Abstract
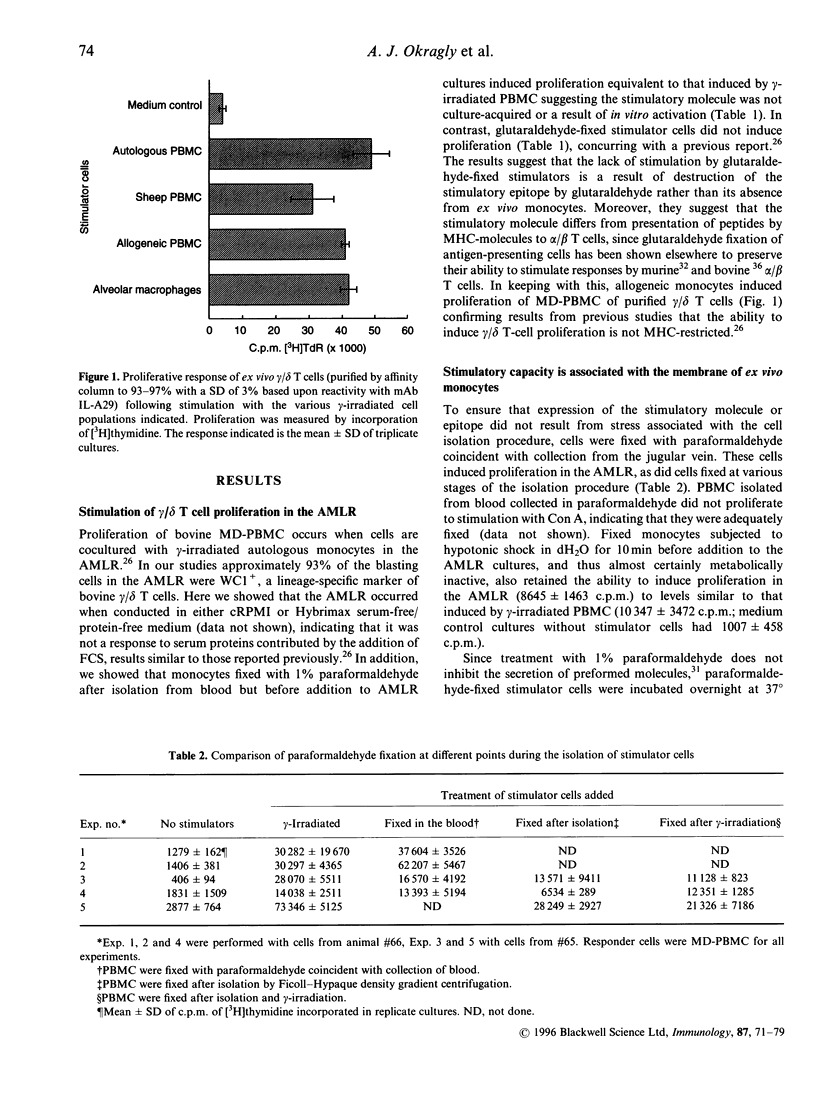
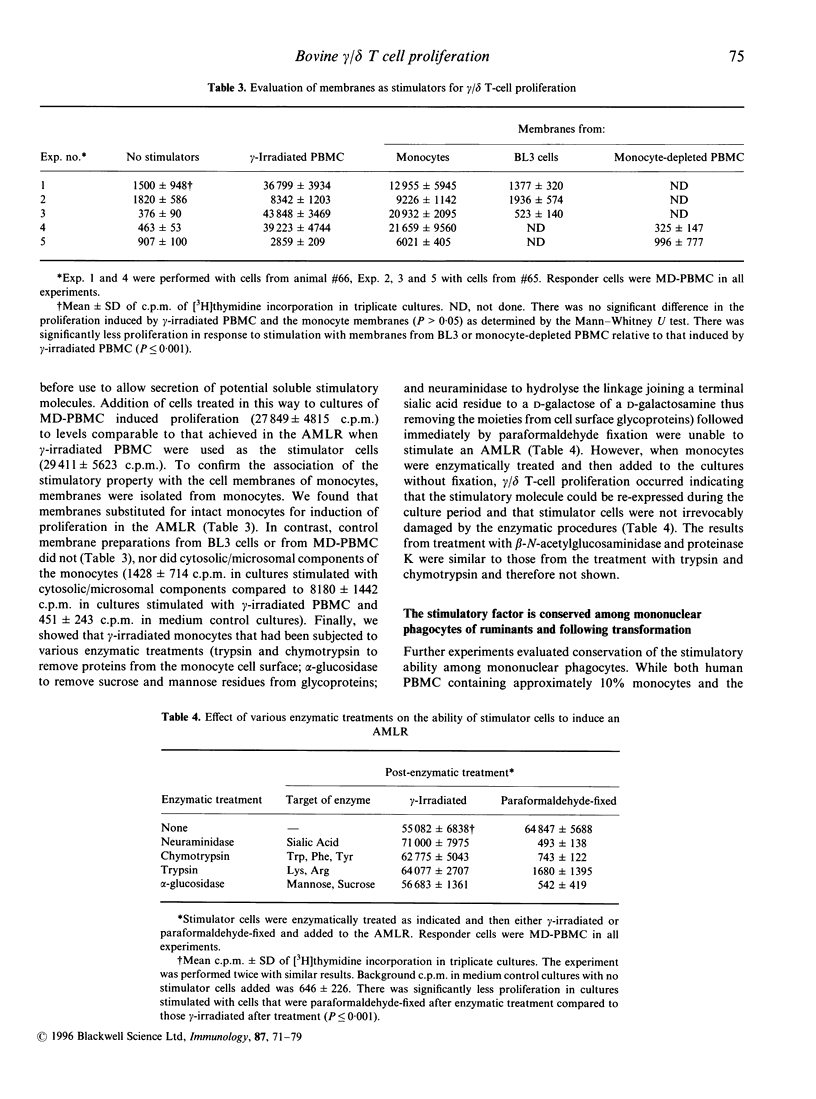
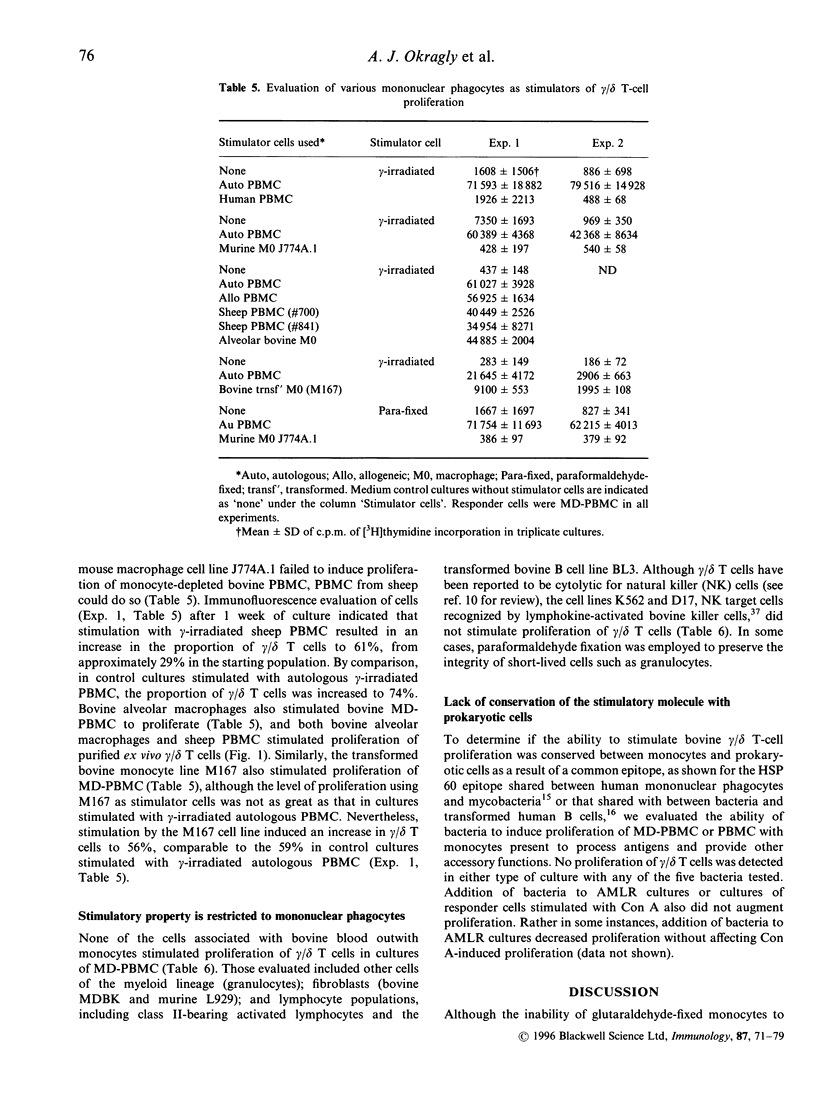
Bovine gamma/delta T cells have been shown previously to proliferate when cocultured with gamma-irradiated bovine monocytes in the 'autologous mixed leucocyte reaction' (AMLR). It was suggested that the response may be to culture-derived or culture-induced antigenic epitopes. Data presented here indicate that the gamma/delta T-cell stimulatory activity is attributable to a self-derived cell-surface molecule of mononuclear phagocytes that is constitutively expressed in vivo. The ability to induce an AMLR did not require in vitro culture or stress associated with in vitro isolation of cells or increased temperature since it could be induced by monocytes fixed by paraformaldehyde during blood collection from normal animals. Furthermore, stimulation by monocytes did not depend upon secreted molecules since fixed monocytes that had been incubated overnight at 37 degrees to allow secretion of preformed molecules, or subjected to hypotonic shock in H2O for 10 min before addition to the cultures, induced an AMLR as did plasma membranes prepared from ex vivo monocytes. In contrast, enzymatic treatment of monocytes to digest surface molecules followed by fixation destroyed their ability to stimulate an AMLR. The ability of monocytes to stimulate proliferation of gamma/delta T cells was distinguishable from their ability to stimulate alpha/beta T cells, since the former was destroyed by glutaraldehyde fixation whereas stimulation of alpha/beta T cells by major histocompatibility complex (MHC)-presented antigenic epitopes is not. Moreover, induction of proliferation of bovine gamma/delta T cells was not MHC-restricted. Finally, bovine alveolar macrophages, sheep monocytes and transformed bovine monocytes stimulated proliferation of bovine gamma/delta T cells whereas none of the following did so: human monocytes, murine macrophages, bovine myeloid cells other than mononuclear phagocytes, other nucleated cells found in bovine blood including activated MHC class II-bearing B cells, and a variety of species of bacteria. Thus, the stimulatory epitope is unique to and conserved among mononuclear phagocytes of ruminants. Demonstration of stimulation of bovine gamma/delta T cells by self-derived molecules is consistent with reports for murine gamma/delta T cells.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Balbi B., Moller D. R., Kirby M., Holroyd K. J., Crystal R. G. Increased numbers of T lymphocytes with gamma delta-positive antigen receptors in a subgroup of individuals with pulmonary sarcoidosis. J Clin Invest. 1990 May;85(5):1353–1361. doi: 10.1172/JCI114579. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baldwin C. L., Teale A. J., Naessens J. G., Goddeeris B. M., MacHugh N. D., Morrison W. I. Characterization of a subset of bovine T lymphocytes that express BoT4 by monoclonal antibodies and function: similarity to lymphocytes defined by human T4 and murine L3T4. J Immunol. 1986 Jun 15;136(12):4385–4391. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Behr C., Dubois P. Preferential expansion of V gamma 9 V delta 2 T cells following stimulation of peripheral blood lymphocytes with extracts of Plasmodium falciparum. Int Immunol. 1992 Mar;4(3):361–366. doi: 10.1093/intimm/4.3.361. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bender A., Kabelitz D. Preferential activation of peripheral blood V gamma 9+ gamma/delta T cells by group A, B and C but not group D or F streptococci. Clin Exp Immunol. 1992 Aug;89(2):301–304. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.1992.tb06949.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bertotto A., Gerli R., Spinozzi F., Muscat C., Scalise F., Castellucci G., Sposito M., Candio F., Vaccaro R. Lymphocytes bearing the gamma delta T cell receptor in acute Brucella melitensis infection. Eur J Immunol. 1993 May;23(5):1177–1180. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830230531. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Born W. K., Harshan K., Modlin R. L., O'Brien R. L. The role of gamma delta T lymphocytes in infection. Curr Opin Immunol. 1991 Aug;3(4):455–459. doi: 10.1016/0952-7915(91)90002-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brian A. A. Stimulation of B-cell proliferation by membrane-associated molecules from activated T cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jan;85(2):564–568. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.2.564. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clevers H., MacHugh N. D., Bensaid A., Dunlap S., Baldwin C. L., Kaushal A., Iams K., Howard C. J., Morrison W. I. Identification of a bovine surface antigen uniquely expressed on CD4-CD8- T cell receptor gamma/delta+ T lymphocytes. Eur J Immunol. 1990 Apr;20(4):809–817. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830200415. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis M. M., Chien Y. Issues concerning the nature of antigen recognition by alpha beta and gamma delta T-cell receptors. Immunol Today. 1995 Jul;16(7):316–318. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(95)80143-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellis J. A., Baldwin C. L., MacHugh N. D., Bensaid A., Teale A. J., Goddeeris B. M., Morrison W. I. Characterization by a monoclonal antibody and functional analysis of a subset of bovine T lymphocytes that express BoT8, a molecule analogous to human CD8. Immunology. 1986 Jul;58(3):351–358. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrick D. A., Gemmell-Hori L. Potential developmental role for self-reactive T cells bearing gamma-delta T cell receptors specific for heat-shock proteins. Chem Immunol. 1992;53:17–31. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finnegan A., Needleman B. W., Hodes R. J. Function of autoreactive T cells in immune responses. Immunol Rev. 1990 Aug;116:15–31. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1990.tb00802.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerli R., Agea E., Bertotto A., Tognellini R., Flenghi L., Spinozzi F., Velardi A., Grignani F. Analysis of T cells bearing different isotypic forms of the gamma/delta T cell receptor in patients with systemic autoimmune diseases. J Rheumatol. 1991 Oct;18(10):1504–1510. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goddeeris B. M., Baldwin C. L., ole-MoiYoi O., Morrison W. I. Improved methods for purification and depletion of monocytes from bovine peripheral blood mononuclear cells. Functional evaluation of monocytes in responses to lectins. J Immunol Methods. 1986 May 22;89(2):165–173. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(86)90354-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goddeeris B. M., Morrison W. I., Naessens J., Magondu J. G. The bovine autologous mixed leukocyte reaction: a proliferative response of non-T cells under the control of monocytes. Immunobiology. 1987 Dec;176(1-2):47–62. doi: 10.1016/S0171-2985(87)80099-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goddeeris B. M., Morrison W. I. The bovine autologous Theileria mixed leucocyte reaction: influence of monocytes and phenotype of the parasitized stimulator cell on proliferation and parasite specificity. Immunology. 1987 Jan;60(1):63–69. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haas W., Pereira P., Tonegawa S. Gamma/delta cells. Annu Rev Immunol. 1993;11:637–685. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.11.040193.003225. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haregewoin A., Soman G., Hom R. C., Finberg R. W. Human gamma delta+ T cells respond to mycobacterial heat-shock protein. Nature. 1989 Jul 27;340(6231):309–312. doi: 10.1038/340309a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Havran W. L., Chien Y. H., Allison J. P. Recognition of self antigens by skin-derived T cells with invariant gamma delta antigen receptors. Science. 1991 Jun 7;252(5011):1430–1432. doi: 10.1126/science.1828619. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hein W. R., Dudler L., Beya M. F., Marcuz A., Grossberger D. T cell receptor gene expression in sheep: differential usage of TcR1 in the periphery and thymus. Eur J Immunol. 1989 Dec;19(12):2297–2301. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830191218. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hohlfeld R., Engel A. G., Ii K., Harper M. C. Polymyositis mediated by T lymphocytes that express the gamma/delta receptor. N Engl J Med. 1991 Mar 28;324(13):877–881. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199103283241303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Häcker G., Kromer S., Falk M., Heeg K., Wagner H., Pfeffer K. V delta 1+ subset of human gamma delta T cells responds to ligands expressed by EBV-infected Burkitt lymphoma cells and transformed B lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1992 Dec 15;149(12):3984–3989. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaur I., Voss S. D., Gupta R. S., Schell K., Fisch P., Sondel P. M. Human peripheral gamma delta T cells recognize hsp60 molecules on Daudi Burkitt's lymphoma cells. J Immunol. 1993 Mar 1;150(5):2046–2055. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mackay C. R., Maddox J. F., Brandon M. R. Three distinct subpopulations of sheep T lymphocytes. Eur J Immunol. 1986 Jan;16(1):19–25. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830160105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller J. F. The discovery of the immunological function of the thymus. Immunol Today. 1991 Jan;12(1):42–45. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(91)90111-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munk M. E., Gatrill A. J., Kaufmann S. H. Target cell lysis and IL-2 secretion by gamma/delta T lymphocytes after activation with bacteria. J Immunol. 1990 Oct 15;145(8):2434–2439. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagler-Anderson C., McNair L. A., Cradock A. Self-reactive, T cell receptor-gamma delta+, lymphocytes from the intestinal epithelium of weanling mice. J Immunol. 1992 Oct 1;149(7):2315–2322. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfeffer K., Schoel B., Plesnila N., Lipford G. B., Kromer S., Deusch K., Wagner H. A lectin-binding, protease-resistant mycobacterial ligand specifically activates V gamma 9+ human gamma delta T cells. J Immunol. 1992 Jan 15;148(2):575–583. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porcelli S., Brenner M. B., Greenstein J. L., Balk S. P., Terhorst C., Bleicher P. A. Recognition of cluster of differentiation 1 antigens by human CD4-CD8-cytolytic T lymphocytes. Nature. 1989 Oct 5;341(6241):447–450. doi: 10.1038/341447a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raziuddin S., Telmasani A. W., el-Hag el-Awad M., al-Amari O., al-Janadi M. Gamma delta T cells and the immune response in visceral leishmaniasis. Eur J Immunol. 1992 May;22(5):1143–1148. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830220506. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts K., Yokoyama W. M., Kehn P. J., Shevach E. M. The vitronectin receptor serves as an accessory molecule for the activation of a subset of gamma/delta T cells. J Exp Med. 1991 Jan 1;173(1):231–240. doi: 10.1084/jem.173.1.231. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimonkevitz R., Kappler J., Marrack P., Grey H. Antigen recognition by H-2-restricted T cells. I. Cell-free antigen processing. J Exp Med. 1983 Aug 1;158(2):303–316. doi: 10.1084/jem.158.2.303. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sordillo L. M., Campos M., Babiuk L. A. Antibacterial activity of bovine mammary gland lymphocytes following treatment with interleukin-2. J Dairy Sci. 1991 Oct;74(10):3370–3375. doi: 10.3168/jds.S0022-0302(91)78526-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Speer C. A., Reduker D. W., Burgess D. E., Whitmire W. M., Splitter G. A. Lymphokine-induced inhibition of growth of Eimeria bovis and Eimeria papillata (Apicomplexa) in cultured bovine monocytes. Infect Immun. 1985 Nov;50(2):566–571. doi: 10.1128/iai.50.2.566-571.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strominger J. L. The gamma delta T cell receptor and class Ib MHC-related proteins: enigmatic molecules of immune recognition. Cell. 1989 Jun 16;57(6):895–898. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90326-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suttles J., Carruth L. M., Mizel S. B. Detection of IL-1 alpha and IL-1 beta in the supernatants of paraformaldehyde-treated human monocytes. Evidence against a membrane form of IL-1. J Immunol. 1990 Jan 1;144(1):170–174. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tonegawa S., Berns A., Bonneville M., Farr A., Ishida I., Ito K., Itohara S., Janeway C. A., Jr, Kanagawa O., Katsuki M. Diversity, development, ligands, and probable functions of gamma delta T cells. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1989;54(Pt 1):31–44. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1989.054.01.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wand-Württenberger A., Schoel B., Ivanyi J., Kaufmann S. H. Surface expression by mononuclear phagocytes of an epitope shared with mycobacterial heat shock protein 60. Eur J Immunol. 1991 Apr;21(4):1089–1092. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830210437. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams D. J., Newson J., Naessens J. Quantitation of bovine immunoglobulin isotypes and allotypes using monoclonal antibodies. Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 1990 Mar;24(3):267–283. doi: 10.1016/0165-2427(90)90042-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


