Abstract
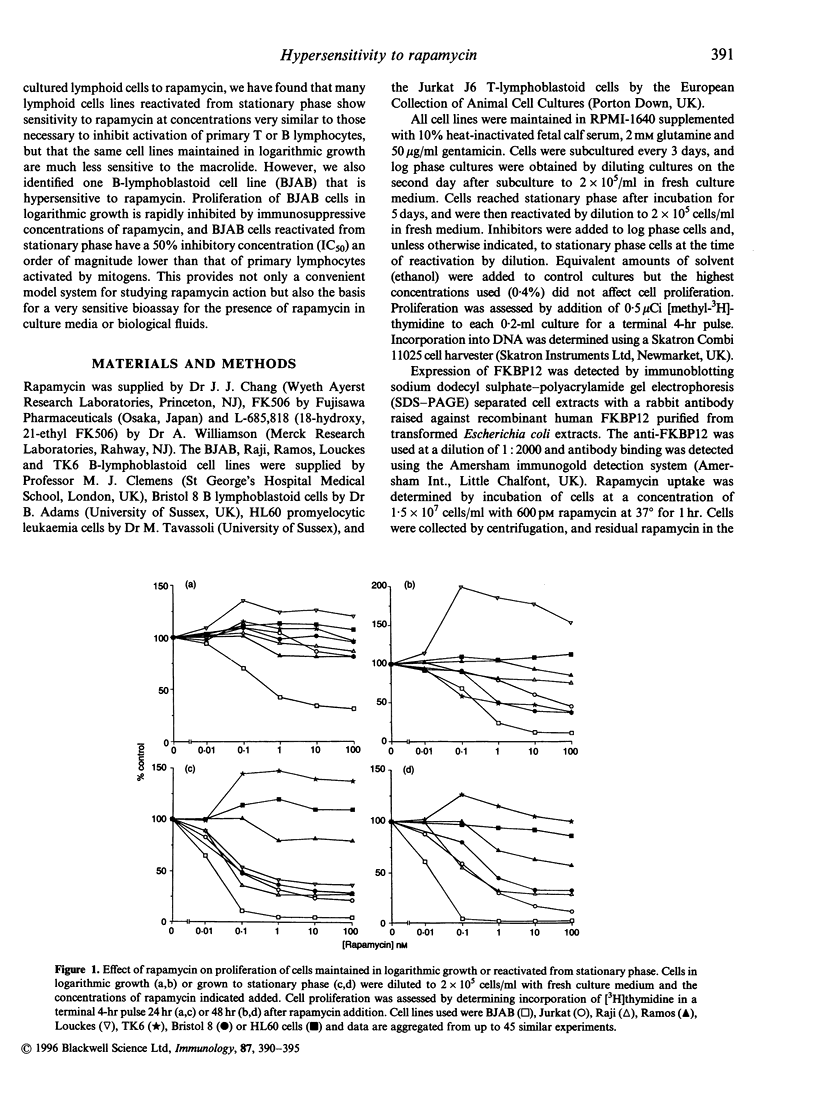
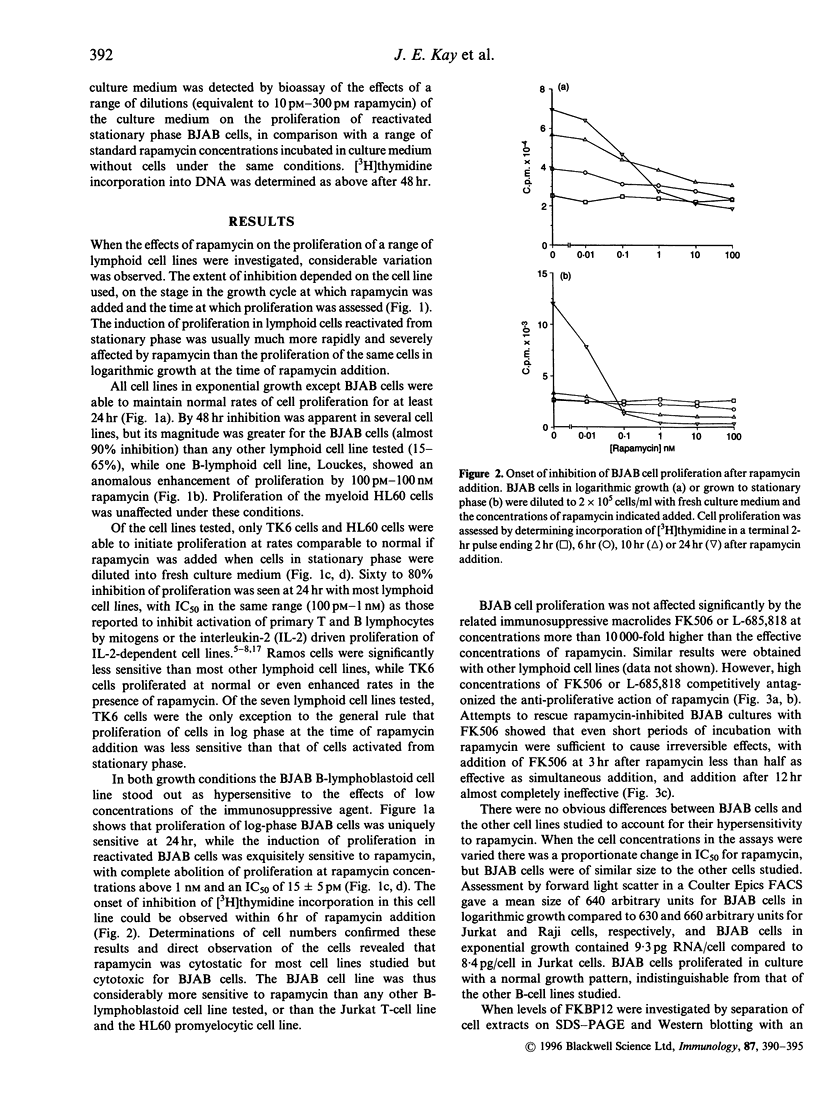
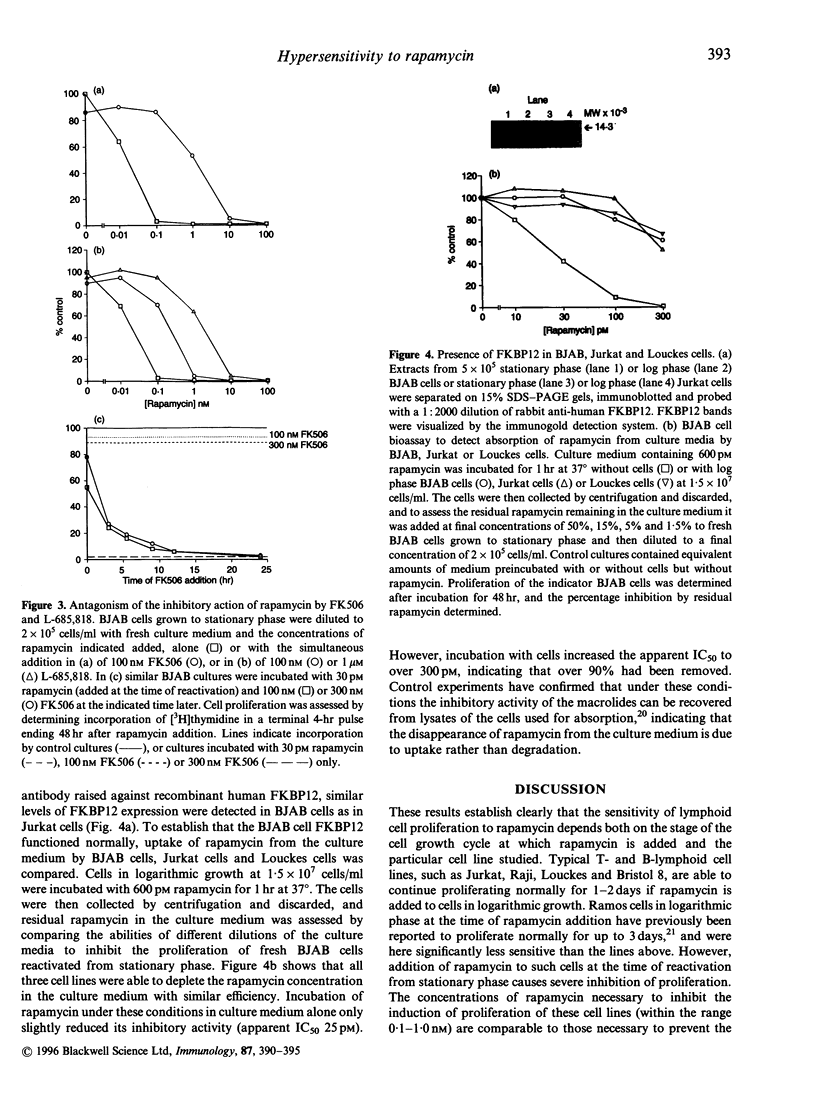
Proliferation of the BJAB B-lymphoblastoid cell line was rapidly and almost completely suppressed by picomolar concentrations of the immunosuppressive macrolide rapamycin (50% inhibitory concentration 10-20 pM for cells reactivated from stationary phase). This cell line was considerably more sensitive to rapamycin than any other B-lymphoblastoid cell line tested, the Jurkat T-cell line or the HL60 promyelocytic cell line. BJAB cell proliferation was not affected by the related immunosuppressive macrolides FK506 or L-685,818, which bind to the immunophilin FKBP12 competitively with rapamycin and also inhibit its peptidylprolyl cis-trans isomerase activity. Excess FK506 or L-685,818 added simultaneously competitively antagonized rapamycin's anti-proliferative action. Levels of FKBP12 and uptake of rapamycin from the culture medium were also normal in BJAB cells. The hypersensitivity to rapamycin of BJAB cells thus reflects an unusual dependence on the intracellular signalling system targeted by the rapamycin-FKBP12 complex, and may provide a model system for elucidating the role played by this pathway in lymphocyte activation. The proliferation of BJAB cells reactivated from stationary phase can also be used as the basis for a highly sensitive bioassay for the presence of rapamycin in culture media or other biological fluids.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akselband Y., Harding M. W., Nelson P. A. Rapamycin inhibits spontaneous and fibroblast growth factor beta-stimulated proliferation of endothelial cells and fibroblasts. Transplant Proc. 1991 Dec;23(6):2833–2836. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Albers M. W., Williams R. T., Brown E. J., Tanaka A., Hall F. L., Schreiber S. L. FKBP-rapamycin inhibits a cyclin-dependent kinase activity and a cyclin D1-Cdk association in early G1 of an osteosarcoma cell line. J Biol Chem. 1993 Oct 25;268(30):22825–22829. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bierer B. E., Mattila P. S., Standaert R. F., Herzenberg L. A., Burakoff S. J., Crabtree G., Schreiber S. L. Two distinct signal transmission pathways in T lymphocytes are inhibited by complexes formed between an immunophilin and either FK506 or rapamycin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Dec;87(23):9231–9235. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.23.9231. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bierer B. E., Somers P. K., Wandless T. J., Burakoff S. J., Schreiber S. L. Probing immunosuppressant action with a nonnatural immunophilin ligand. Science. 1990 Oct 26;250(4980):556–559. doi: 10.1126/science.1700475. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown E. J., Albers M. W., Shin T. B., Ichikawa K., Keith C. T., Lane W. S., Schreiber S. L. A mammalian protein targeted by G1-arresting rapamycin-receptor complex. Nature. 1994 Jun 30;369(6483):756–758. doi: 10.1038/369756a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cafferkey R., McLaughlin M. M., Young P. R., Johnson R. K., Livi G. P. Yeast TOR (DRR) proteins: amino-acid sequence alignment and identification of structural motifs. Gene. 1994 Apr 8;141(1):133–136. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(94)90141-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calvo V., Wood M., Gjertson C., Vik T., Bierer B. E. Activation of 70-kDa S6 kinase, induced by the cytokines interleukin-3 and erythropoietin and inhibited by rapamycin, is not an absolute requirement for cell proliferation. Eur J Immunol. 1994 Nov;24(11):2664–2671. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830241115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chung J., Kuo C. J., Crabtree G. R., Blenis J. Rapamycin-FKBP specifically blocks growth-dependent activation of and signaling by the 70 kd S6 protein kinases. Cell. 1992 Jun 26;69(7):1227–1236. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90643-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dumont F. J., Altmeyer A., Kastner C., Fischer P. A., Lemon K. P., Chung J., Blenis J., Staruch M. J. Relationship between multiple biologic effects of rapamycin and the inhibition of pp70S6 protein kinase activity. Analysis in mutant clones of a T cell lymphoma. J Immunol. 1994 Feb 1;152(3):992–1003. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dumont F. J., Melino M. R., Staruch M. J., Koprak S. L., Fischer P. A., Sigal N. H. The immunosuppressive macrolides FK-506 and rapamycin act as reciprocal antagonists in murine T cells. J Immunol. 1990 Feb 15;144(4):1418–1424. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dumont F. J., Staruch M. J., Koprak S. L., Melino M. R., Sigal N. H. Distinct mechanisms of suppression of murine T cell activation by the related macrolides FK-506 and rapamycin. J Immunol. 1990 Jan 1;144(1):251–258. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dumont F. J., Staruch M. J., Koprak S. L., Siekierka J. J., Lin C. S., Harrison R., Sewell T., Kindt V. M., Beattie T. R., Wyvratt M. The immunosuppressive and toxic effects of FK-506 are mechanistically related: pharmacology of a novel antagonist of FK-506 and rapamycin. J Exp Med. 1992 Sep 1;176(3):751–760. doi: 10.1084/jem.176.3.751. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrari S., Pearson R. B., Siegmann M., Kozma S. C., Thomas G. The immunosuppressant rapamycin induces inactivation of p70s6k through dephosphorylation of a novel set of sites. J Biol Chem. 1993 Aug 5;268(22):16091–16094. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kay J. E., Kromwel L., Doe S. E., Denyer M. Inhibition of T and B lymphocyte proliferation by rapamycin. Immunology. 1991 Apr;72(4):544–549. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kay J. E., Sampare-Kwateng E., Geraghty F., Morgan G. Y. Uptake of FK 506 by lymphocytes and erythrocytes. Transplant Proc. 1991 Dec;23(6):2760–2762. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kay J. E., Wellhausen A., Frost V., Morgan G. Y., Smith M. C., Morley S. J. Rapamycin-resistant human lymphoid cell lines. Biochem Soc Trans. 1996 Feb;24(1):89S–89S. doi: 10.1042/bst024089s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunz J., Henriquez R., Schneider U., Deuter-Reinhard M., Movva N. R., Hall M. N. Target of rapamycin in yeast, TOR2, is an essential phosphatidylinositol kinase homolog required for G1 progression. Cell. 1993 May 7;73(3):585–596. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90144-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu J. FK506 and cyclosporin, molecular probes for studying intracellular signal transduction. Immunol Today. 1993 Jun;14(6):290–295. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(93)90048-P. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKeon F. When worlds collide: immunosuppressants meet protein phosphatases. Cell. 1991 Sep 6;66(5):823–826. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90426-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Napoli K. L., Kahan B. D. Sample clean-up and high-performance liquid chromatographic techniques for measurement of whole blood rapamycin concentrations. J Chromatogr B Biomed Appl. 1994 Mar 18;654(1):111–120. doi: 10.1016/0378-4347(93)e0456-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ocain T. D., Longhi D., Steffan R. J., Caccese R. G., Sehgal S. N. A nonimmunosuppressive triene-modified rapamycin analog is a potent inhibitor of peptidyl prolyl cis-trans isomerase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1993 May 14;192(3):1340–1346. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1993.1563. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Price D. J., Grove J. R., Calvo V., Avruch J., Bierer B. E. Rapamycin-induced inhibition of the 70-kilodalton S6 protein kinase. Science. 1992 Aug 14;257(5072):973–977. doi: 10.1126/science.1380182. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schreiber S. L. Immunophilin-sensitive protein phosphatase action in cell signaling pathways. Cell. 1992 Aug 7;70(3):365–368. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90158-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sehgal S. N. Immunosuppressive profile of rapamycin. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1993 Nov 30;696:1–8. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1993.tb17136.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terada N., Franklin R. A., Lucas J. J., Blenis J., Gelfand E. W. Failure of rapamycin to block proliferation once resting cells have entered the cell cycle despite inactivation of p70 S6 kinase. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jun 5;268(16):12062–12068. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terada N., Patel H. R., Takase K., Kohno K., Nairn A. C., Gelfand E. W. Rapamycin selectively inhibits translation of mRNAs encoding elongation factors and ribosomal proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Nov 22;91(24):11477–11481. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.24.11477. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai M., Chen R. H., Tam S. Y., Blenis J., Galli S. J. Activation of MAP kinases, pp90rsk and pp70-S6 kinases in mouse mast cells by signaling through the c-kit receptor tyrosine kinase or Fc epsilon RI: rapamycin inhibits activation of pp70-S6 kinase and proliferation in mouse mast cells. Eur J Immunol. 1993 Dec;23(12):3286–3291. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830231234. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]