Abstract
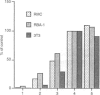
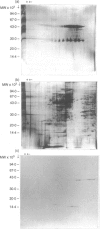
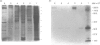
Affinity-purified polyclonal anti-double-stranded DNA (anti-dsDNA) antibodies from patients with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) exert a cytostatic effect on cultured rat glomerular mesangial cells (MC). The cognate antigens expressed on the surface of MC have been proved to be acidic ribosomal phosphoproteins (P proteins) in our previous study. The mesangial cytostatic effect of anti-dsDNA antibodies is attributed to the cross-reactivity of the antibodies with membrane-expressed P proteins, but not to the effect of minute amounts of anti-ribosomal P proteins antibodies contained in the anti-dsDNA preparations. Immunofluorescence staining of the native cells demonstrated that anti-dsDNA antibodies bound to the surface of rat mesangial cells, rat brain astrocytes (RBA-1) and mouse fibroblasts (3T3). Anti-dsDNA antibodies also exert potent cytostatic effects on these cells in a dose-dependent manner. In addition, the plasma membranes of different cell lines and tissues from normal and autoimmune mice were isolated and probed by anti-dsDNA antibodies in Western blot analysis. We found the actively proliferating cells such as MC, RBA-1 and 3T3 may express both P0 (38,000 MW) and P1 (19,000 MW) on the surface membrane. In addition, the kidney, liver and spleen from either autoimmune MRL-lpr/lpr or BALB/c mice may constantly express P0 protein, but the expression of P1 is inconsistent. In contrast, brain and muscle from either mice failed to express P proteins on their surface. Unexpectedly, a high molecular weight substance (larger than 205,000 MW) with unknown nature appears in the membrane of brain and muscle tissues in both mice. Immunoprecipitation of the surface-biotinylated MC-lysate by anti-dsDNA antibodies further confirmed that P1 (19,000 MW) and P2 (17,000 MW) are really expressed on the cell surface. These results suggest that P proteins expressed on the surface of different tissues become the targets for anti-dsDNA antibodies mediating pleomorphic tissue damage in patients with SLE.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- André-Schwartz J., Datta S. K., Shoenfeld Y., Isenberg D. A., Stollar B. D., Schwartz R. S. Binding of cytoskeletal proteins by monoclonal anti-DNA lupus autoantibodies. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1984 May;31(2):261–271. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(84)90246-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Avruch J., Wallach D. F. Preparation and properties of plasma membrane and endoplasmic reticulum fragments from isolated rat fat cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Apr 13;233(2):334–347. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(71)90331-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett R. M., Kotzin B. L., Merritt M. J. DNA receptor dysfunction in systemic lupus erythematosus and kindred disorders. Induction by anti-DNA antibodies, antihistone antibodies, and antireceptor antibodies. J Exp Med. 1987 Oct 1;166(4):850–863. doi: 10.1084/jem.166.4.850. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casciola-Rosen L. A., Anhalt G., Rosen A. Autoantigens targeted in systemic lupus erythematosus are clustered in two populations of surface structures on apoptotic keratinocytes. J Exp Med. 1994 Apr 1;179(4):1317–1330. doi: 10.1084/jem.179.4.1317. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elkon K. B. Apoptosis in SLE--too little or too much? Clin Exp Rheumatol. 1994 Sep-Oct;12(5):553–559. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elkon K. B., Parnassa A. P., Foster C. L. Lupus autoantibodies target ribosomal P proteins. J Exp Med. 1985 Aug 1;162(2):459–471. doi: 10.1084/jem.162.2.459. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emlen W., Niebur J., Kadera R. Accelerated in vitro apoptosis of lymphocytes from patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. J Immunol. 1994 Apr 1;152(7):3685–3692. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faaber P., Capel P. J., Rijke G. P., Vierwinden G., van de Putte L. B., Koene R. A. Cross-reactivity of anti-DNA antibodies with proteoglycans. Clin Exp Immunol. 1984 Mar;55(3):502–508. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faaber P., Rijke T. P., van de Putte L. B., Capel P. J., Berden J. H. Cross-reactivity of human and murine anti-DNA antibodies with heparan sulfate. The major glycosaminoglycan in glomerular basement membranes. J Clin Invest. 1986 Jun;77(6):1824–1830. doi: 10.1172/JCI112508. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Floege J., Alpers C. E., Sage E. H., Pritzl P., Gordon K., Johnson R. J., Couser W. G. Markers of complement-dependent and complement-independent glomerular visceral epithelial cell injury in vivo. Expression of antiadhesive proteins and cytoskeletal changes. Lab Invest. 1992 Oct;67(4):486–497. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Francoeur A. M., Peebles C. L., Heckman K. J., Lee J. C., Tan E. M. Identification of ribosomal protein autoantigens. J Immunol. 1985 Oct;135(4):2378–2384. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilliam A. C., Lang D., LoSpalluto J. J. Antibodies to double-stranded DNA: purification and characterization of binding specificities. J Immunol. 1980 Aug;125(2):874–885. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Golan T. D., Elkon K. B., Gharavi A. E., Krueger J. G. Enhanced membrane binding of autoantibodies to cultured keratinocytes of systemic lupus erythematosus patients after ultraviolet B/ultraviolet A irradiation. J Clin Invest. 1992 Sep;90(3):1067–1076. doi: 10.1172/JCI115922. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hines J. J., Weissbach H., Brot N., Elkon K. Anti-P autoantibody production requires P1/P2 as immunogens but is not driven by exogenous self-antigen in MRL mice. J Immunol. 1991 May 15;146(10):3386–3395. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holers V. M., Kotzin B. L. Human peripheral blood monocytes display surface antigens recognized by monoclonal antinuclear antibodies. J Clin Invest. 1985 Sep;76(3):991–998. doi: 10.1172/JCI112100. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hulsey M., Goldstein R., Scully L., Surbeck W., Reichlin M. Anti-ribosomal P antibodies in systemic lupus erythematosus: a case-control study correlating hepatic and renal disease. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1995 Mar;74(3):252–256. doi: 10.1006/clin.1995.1037. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hurez V., Dietrich G., Kaveri S. V., Kazatchkine M. D. Polyreactivity is a property of natural and disease-associated human autoantibodies. Scand J Immunol. 1993 Aug;38(2):190–196. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1993.tb01712.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacob L., Lety M. A., Louvard D., Bach J. F. Binding of a monoclonal anti-DNA autoantibody to identical protein(s) present at the surface of several human cell types involved in lupus pathogenesis. J Clin Invest. 1985 Jan;75(1):315–317. doi: 10.1172/JCI111692. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacob L., Tron F., Bach J. F., Louvard D. A monoclonal anti-DNA antibody also binds to cell-surface protein(s). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jun;81(12):3843–3845. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.12.3843. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jou T. C., Jou M. J., Chen J. Y., Lee S. Y. [Properties of rat brain astrocytes in long-term culture]. Taiwan Yi Xue Hui Za Zhi. 1985 Aug;84(8):865–881. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koffler D., Schur P. H., Kunkel H. G. Immunological studies concerning the nephritis of systemic lupus erythematosus. J Exp Med. 1967 Oct 1;126(4):607–624. doi: 10.1084/jem.126.4.607. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koren E., Reichlin M. W., Koscec M., Fugate R. D., Reichlin M. Autoantibodies to the ribosomal P proteins react with a plasma membrane-related target on human cells. J Clin Invest. 1992 Apr;89(4):1236–1241. doi: 10.1172/JCI115707. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lafer E. M., Rauch J., Andrzejewski C., Jr, Mudd D., Furie B., Furie B., Schwartz R. S., Stollar B. D. Polyspecific monoclonal lupus autoantibodies reactive with both polynucleotides and phospholipids. J Exp Med. 1981 Apr 1;153(4):897–909. doi: 10.1084/jem.153.4.897. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lambert P. H., Dixon F. J. Pathogenesis of the glomerulonephritis of NZB/W mice. J Exp Med. 1968 Mar 1;127(3):507–522. doi: 10.1084/jem.127.3.507. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LeFeber W. P., Norris D. A., Ryan S. R., Huff J. C., Lee L. A., Kubo M., Boyce S. T., Kotzin B. L., Weston W. L. Ultraviolet light induces binding of antibodies to selected nuclear antigens on cultured human keratinocytes. J Clin Invest. 1984 Oct;74(4):1545–1551. doi: 10.1172/JCI111569. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levinsky R. J., Cameron J. S., Soothill J. F. Serum immune complexes and disease activity in lupus nephritis. Lancet. 1977 Mar 12;1(8011):564–567. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(77)91998-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madaio M. P., Carlson J., Cataldo J., Ucci A., Migliorini P., Pankewycz O. Murine monoclonal anti-DNA antibodies bind directly to glomerular antigens and form immune deposits. J Immunol. 1987 May 1;138(9):2883–2889. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meier T., Arni S., Malarkannan S., Poincelet M., Hoessli D. Immunodetection of biotinylated lymphocyte-surface proteins by enhanced chemiluminescence: a nonradioactive method for cell-surface protein analysis. Anal Biochem. 1992 Jul;204(1):220–226. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(92)90165-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nojima Y., Minota S., Yamada A., Takaku F., Aotsuka S., Yokohari R. Correlation of antibodies to ribosomal P protein with psychosis in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Ann Rheum Dis. 1992 Sep;51(9):1053–1055. doi: 10.1136/ard.51.9.1053. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Farrell P. H. High resolution two-dimensional electrophoresis of proteins. J Biol Chem. 1975 May 25;250(10):4007–4021. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prabhakar B. S., Allaway G. P., Srinivasappa J., Notkins A. L. Cell surface expression of the 70-kD component of Ku, a DNA-binding nuclear autoantigen. J Clin Invest. 1990 Oct;86(4):1301–1305. doi: 10.1172/JCI114838. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raz E., Ben-Bassat H., Davidi T., Shlomai Z., Eilat D. Cross-reactions of anti-DNA autoantibodies with cell surface proteins. Eur J Immunol. 1993 Feb;23(2):383–390. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830230213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raz E., Brezis M., Rosenmann E., Eilat D. Anti-DNA antibodies bind directly to renal antigens and induce kidney dysfunction in the isolated perfused rat kidney. J Immunol. 1989 May 1;142(9):3076–3082. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneebaum A. B., Singleton J. D., West S. G., Blodgett J. K., Allen L. G., Cheronis J. C., Kotzin B. L. Association of psychiatric manifestations with antibodies to ribosomal P proteins in systemic lupus erythematosus. Am J Med. 1991 Jan;90(1):54–62. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(91)90506-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Striker G. E., Striker L. J. Glomerular cell culture. Lab Invest. 1985 Aug;53(2):122–131. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sun K. H., Liu W. T., Tsai C. Y., Tang S. J., Han S. H., Yu C. L. Anti-dsDNA antibodies cross-react with ribosomal P proteins expressed on the surface of glomerular mesangial cells to exert a cytostatic effect. Immunology. 1995 Jun;85(2):262–269. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tan E. M. Autoimmunity and apoptosis. J Exp Med. 1994 Apr 1;179(4):1083–1086. doi: 10.1084/jem.179.4.1083. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teh L. S., Isenberg D. A. Antiribosomal P protein antibodies in systemic lupus erythematosus. A reappraisal. Arthritis Rheum. 1994 Mar;37(3):307–315. doi: 10.1002/art.1780370303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai C. Y., Wu T. H., Sun K. H., Liao T. S., Lin W. M., Yu C. L. Polyclonal IgG anti-dsDNA antibodies exert cytotoxic effect on cultured rat mesangial cells by binding to cell membrane and augmenting apoptosis. Scand J Rheumatol. 1993;22(4):162–171. doi: 10.3109/03009749309099265. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai C. Y., Wu T. H., Sun K. H., Yu C. L. Effect of antibodies to double stranded DNA, purified from serum samples of patients with active systemic lupus erythematosus, on the glomerular mesangial cells. Ann Rheum Dis. 1992 Feb;51(2):162–167. doi: 10.1136/ard.51.2.162. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu C. L., Chang K. L., Chiu C. C., Chiang B. N., Han S. H., Wang S. R. Alteration of mitogenic responses of mononuclear cells by anti-ds DNA antibodies resembling immune disorders in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Scand J Rheumatol. 1989;18(5):265–276. doi: 10.3109/03009748909095029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zack D. J., Yamamoto K., Wong A. L., Stempniak M., French C., Weisbart R. H. DNA mimics a self-protein that may be a target for some anti-DNA antibodies in systemic lupus erythematosus. J Immunol. 1995 Feb 15;154(4):1987–1994. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Agthoven A., Kriek J., Amons R., Möller W. Isolation and characterization of the acidic phosphoproteins of 60-S ribosomes from Artemia salina and rat liver. Eur J Biochem. 1978 Nov 15;91(2):553–565. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1978.tb12709.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]