T. A., Allen E. M., Dasgupta S., Sandri-Goldin R., Rouse B. T. Herpes simplex virus type 1-specific cytotoxic T lymphocytes recognize immediate-early protein ICP27. J Virol. 1991 Jun;65(6):3185–3191. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.6.3185-3191.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Banks T. A., Rouse B. T. Herpesviruses--immune escape artists? Clin Infect Dis. 1992 Apr;14(4):933–941. doi: 10.1093/clinids/14.4.933. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eis-Hübinger A. M., Schmidt D. S., Schneweis K. E. Anti-glycoprotein B monoclonal antibody protects T cell-depleted mice against herpes simplex virus infection by inhibition of virus replication at the inoculated mucous membranes. J Gen Virol. 1993 Mar;74(Pt 3):379–385. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-74-3-379. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fitzgerald-Bocarsly P., Howell D. M., Pettera L., Tehrani S., Lopez C. Immediate-early gene expression is sufficient for induction of natural killer cell-mediated lysis of herpes simplex virus type 1-infected fibroblasts. J Virol. 1991 Jun;65(6):3151–3160. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.6.3151-3160.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghiasi H., Kaiwar R., Nesburn A. B., Slanina S., Wechsler S. L. Expression of seven herpes simplex virus type 1 glycoproteins (gB, gC, gD, gE, gG, gH, and gI): comparative protection against lethal challenge in mice. J Virol. 1994 Apr;68(4):2118–2126. doi: 10.1128/jvi.68.4.2118-2126.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammerberg C., Schurig G. G. Characterization of monoclonal antibodies directed against swine leukocytes. Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 1986 Feb;11(2):107–121. doi: 10.1016/0165-2427(86)90092-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horohov D. W., Moore R. N., Rouse B. T. Production of soluble suppressor factors by herpes simplex virus-stimulated splenocytes from herpes simplex virus-immune mice. J Virol. 1985 Jun;54(3):798–803. doi: 10.1128/jvi.54.3.798-803.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jonjić S., Koszinowski U. H. Monoclonal antibodies reactive with swine lymphocytes. I. Antibodies to membrane structures that define the cytolytic T lymphocyte subset in the swine. J Immunol. 1984 Aug;133(2):647–652. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jonjić S., Pavić I., Lucin P., Rukavina D., Koszinowski U. H. Efficacious control of cytomegalovirus infection after long-term depletion of CD8+ T lymphocytes. J Virol. 1990 Nov;64(11):5457–5464. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.11.5457-5464.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaeffer B., Bottreau E., Phan Thanh L., Olivier M., Salmon H. Histocompatible miniature, boar model: selection of transformed cell lines of B and T lineages producing retrovirus. Int J Cancer. 1990 Sep 15;46(3):481–488. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910460326. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kapoor A. K., Nash A. A., Wildy P. Pathogenesis of herpes simplex virus in B cell-suppressed mice: the relative roles of cell-mediated and humoral immunity. J Gen Virol. 1982 Jul;61(Pt 50):127–131. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-61-1-127. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimman T. G., Bianchi A. T., Wensvoort G., de Bruin T. G., Meliefste C. Cellular immune response to hog cholera virus (HCV): T cells of immune pigs proliferate in vitro upon stimulation with live HCV, but the E1 envelope glycoprotein is not a major T-cell antigen. J Virol. 1993 May;67(5):2922–2927. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.5.2922-2927.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimman T. G., De Wind N., De Bruin T., de Visser Y., Voermans J. Inactivation of glycoprotein gE and thymidine kinase or the US3-encoded protein kinase synergistically decreases in vivo replication of pseudorabies virus and the induction of protective immunity. Virology. 1994 Dec;205(2):511–518. doi: 10.1006/viro.1994.1672. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimman T. G., de Wind N., Oei-Lie N., Pol J. M., Berns A. J., Gielkens A. L. Contribution of single genes within the unique short region of Aujeszky's disease virus (suid herpesvirus type 1) to virulence, pathogenesis and immunogenicity. J Gen Virol. 1992 Feb;73(Pt 2):243–251. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-73-2-243. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larsson B., Fossum C. Bovine virus diarrhoea virus induces in vitro a proliferative response of peripheral blood mononuclear cells from cattle immunized by infection. Vet Microbiol. 1992 Jun 15;31(4):317–325. doi: 10.1016/0378-1135(92)90124-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin S., Moss B., Berman P. W., Laskey L. A., Rouse B. T. Mechanisms of antiviral immunity induced by a vaccinia virus recombinant expressing herpes simplex virus type 1 glycoprotein D: cytotoxic T cells. J Virol. 1987 Mar;61(3):726–734. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.3.726-734.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moormann R. J., de Rover T., Briaire J., Peeters B. P., Gielkens A. L., van Oirschot J. T. Inactivation of the thymidine kinase gene of a gI deletion mutant of pseudorabies virus generates a safe but still highly immunogenic vaccine strain. J Gen Virol. 1990 Jul;71(Pt 7):1591–1595. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-71-7-1591. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peeters B., de Wind N., Hooisma M., Wagenaar F., Gielkens A., Moormann R. Pseudorabies virus envelope glycoproteins gp50 and gII are essential for virus penetration, but only gII is involved in membrane fusion. J Virol. 1992 Feb;66(2):894–905. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.2.894-905.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pescovitz M. D., Lunney J. K., Sachs D. H. Murine anti-swine T4 and T8 monoclonal antibodies: distribution and effects on proliferative and cytotoxic T cells. J Immunol. 1985 Jan;134(1):37–44. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pescovitz M. D., Lunney J. K., Sachs D. H. Preparation and characterization of monoclonal antibodies reactive with porcine PBL. J Immunol. 1984 Jul;133(1):368–375. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sachs D. H., Leight G., Cone J., Schwarz S., Stuart L., Rosenberg S. Transplantation in miniature swine. I. Fixation of the major histocompatibility complex. Transplantation. 1976 Dec;22(6):559–567. doi: 10.1097/00007890-197612000-00004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sáiz J. C., Rodríguez A., González M., Alonso F., Sobrino F. Heterotypic lymphoproliferative response in pigs vaccinated with foot-and-mouth disease virus. Involvement of isolated capsid proteins. J Gen Virol. 1992 Oct;73(Pt 10):2601–2607. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-73-10-2601. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welch S. K., Saif L. J., Ram S. Cell-mediated immune responses of suckling pigs inoculated with attenuated or virulent transmissible gastroenteritis virus. Am J Vet Res. 1988 Aug;49(8):1228–1234. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Witmer L. A., Rosenthal K. L., Graham F. L., Friedman H. M., Yee A., Johnson D. C. Cytotoxic T lymphocytes specific for herpes simplex virus (HSV) studied using adenovirus vectors expressing HSV glycoproteins. J Gen Virol. 1990 Feb;71(Pt 2):387–396. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-71-2-387. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zuckermann F. A., Zsak L., Mettenleiter T. C., Ben-Porat T. Pseudorabies virus glycoprotein gIII is a major target antigen for murine and swine virus-specific cytotoxic T lymphocytes. J Virol. 1990 Feb;64(2):802–812. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.2.802-812.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


