Abstract
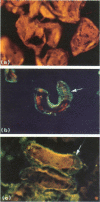
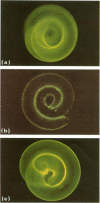
Rat pups suckling dams parasitized by Trichinella spiralis express rapid expulsion, a protective response that is associated with the entrapment of infectious muscle larvae in intestinal mucus. Immunofluorescent studies revealed that antibodies were bound to the surfaces of the entrapped larvae. Mucus binding and rapid expulsion occurred in normal pups dosed with larvae coated with antibodies prepared from infected rat serum. Subsequent experiments revealed that entrapped larvae escaped from mucus after 2 hr in vitro incubation in saline. Escape correlated with the loss of the surface-bound antibodies, suggesting that mucus entrapment was reversible and dependent on antibody coating. Finally, when protective antibodies were injected 1, 2 or 6 hr after larvae were administered to pups, the parasites were forced to leave their epithelial niche and became enveloped in mucus. The above findings suggest that mucus trapping of T. spiralis larvae is dependent upon the coating of larvae by antibody, but that trapping is reversible, and is not in itself the pivotal event in rapid expulsion. The primary mechanism of rapid expulsion appears to be antibody-mediated inhibition of processes required for the parasite to maintain itself in the epithelium.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aitken R. J., Parslow J. M., Hargreave T. B., Hendry W. F. Influence of antisperm antibodies on human sperm function. Br J Urol. 1988 Oct;62(4):367–373. doi: 10.1111/j.1464-410x.1988.tb04367.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allen A., Bell A., Mantle M., Pearson J. P. The structure and physiology of gastrointestinal mucus. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1982;144:115–133. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4615-9254-9_15. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Appleton J. A., McGregor D. D. Characterization of the immune mediator of rapid expulsion of Trichinella spiralis in suckling rats. Immunology. 1987 Nov;62(3):477–484. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Appleton J. A., McGregor D. D. Life-phase specific induction and expression of rapid expulsion in rats suckling Trichinella spiralis-infected dams. Immunology. 1985 Jun;55(2):225–232. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Appleton J. A., Schain L. R., McGregor D. D. Rapid expulsion of Trichinella spiralis in suckling rats: mediation by monoclonal antibodies. Immunology. 1988 Nov;65(3):487–492. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bazin H., Cormont F., De Clercq L. Rat monoclonal antibodies. II. A rapid and efficient method of purification from ascitic fluid or serum. J Immunol Methods. 1984 Jun 8;71(1):9–16. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(84)90200-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bell R. G., Adams L. S., Ogden R. W. Intestinal mucus trapping in the rapid expulsion of Trichinella spiralis by rats: induction and expression analyzed by quantitative worm recovery. Infect Immun. 1984 Jul;45(1):267–272. doi: 10.1128/iai.45.1.267-272.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FLOREY H. W. The secretion and function of intestinal mucus. Gastroenterology. 1962 Sep;43:326–329. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jager S., Kremer J., Kuiken J., van Slochteren-Draaisma T., Mulder I., de Wilde-Janssen I. W. Induction of the shaking phenomenon by pretreatment of spermatozoa with sera containing antispermatozoal antibodies. Fertil Steril. 1981 Dec;36(6):784–791. doi: 10.1016/s0015-0282(16)45926-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson G. D., Davidson R. S., McNamee K. C., Russell G., Goodwin D., Holborow E. J. Fading of immunofluorescence during microscopy: a study of the phenomenon and its remedy. J Immunol Methods. 1982 Dec 17;55(2):231–242. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(82)90035-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim C. W., Ledbetter M. C. Surface morphology of Trichinella spiralis by scanning electron microscopy. J Parasitol. 1980 Feb;66(1):75–81. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mackenzie N. M., Morris B., Morris R. The binding of proteins to isolated enterocytes from the small intestine of the neonatal rat. Immunology. 1983 Mar;48(3):489–496. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller H. R., Huntley J. F. Protection against nematodes by intestinal mucus. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1982;144:243–245. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4615-9254-9_37. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller H. R., Huntley J. F., Wallace G. R. Immune exclusion and mucus trapping during the rapid expulsion of Nippostrongylus brasiliensis from primed rats. Immunology. 1981 Oct;44(2):419–429. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pang K. Y., Walker W. A., Bloch K. J. Intestinal uptake of macromolecules. Differences in distribution and degradation of protein antigen in control and immunised rats. Gut. 1981 Dec;22(12):1018–1024. doi: 10.1136/gut.22.12.1018. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parkhouse R. M., Clark N. W. Stage specific secreted and somatic antigens of Trichinella spiralis. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1983 Dec;9(4):319–327. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(83)90088-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parkhouse R. M., Ortega-Pierres G. Stage-specific antigens of Trichinella spiralis. Parasitology. 1984 Aug;88(Pt 4):623–630. doi: 10.1017/s003118200008553x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Philipp M., Parkhouse R. M., Ogilvie B. M. Changing proteins on the surface of a parasitic nematode. Nature. 1980 Oct 9;287(5782):538–540. doi: 10.1038/287538a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Price R. J., Boettcher B. The presence of complement in human cervical mucus and its possible relevance to infertility in women with complement-dependent sperm-immobilizing antibodies. Fertil Steril. 1979 Jul;32(1):61–66. doi: 10.1016/s0015-0282(16)44117-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]