Abstract
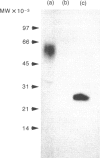
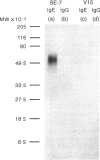
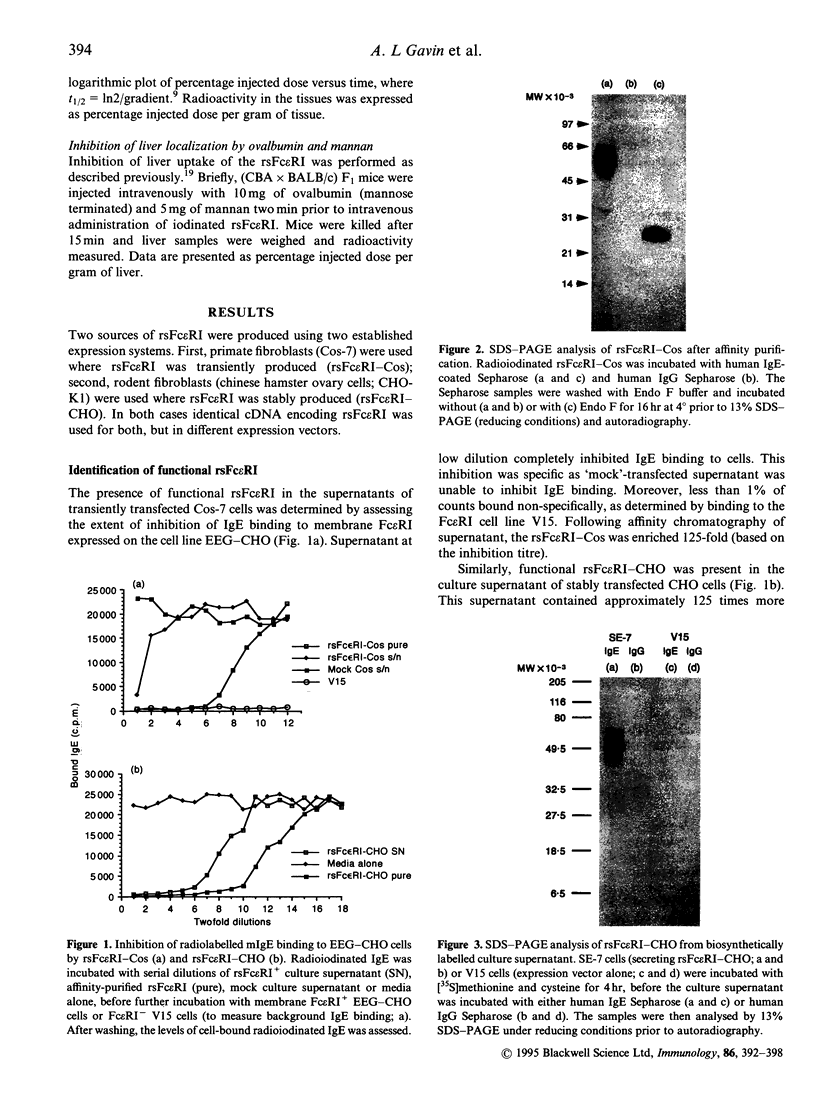
Recombinant soluble IgE Fc receptors (rsFc epsilon RI) are potent inhibitors of type I hypersensitivity reactions tested in a local inflammatory setting. However, the fate of these receptors in vivo is dependent on the cellular source of the rsFc epsilon RI. We have produced these by transiently transfecting Cos-7 cells with a cDNA encoding the extracellular domains of human Fc epsilon RI alpha-chain. Following affinity purification, the rsFc epsilon RI was characterized as 58,000 MW, which was reduced to 23,000 MW following endoglycosidase F treatment. The purified rsFc epsilon RI could inhibit mouse IgE binding to Fc epsilon RI+ transfected CHO-K1 cells in vitro, bind sIgE+ B lymphoma cells in vitro, and inhibit the passive cutaneous anaphylaxis model in vivo in Sprague-Dawley rats. Pharmacokinetic studies in vivo involving intravenous injection of radiolabelled rsFc epsilon RI in mice revealed the receptor to have a rapid initial blood clearance (t1/2 early phase of 15 min) and to accumulate in the liver before being detected in urine. The localization of rsFc epsilon RI in the liver could be blocked by administration of mannose glycosylated ovalbumin and mannan, demonstrating that liver uptake involved the mannose receptor that is expressed on liver sinusoid cells and Kupffer cells. The production of rsFc epsilon RI using a stable expression system in CHO-K1 cells produced functional receptor of the same molecular weight as the Cos-7 system by sodium dodecyl sulphate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE). However, biodistribution studies demonstrated differences; the CHO-K1 cell-produced material did not localize to the liver in comparison to the Cos-7-produced rsFc epsilon RI.
Full text
PDF

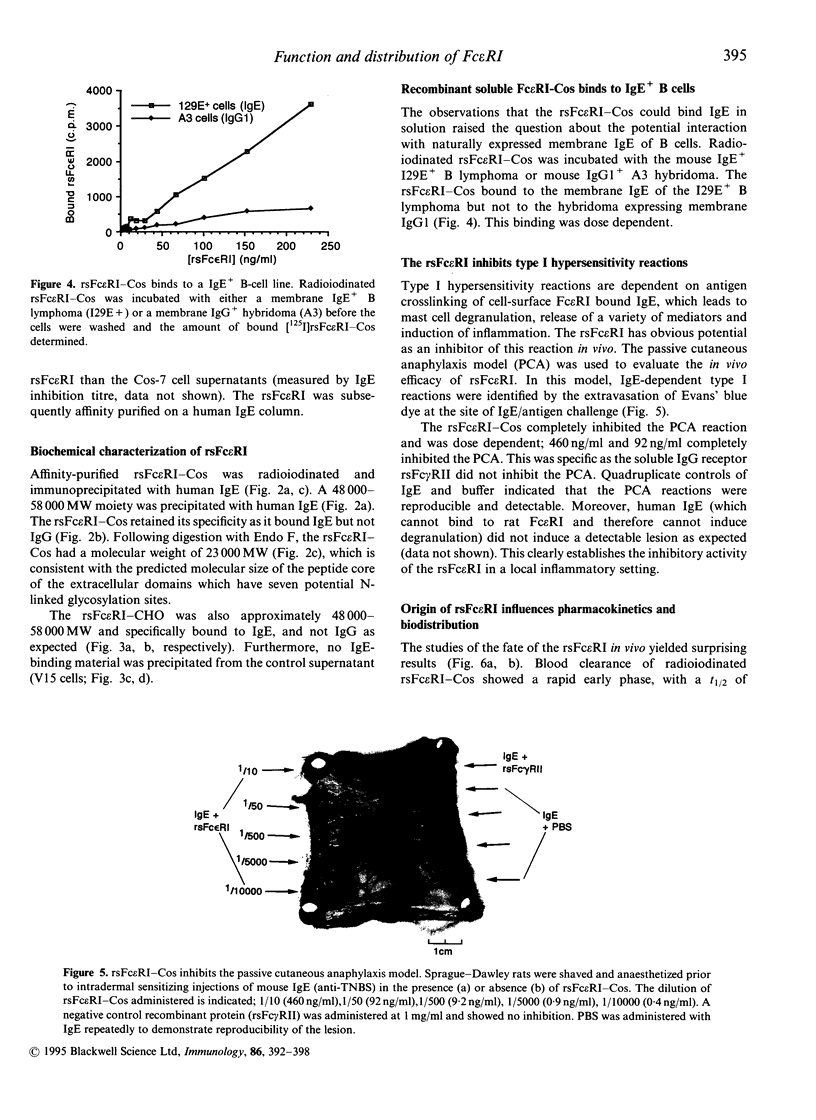
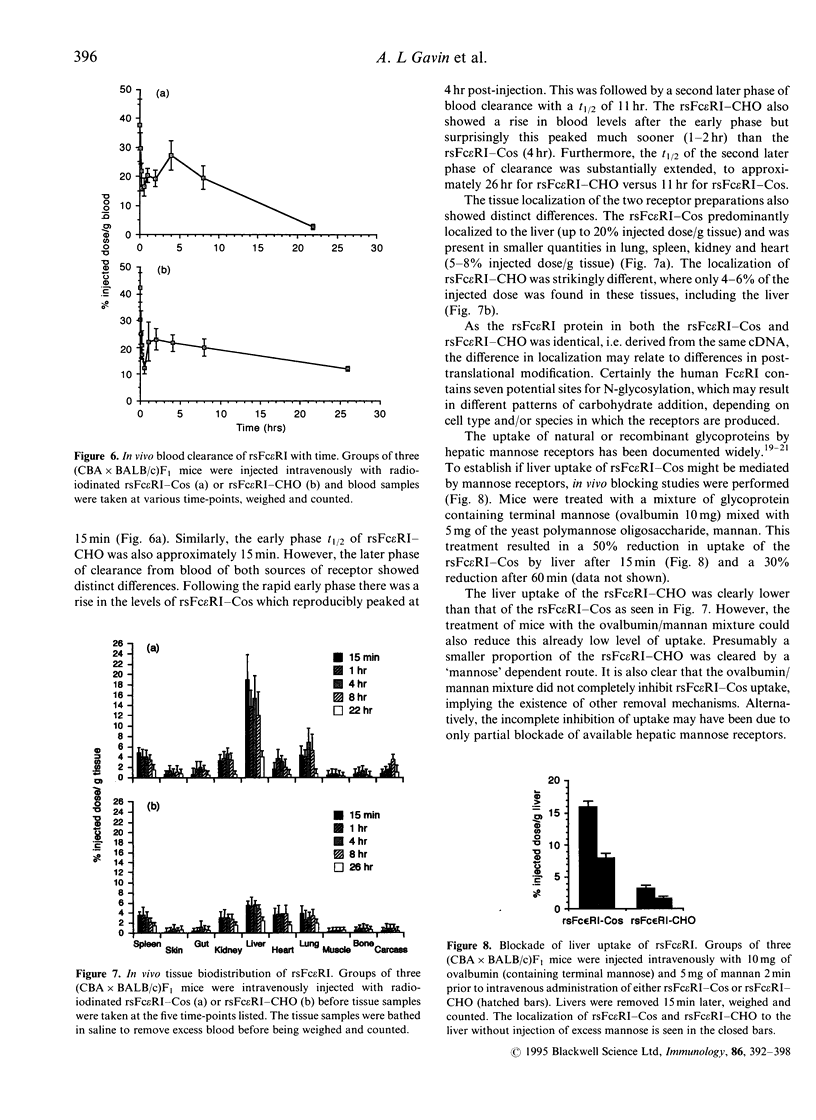


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Byrn R. A., Mordenti J., Lucas C., Smith D., Marsters S. A., Johnson J. S., Cossum P., Chamow S. M., Wurm F. M., Gregory T. Biological properties of a CD4 immunoadhesin. Nature. 1990 Apr 12;344(6267):667–670. doi: 10.1038/344667a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Couser W. G. Mechanisms of glomerular injury in immune-complex disease. Kidney Int. 1985 Sep;28(3):569–583. doi: 10.1038/ki.1985.167. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galili U., Shohet S. B., Kobrin E., Stults C. L., Macher B. A. Man, apes, and Old World monkeys differ from other mammals in the expression of alpha-galactosyl epitopes on nucleated cells. J Biol Chem. 1988 Nov 25;263(33):17755–17762. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haak-Frendscho M., Ridgway J., Shields R., Robbins K., Gorman C., Jardieu P. Human IgE receptor alpha-chain IgG chimera blocks passive cutaneous anaphylaxis reaction in vivo. J Immunol. 1993 Jul 1;151(1):351–358. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hulett M. D., McKenzie I. F., Hogarth P. M. Chimeric Fc receptors identify immunoglobulin-binding regions in human Fc gamma RII and Fc epsilon RI. Eur J Immunol. 1993 Mar;23(3):640–645. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830230310. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ierino F. L., Powell M. S., McKenzie I. F., Hogarth P. M. Recombinant soluble human Fc gamma RII: production, characterization, and inhibition of the Arthus reaction. J Exp Med. 1993 Nov 1;178(5):1617–1628. doi: 10.1084/jem.178.5.1617. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koffler D., Agnello V., Thoburn R., Kunkel H. G. Systemic lupus erythematosus: prototype of immune complex nephritis in man. J Exp Med. 1971 Sep 1;134(3 Pt 2):169s–179s. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lucore C. L., Fry E. T., Nachowiak D. A., Sobel B. E. Biochemical determinants of clearance of tissue-type plasminogen activator from the circulation. Circulation. 1988 Apr;77(4):906–914. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.77.4.906. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- López A. F., Strath M., Sanderson C. J. Mouse immunoglobulin isotypes mediating cytotoxicity of target cells by eosinophils and neutrophils. Immunology. 1983 Mar;48(3):503–509. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller L., Blank U., Metzger H., Kinet J. P. Expression of high-affinity binding of human immunoglobulin E by transfected cells. Science. 1989 Apr 21;244(4902):334–337. doi: 10.1126/science.2523561. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mills J. A. Systemic lupus erythematosus. N Engl J Med. 1994 Jun 30;330(26):1871–1879. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199406303302608. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naclerio R. M. Allergic rhinitis. N Engl J Med. 1991 Sep 19;325(12):860–869. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199109193251206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ra C., Kuromitsu S., Hirose T., Yasuda S., Furuichi K., Okumura K. Soluble human high-affinity receptor for IgE abrogates the IgE-mediated allergic reaction. Int Immunol. 1993 Jan;5(1):47–54. doi: 10.1093/intimm/5.1.47. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stavnezer J., Sirlin S., Abbott J. Induction of immunoglobulin isotype switching in cultured I.29 B lymphoma cells. Characterization of the accompanying rearrangements of heavy chain genes. J Exp Med. 1985 Mar 1;161(3):577–601. doi: 10.1084/jem.161.3.577. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor M. E., Leaning M. S., Summerfield J. A. Uptake and processing of glycoproteins by rat hepatic mannose receptor. Am J Physiol. 1987 May;252(5 Pt 1):E690–E698. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1987.252.5.E690. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Doren K., Hanahan D., Gluzman Y. Infection of eucaryotic cells by helper-independent recombinant adenoviruses: early region 1 is not obligatory for integration of viral DNA. J Virol. 1984 May;50(2):606–614. doi: 10.1128/jvi.50.2.606-614.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yeh C. G., Marsh H. C., Jr, Carson G. R., Berman L., Concino M. F., Scesney S. M., Kuestner R. E., Skibbens R., Donahue K. A., Ip S. H. Recombinant soluble human complement receptor type 1 inhibits inflammation in the reversed passive arthus reaction in rats. J Immunol. 1991 Jan 1;146(1):250–256. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yeh P., Landais D., Lemaître M., Maury I., Crenne J. Y., Becquart J., Murry-Brelier A., Boucher F., Montay G., Fleer R. Design of yeast-secreted albumin derivatives for human therapy: biological and antiviral properties of a serum albumin-CD4 genetic conjugate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Mar 1;89(5):1904–1908. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.5.1904. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]