Abstract
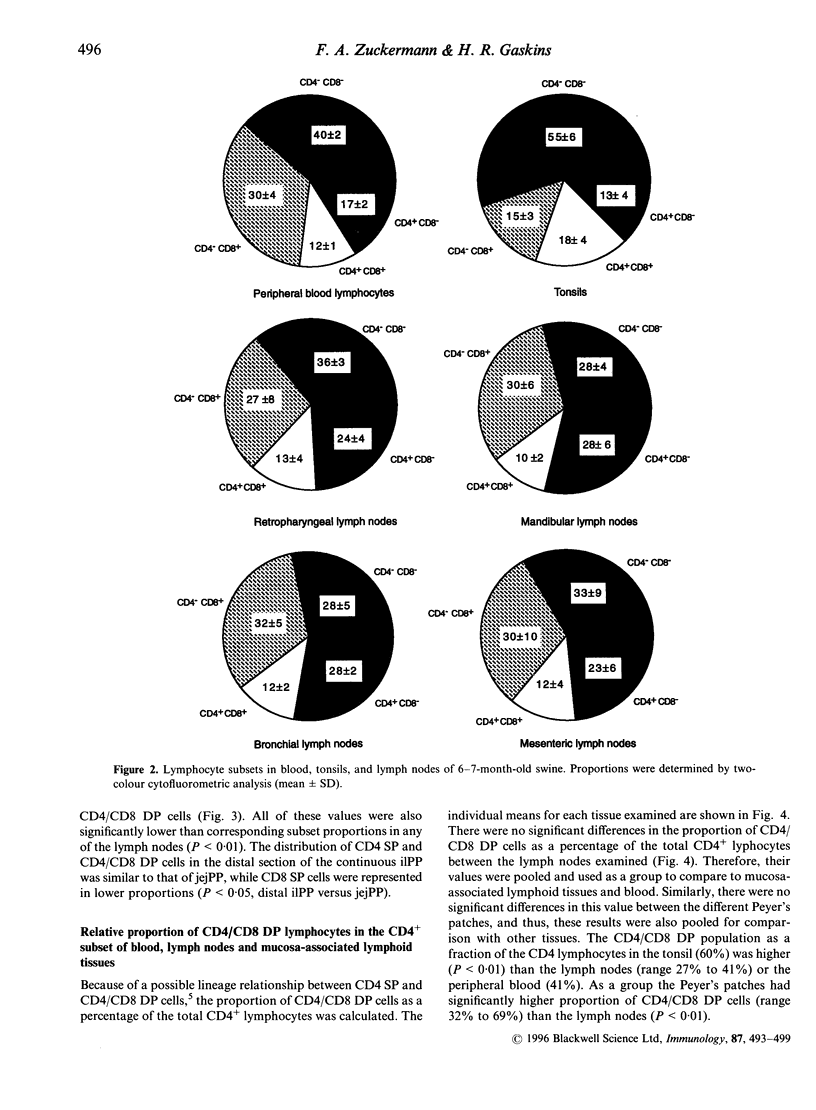
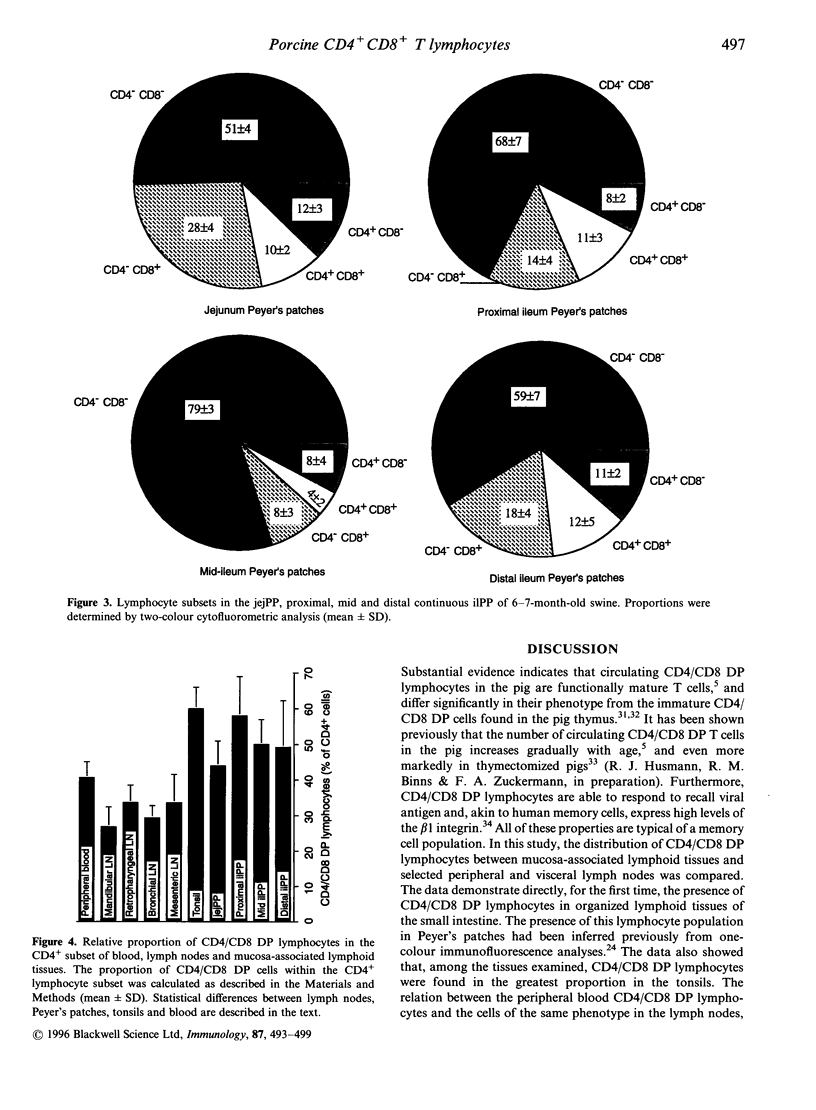
The present study describes the distribution of CD4/CD8 double-positive (DP) T cells in lymph nodes and mucosa-associated lymphoid tissues of pigs at 6-7 months of age. Proportions of lymphocytes isolated from peripheral, bronchial and mesenteric lymph nodes expressing CD4 and/or CD8 molecules were similar and ranged from 10-13% CD4/CD8 DP cells, 25-27% CD4 single-positive (SP) cells, and 27-32% CD8 SP cells. Mucosa-associated lymphoid tissues had significantly smaller proportions of CD4+ and/or CD8+ T cells than lymph nodes and CD4/CD8 DP cells accounted for a larger proportion of the total CD4+ lymphocytes than in lymph nodes. Compared to the lymph nodes, the predominant CD4+ and/or CD8+ T-cell subset in tonsils was the CD4/CD8 DP population (18%), because of both a higher proportion of these cells and a lower proportion of CD4 SP (12%) and CD8 SP (14%) lymphocyte subsets. Jejunal Peyer's patches were comprised of 12% CD4 SP, 28% CD8 SP and 10% CD4/CD8 DP lymphocytes. In contrast, the mid-section of the continuous Peyer's patch in the ileum contained 7% CD4 SP, 8% CD8 SP and 4% CD4/CD8 DP lymphocytes. The distribution of T lymphocytes in porcine mucosal lymphoid aggregates agrees with the reported correlation between high and low rates of lymphocyte entry into these tissues and the abundance or scarcity of T cells, respectively. Defining the role of CD4/CD8 DP lymphocytes and their unique distribution in mucosa-associated lymphoid tissues in the pig may reveal novel T-cell-mediated regulatory pathways.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bianchi A. T., Zwart R. J., Jeurissen S. H., Moonen-Leusen H. W. Development of the B- and T-cell compartments in porcine lymphoid organs from birth to adult life: an immunohistological approach. Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 1992 Aug;33(3):201–221. doi: 10.1016/0165-2427(92)90182-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Binns R. M., Duncan I. A., Powis S. J., Hutchings A., Butcher G. W. Subsets of null and gamma delta T-cell receptor+ T lymphocytes in the blood of young pigs identified by specific monoclonal antibodies. Immunology. 1992 Oct;77(2):219–227. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Binns R. M., Licence S. T. Patterns of migration of labelled blood lymphocyte subpopulations: evidence for two types of Peyer's patch in the young pig. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1985;186:661–668. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4613-2463-8_81. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Binns R. M. The Null/gamma delta TCR+ T cell family in the pig. Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 1994 Oct;43(1-3):69–77. doi: 10.1016/0165-2427(94)90122-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blue M. L., Daley J. F., Levine H., Craig K. A., Schlossman S. F. Biosynthesis and surface expression of T8 by peripheral blood T4+ cells in vitro. J Immunol. 1986 Aug 15;137(4):1202–1207. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burdick J. F., Beschorner W. E., Smith W. J., McGraw D., Bender W. L., Williams G. M., Solez K. Characteristics of early routine renal allograft biopsies. Transplantation. 1984 Dec;38(6):679–684. doi: 10.1097/00007890-198412000-00026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Maria A., Malnati M., Moretta A., Pende D., Bottino C., Casorati G., Cottafava F., Melioli G., Mingari M. C., Migone N. CD3+4-8-WT31-(T cell receptor gamma+) cells and other unusual phenotypes are frequently detected among spontaneously interleukin 2-responsive T lymphocytes present in the joint fluid in juvenile rheumatoid arthritis. A clonal analysis. Eur J Immunol. 1987 Dec;17(12):1815–1819. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830171221. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dillender M. J., Lunney J. K. Characteristics of T lymphocyte cell lines established from NIH minipigs challenge inoculated with Trichinella spiralis. Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 1993 Jan;35(3-4):301–319. doi: 10.1016/0165-2427(93)90041-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gianello P. R., Blancho G., Fishbein J. F., Lorf T., Nickeleit V., Vitiello D., Sachs D. H. Mechanism of cyclosporin-induced tolerance to primarily vascularized allografts in miniature swine. Effect of administration of exogenous IL-2. J Immunol. 1994 Nov 15;153(10):4788–4797. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirt W., Saalmüller A., Reddehase M. J. Distinct gamma/delta T cell receptors define two subsets of circulating porcine CD2-CD4-CD8- T lymphocytes. Eur J Immunol. 1990 Feb;20(2):265–269. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830200206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson S., Sogn J. A., Kindt T. J. Microdetermination of rabbit immunoglobulin allotypes by ELISA using specific antibodies conjugated with peroxidase or with biotin. J Immunol Methods. 1982;48(3):299–309. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(82)90331-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jonjić N., Jonjić S., Saalmüller A., Rukavina D., Koszinowski U. H. Distribution of T-lymphocyte subsets in porcine lymphoid tissues. Immunology. 1987 Mar;60(3):395–401. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lefrancois L. Phenotypic complexity of intraepithelial lymphocytes of the small intestine. J Immunol. 1991 Sep 15;147(6):1746–1751. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Licence S. T., Binns R. M. Major long-term changes in gamma delta T-cell receptor-positive and CD2+ T-cell subsets after neonatal thymectomy in the pig: a longitudinal study lasting nearly 2 years. Immunology. 1995 Jun;85(2):276–284. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lunney J. K. Characterization of swine leukocyte differentiation antigens. Immunol Today. 1993 Apr;14(4):147–148. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(93)90227-C. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lunney J. K., Pescovitz M. D. Phenotypic and functional characterization of pig lymphocyte populations. Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 1987 Dec;17(1-4):135–144. doi: 10.1016/0165-2427(87)90134-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosley R. L., Styre D., Klein J. R. CD4+CD8+ murine intestinal intraepithelial lymphocytes. Int Immunol. 1990;2(4):361–365. doi: 10.1093/intimm/2.4.361. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ortolani C., Forti E., Radin E., Cibin R., Cossarizza A. Cytofluorimetric identification of two populations of double positive (CD4+,CD8+) T lymphocytes in human peripheral blood. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1993 Mar 15;191(2):601–609. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1993.1260. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pabst R., Binns R. M. Heterogeneity of lymphocyte homing physiology: several mechanisms operate in the control of migration to lymphoid and non-lymphoid organs in vivo. Immunol Rev. 1989 Apr;108:83–109. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1989.tb00014.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pescovitz M. D., Hsu S. M., Katz S. I., Lunney J. K., Shimada S., Sachs D. H. Characterization of a porcine CD1-specific mAb that distinguishes CD4/CD8 double-positive thymic from peripheral T lymphocytes. Tissue Antigens. 1990 Apr;35(4):151–156. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0039.1990.tb01772.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pescovitz M. D., Lunney J. K., Sachs D. H. Murine anti-swine T4 and T8 monoclonal antibodies: distribution and effects on proliferative and cytotoxic T cells. J Immunol. 1985 Jan;134(1):37–44. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pescovitz M. D., Lunney J. K., Sachs D. H. Preparation and characterization of monoclonal antibodies reactive with porcine PBL. J Immunol. 1984 Jul;133(1):368–375. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pescovitz M. D., Sakopoulos A. G., Gaddy J. A., Husmann R. J., Zuckermann F. A. Porcine peripheral blood CD4+/CD8+ dual expressing T-cells. Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 1994 Oct;43(1-3):53–62. doi: 10.1016/0165-2427(94)90120-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quiding M., Granström G., Nordström I., Ferrua B., Holmgren J., Czerkinsky C. High frequency of spontaneous interferon-gamma-producing cells in human tonsils: role of local accessory cells and soluble factors. Clin Exp Immunol. 1993 Jan;91(1):157–163. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.1993.tb03372.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothkötter H. J., Hriesik C., Pabst R. More newly formed T than B lymphocytes leave the intestinal mucosa via lymphatics. Eur J Immunol. 1995 Mar;25(3):866–869. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830250336. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothkötter H. J., Pabst R. Lymphocyte subsets in jejunal and ileal Peyer's patches of normal and gnotobiotic minipigs. Immunology. 1989 May;67(1):103–108. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saalmüller A., Hirt W., Reddehase M. J. Phenotypic discrimination between thymic and extrathymic CD4-CD8- and CD4+CD8+ porcine T lymphocytes. Eur J Immunol. 1989 Nov;19(11):2011–2016. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830191107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saalmüller A., Reddehase M. J., Bühring H. J., Jonjić S., Koszinowski U. H. Simultaneous expression of CD4 and CD8 antigens by a substantial proportion of resting porcine T lymphocytes. Eur J Immunol. 1987 Sep;17(9):1297–1301. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830170912. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Secrist H., Egan M., Peters M. G. Tissue-specific regulation of IL-4 mRNA expression in human tonsil. J Immunol. 1994 Feb 1;152(3):1120–1126. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stokes C. R., Bailey M., Wilson A. D. Immunology of the porcine gastrointestinal tract. Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 1994 Oct;43(1-3):143–150. doi: 10.1016/0165-2427(94)90130-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takimoto H., Nakamura T., Takeuchi M., Sumi Y., Tanaka T., Nomoto K., Yoshikai Y. Age-associated increase in number of CD4+CD8+ intestinal intraepithelial lymphocytes in rats. Eur J Immunol. 1992 Jan;22(1):159–164. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830220124. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]