Abstract
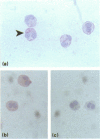
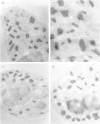
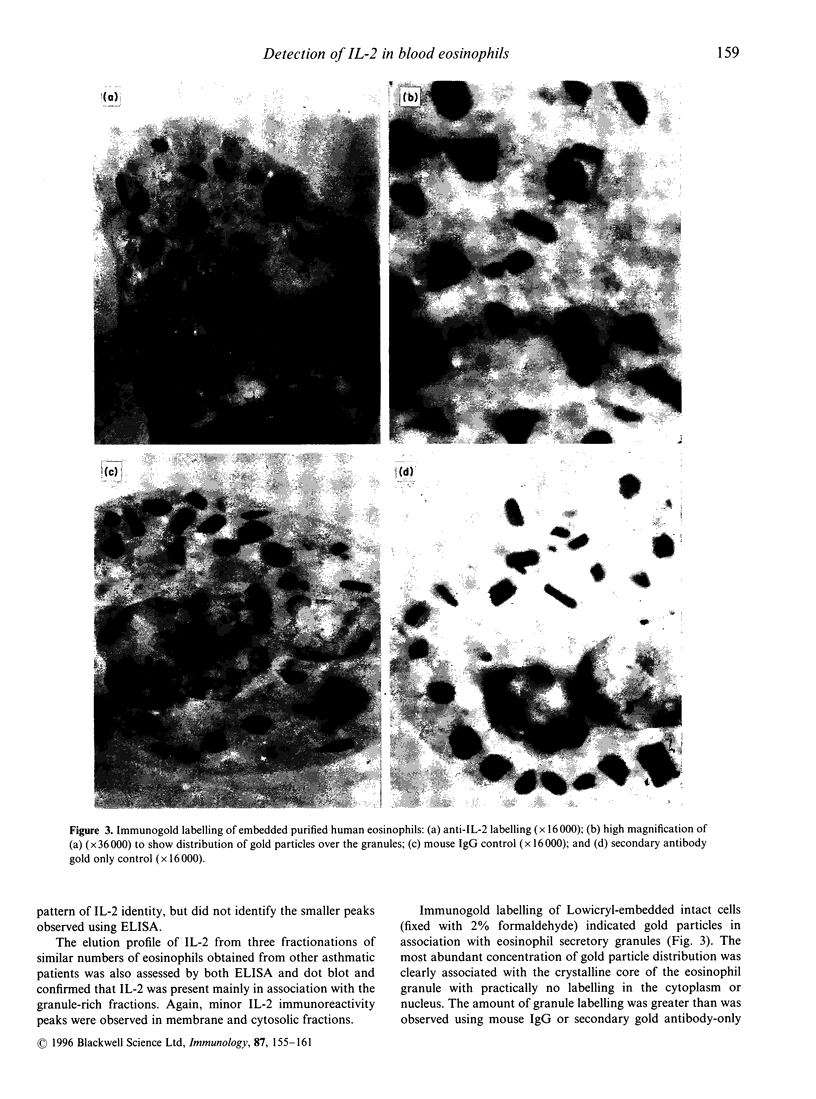
Interleukin-2 (IL-2) is an essential growth factor for T cells. Previous studies have shown that human peripheral eosinophils respond to IL-2 in chemotaxis and express the IL-2 receptor (CD25). In addition, eosinophils have been shown to transcribe messenger RNA for IL-2. The aim of the present study was to determine whether eosinophils translate mRNA for IL-2 and to determine the site of intracellular localization. By immunocytochemistry, an average of 9% of cells showed cytoplasmic staining for IL-2 in freshly isolated unstimulated blood eosinophils obtained from asthmatic subjects who were not receiving oral corticosteroid treatment (n = 5). Freshly isolated, disrupted, highly purified eosinophils (> 99%, by CD16- immunomagnetic selection) contained an average of 6 pg/10(6) cells of IL-2 measured by a specific enzyme linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) (n = 7). Purified eosinophil incubated with serum-coated Sephadex beads showed an increase in the amount of intracellularly-retained IL-2 (26.2 +/- 7.2 pg/10(6) cells) with some evidence for release of this cytokine but only in three out of six eosinophil preparations (range 1.3-5.8 pg/10(6) cells). The intracellular localization of IL-2 was determined by fractionation of the cells on a linear (0-45%) Nycodenz gradient in sucrose buffer followed by detection of IL-2 in the fractions using an IL-2-specific ELISA and dot blotting. The majority of the IL-2 detected co-eluted with known eosinophil granule markers (i.e. major basic protein (MBP), eosinophil cationic protein (ECP), eosinophil peroxidase (EPO) and beta-hexosaminidase) but small quantities were also detected in the cytosolic (lactate dehydrogenase-(LDH) associated) and membrane (CD9+) fractions. Immunogold labelling of intact eosinophils using an anti-IL-2 monoclonal antibody confirmed IL-2 immunoreactivity in association with the eosinophil crystalline granule cores. These data are consistent with the hypothesis that eosinophils synthesize, release and store IL-2 largely within cystalloid granules. This stored IL-2 may serve as a reservoir for rapid release of IL-2 in inflammatory reactions associated with eosinophilia.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beaufay H., Jacques P., Baudhuin P., Sellinger O. Z., Berthet J., De Duve C. Tissue fractionation studies. 18. Resolution of mitochondrial fractions from rat liver into three distinct populations of cytoplasmic particles by means of density equilibration in various gradients. Biochem J. 1964 Jul;92(1):184–205. doi: 10.1042/bj0920184. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beil W. J., Weller P. F., Tzizik D. M., Galli S. J., Dvorak A. M. Ultrastructural immunogold localization of tumor necrosis factor-alpha to the matrix compartment of eosinophil secondary granules in patients with idiopathic hypereosinophilic syndrome. J Histochem Cytochem. 1993 Nov;41(11):1611–1615. doi: 10.1177/41.11.8409368. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bossé M., Audette M., Ferland C., Pelletier G., Chu H. W., Dakhama A., Lavigne S., Boulet L. P., Laviolette M. Gene expression of interleukin-2 in purified human peripheral blood eosinophils. Immunology. 1996 Jan;87(1):149–154. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubucquoi S., Desreumaux P., Janin A., Klein O., Goldman M., Tavernier J., Capron A., Capron M. Interleukin 5 synthesis by eosinophils: association with granules and immunoglobulin-dependent secretion. J Exp Med. 1994 Feb 1;179(2):703–708. doi: 10.1084/jem.179.2.703. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galli S. J. New concepts about the mast cell. N Engl J Med. 1993 Jan 28;328(4):257–265. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199301283280408. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gomperts B. D., Tatham P. E. Regulated exocytotic secretion from permeabilized cells. Methods Enzymol. 1992;219:178–189. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(92)19020-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansel T. T., De Vries I. J., Iff T., Rihs S., Wandzilak M., Betz S., Blaser K., Walker C. An improved immunomagnetic procedure for the isolation of highly purified human blood eosinophils. J Immunol Methods. 1991 Dec 15;145(1-2):105–110. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(91)90315-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lotze M. T., Grimm E. A., Mazumder A., Strausser J. L., Rosenberg S. A. Lysis of fresh and cultured autologous tumor by human lymphocytes cultured in T-cell growth factor. Cancer Res. 1981 Nov;41(11 Pt 1):4420–4425. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moqbel R., Barkans J., Bradley B. L., Durham S. R., Kay A. B. Application of monoclonal antibodies against major basic protein (BMK-13) and eosinophil cationic protein (EG1 and EG2) for quantifying eosinophils in bronchial biopsies from atopic asthma. Clin Exp Allergy. 1992 Feb;22(2):265–273. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2222.1992.tb03082.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moqbel R., Levi-Schaffer F., Kay A. B. Cytokine generation by eosinophils. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1994 Dec;94(6 Pt 2):1183–1188. doi: 10.1016/0091-6749(94)90330-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosmann T. R., Coffman R. L. TH1 and TH2 cells: different patterns of lymphokine secretion lead to different functional properties. Annu Rev Immunol. 1989;7:145–173. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.07.040189.001045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plaut M., Pierce J. H., Watson C. J., Hanley-Hyde J., Nordan R. P., Paul W. E. Mast cell lines produce lymphokines in response to cross-linkage of Fc epsilon RI or to calcium ionophores. Nature. 1989 May 4;339(6219):64–67. doi: 10.1038/339064a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rand T. H., Silberstein D. S., Kornfeld H., Weller P. F. Human eosinophils express functional interleukin 2 receptors. J Clin Invest. 1991 Sep;88(3):825–832. doi: 10.1172/JCI115383. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waldmann T. A., Goldman C. K., Robb R. J., Depper J. M., Leonard W. J., Sharrow S. O., Bongiovanni K. F., Korsmeyer S. J., Greene W. C. Expression of interleukin 2 receptors on activated human B cells. J Exp Med. 1984 Nov 1;160(5):1450–1466. doi: 10.1084/jem.160.5.1450. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White S. R., Kulp G. V., Spaethe S. M., Van Alstyne E., Leff A. R. A kinetic assay for eosinophil peroxidase activity in eosinophils and eosinophil conditioned media. J Immunol Methods. 1991 Nov 22;144(2):257–263. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(91)90094-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]