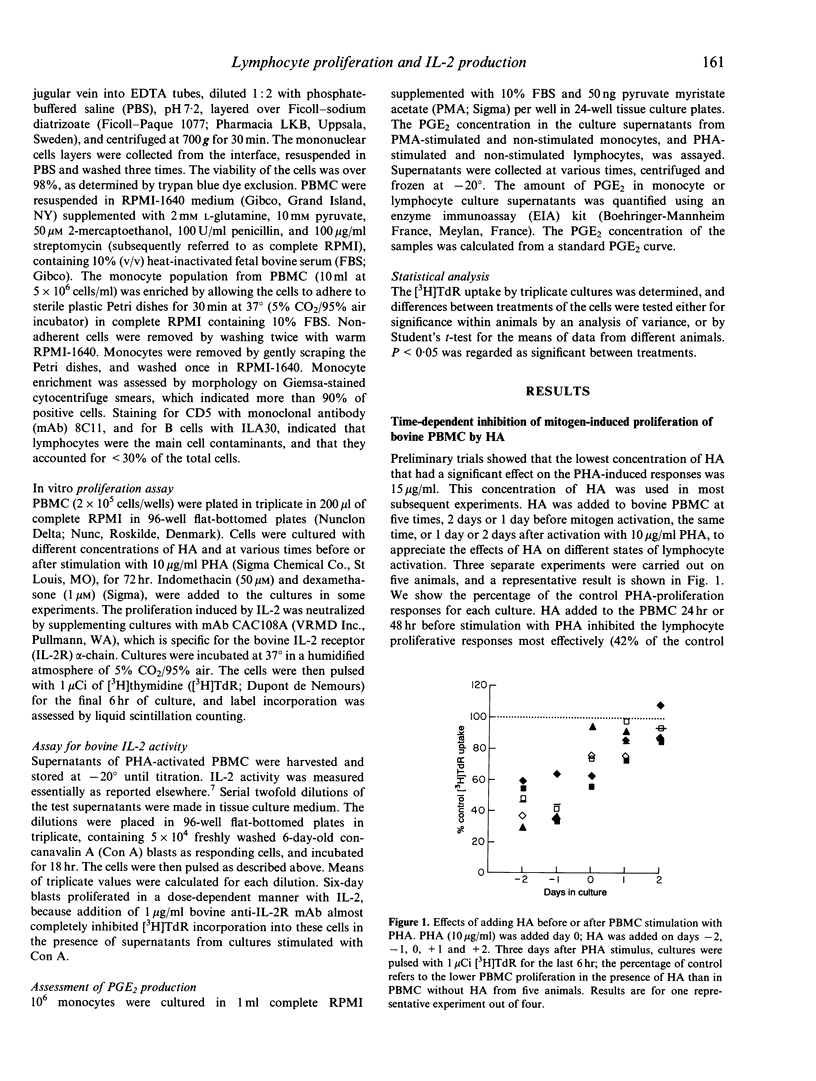
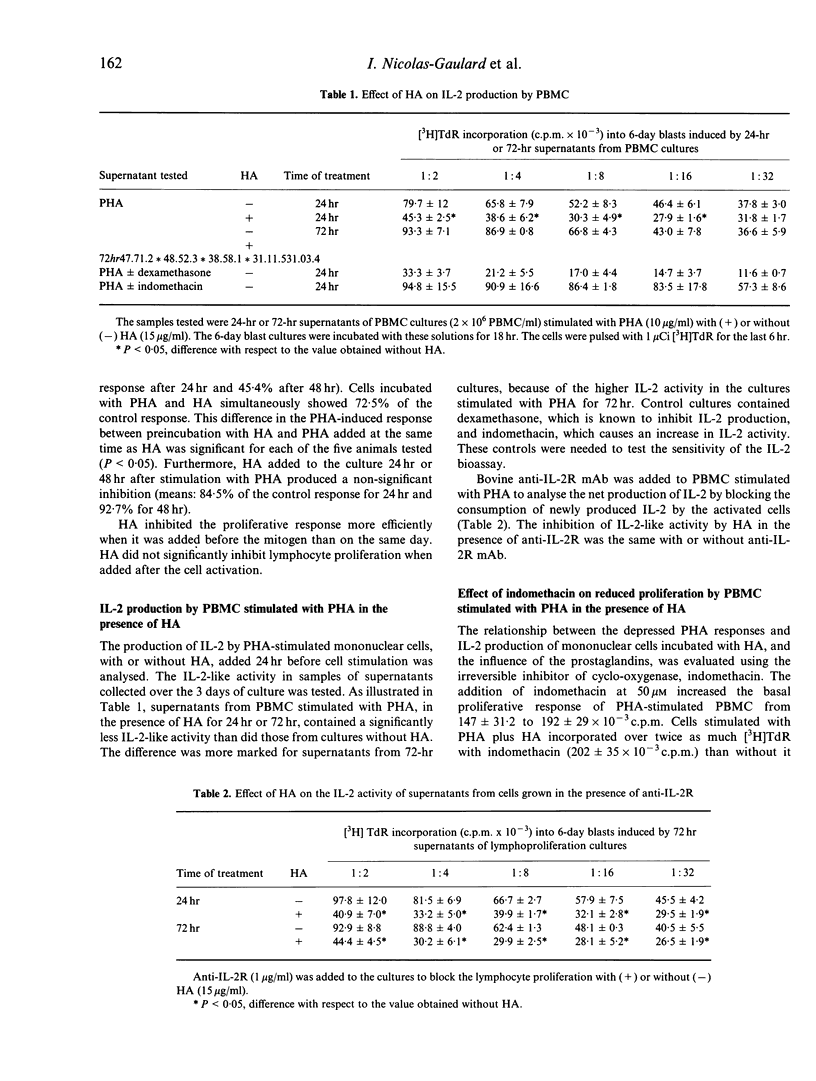
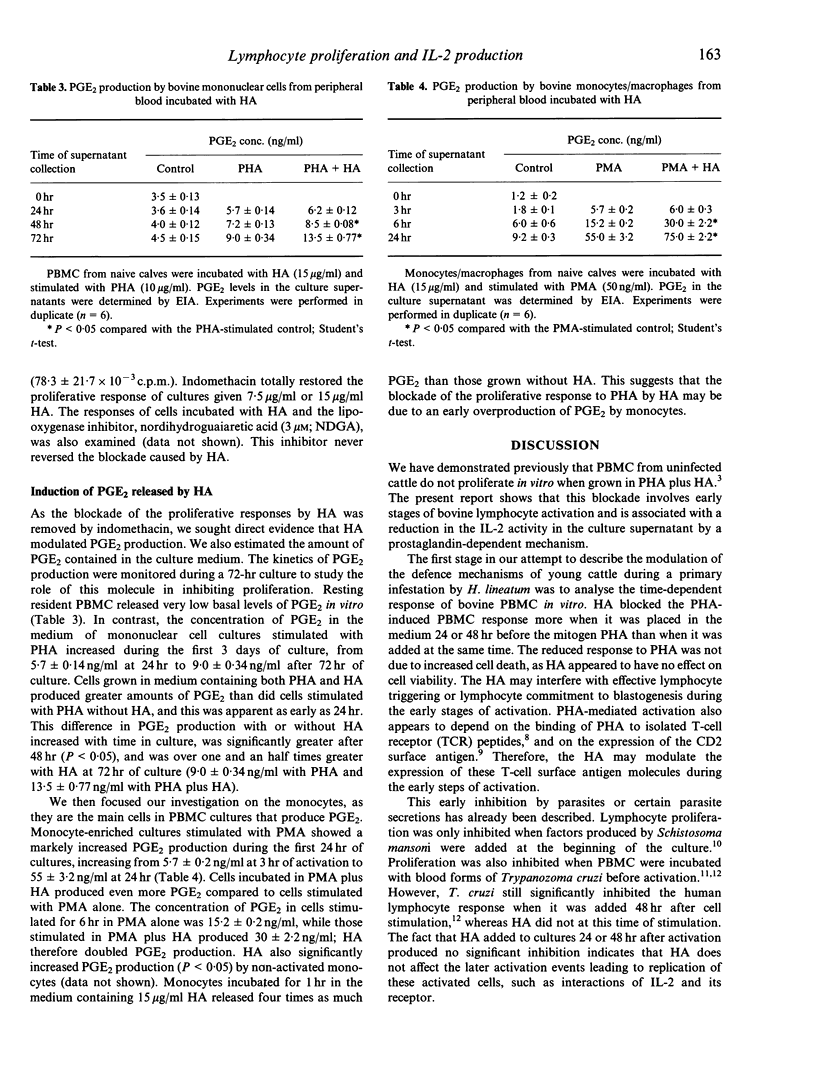
Abstract
The immune function of cattle infected with a primary infestation of Hypoderma lineatum is impaired during the first instar migration of the larvae. Hypodermin A (HA) is an enzyme secreted by the larvae that is implicated in immunosuppression. The response of bovine peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMC) to HA was examined in this study. HA blocked their proliferation in response to phytohaemagglutinin (PHA) and its effect was enhanced when cells were preincubated with HA before activation. This suggests that HA affects the lymphocyte commitment to blastogenesis during the early stages of their activation. HA also markly reduced the production of interleukin-2 (IL-2) in PHA-stimulated bovine PBMC cultures. Furthermore, indomethacin, which inhibits prostaglandin (PG) synthesis, blocked the immunosuppressive effect of HA on the PBMC proliferative response. The concentration of PGE2 in medium of PBMC or PMA-stimulated monocyte cultures was increased by incubation with HA. Thus, the HA appeared to act by reducing IL-2 production via a prostaglandin-dependent pathway.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baron R. W., Weintraub J. Lymphocyte responsiveness in cattle previously infested and uninfested with Hypoderma lineatum (de Vill.) and H. bovis (L.) (Diptera: Oestridae). Vet Parasitol. 1987 May;24(3-4):285–296. doi: 10.1016/0304-4017(87)90050-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beltz L. A., Kierszenbaum F. Suppression of human lymphocyte responses by Trypanosoma cruzi. Immunology. 1987 Feb;60(2):309–315. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonta I. L., Parnham M. J. Immunomodulatory-antiinflammatory functions of E-type prostaglandins. Minireview with emphasis on macrophage-mediated effects. Int J Immunopharmacol. 1982;4(2):103–109. doi: 10.1016/0192-0561(82)90057-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boulard C., Bencharif F. Changes in the haemolytic activity of bovine serum complement by Hypoderma lineatum (insect oestridae) larval proteinases in naive and immune cattle. Parasite Immunol. 1984 Sep;6(5):459–467. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3024.1984.tb00816.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boulard C. Degradation of bovine C3 by serine proteases from parasites Hypoderma lineatum (Diptera, Oestridae). Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 1989 Mar;20(4):387–398. doi: 10.1016/0165-2427(89)90083-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown W. C., Grab D. J. Biological and biochemical characterization of bovine interleukin 2. Studies with cloned bovine T cells. J Immunol. 1985 Nov;135(5):3184–3190. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chabaudie N., Boulard C. Effect of hypodermin A, an enzyme secreted by Hypoderma lineatum (Insect Oestridae), on the bovine immune system. Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 1992 Feb 15;31(1-2):167–177. doi: 10.1016/0165-2427(92)90094-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chouaib S., Chatenoud L., Klatzmann D., Fradelizi D. The mechanisms of inhibition of human IL 2 production. II. PGE2 induction of suppressor T lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1984 Apr;132(4):1851–1857. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dessaint J. P., Camus D., Fischer E., Capron A. Inhibition of lymphocyte proliferation by factor(s) produced by Schistosoma mansoni. Eur J Immunol. 1977 Sep;7(9):624–629. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830070909. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farrell J. P., Kirkpatrick C. E. Experimental cutaneous leishmaniasis. II. A possible role for prostaglandins in exacerbation of disease in Leishmania major-infected BALB/c mice. J Immunol. 1987 Feb 1;138(3):902–907. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher W. F., Pruett J. H., Howard V. M., Scholl P. J. Antigen-specific lymphocyte proliferative responses in vaccinated and Hypoderma lineatum-infested calves. Vet Parasitol. 1991 Oct;40(1-2):135–145. doi: 10.1016/0304-4017(91)90090-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodwin J. S., Ceuppens J. Regulation of the immune response by prostaglandins. J Clin Immunol. 1983 Oct;3(4):295–315. doi: 10.1007/BF00915791. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanellopoulos J. M., De Petris S., Leca G., Crumpton M. J. The mitogenic lectin from Phaseolus vulgaris does not recognize the T3 antigen of human T lymphocytes. Eur J Immunol. 1985 May;15(5):479–486. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830150512. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lecroisey A., Boulard C., Keil B. Chemical and enzymatic characterization of the collagenase from the insect Hypoderma lineatum. Eur J Biochem. 1979 Nov;101(2):385–393. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1979.tb19730.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maleckar J. R., Kierszenbaum F. Inhibition of mitogen-induced proliferation of mouse T and B lymphocytes by bloodstream forms of Trypanosoma cruzi. J Immunol. 1983 Feb;130(2):908–911. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller W., Vandenabeele P. A T cell clone which responds to interleukin 2 but not to interleukin 4. Eur J Immunol. 1987 Apr;17(4):579–580. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830170424. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Flynn K., Krensky A. M., Beverley P. C., Burakoff S. J., Linch D. C. Phytohaemagglutinin activation of T cells through the sheep red blood cell receptor. Nature. 1985 Feb 21;313(6004):686–687. doi: 10.1038/313686a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reiner N. E., Malemud C. J. Arachidonic acid metabolism by murine peritoneal macrophages infected with Leishmania donovani: in vitro evidence for parasite-induced alterations in cyclooxygenase and lipoxygenase pathways. J Immunol. 1985 Jan;134(1):556–563. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sileghem M., Flynn J. N. Suppression of interleukin 2 secretion and interleukin 2 receptor expression during tsetse-transmitted trypanosomiasis in cattle. Eur J Immunol. 1992 Mar;22(3):767–773. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830220321. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tarleton R. L. Trypanosoma cruzi-induced suppression of IL-2 production. II. Evidence for a role for suppressor cells. J Immunol. 1988 Apr 15;140(8):2769–2773. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tilden A. B., Balch C. M. A comparison of PGE2 effects on human suppressor cell function and on interleukin 2 function. J Immunol. 1982 Dec;129(6):2469–2473. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wakasugi N., Virelizier J. L., Arenzana-Seisdedos F., Rothhut B., Huerta J. M., Russo-Marie F., Fiers W. Defective IFN-gamma production in the human neonate. II. Role of increased sensitivity to the suppressive effects of prostaglandin E. J Immunol. 1985 Jan;134(1):172–176. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker C., Kristensen F., Bettens F., deWeck A. L. Lymphokine regulation of activated (G1) lymphocytes. I. Prostaglandin E2-induced inhibition of interleukin 2 production. J Immunol. 1983 Apr;130(4):1770–1773. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


