Abstract
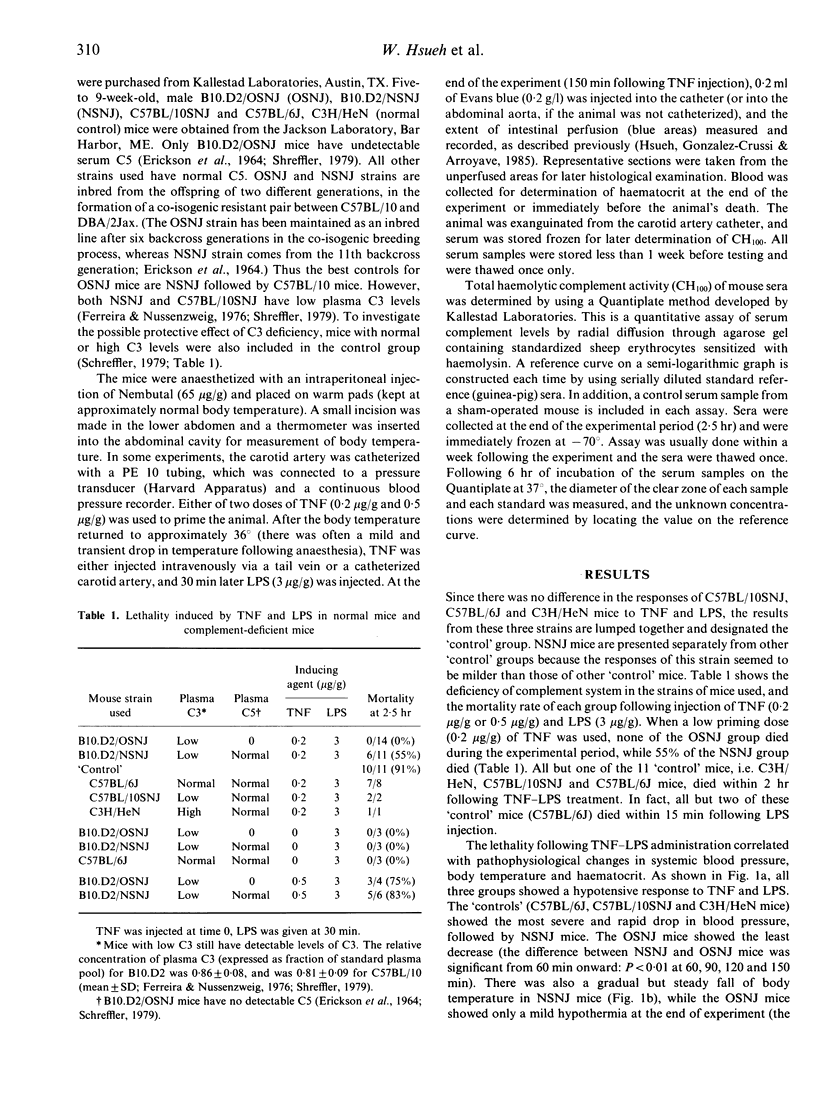
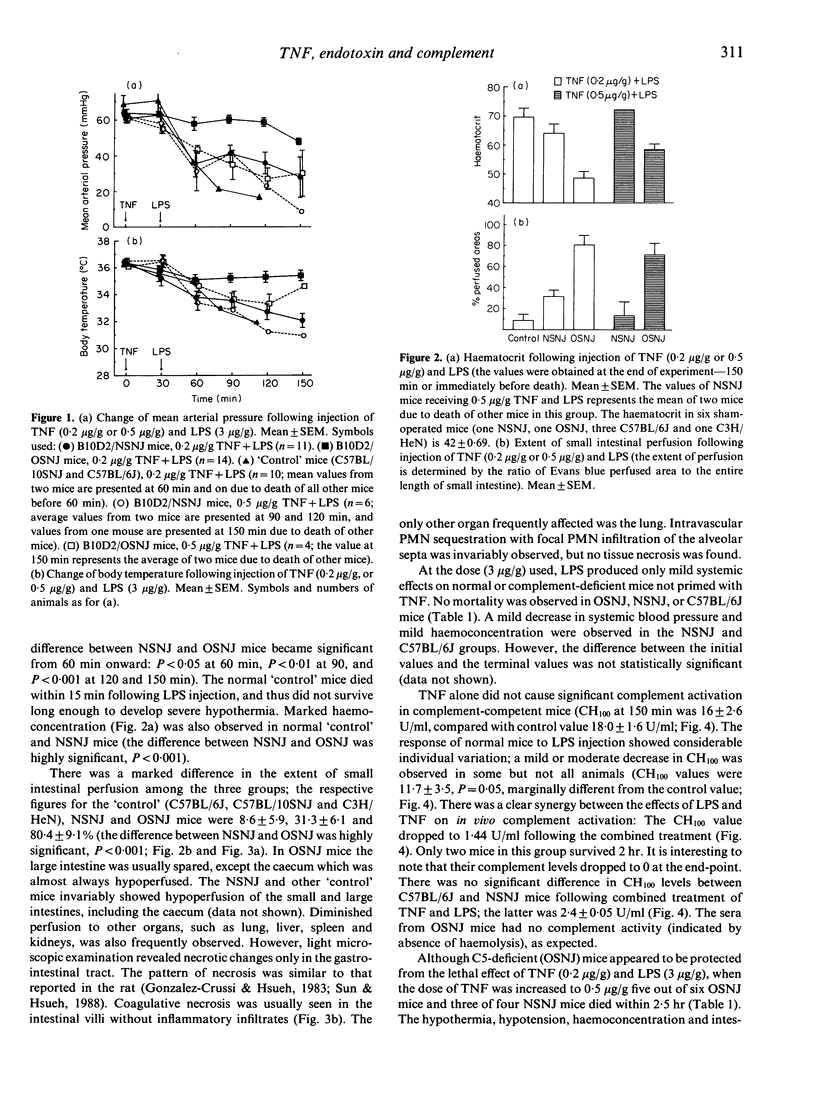
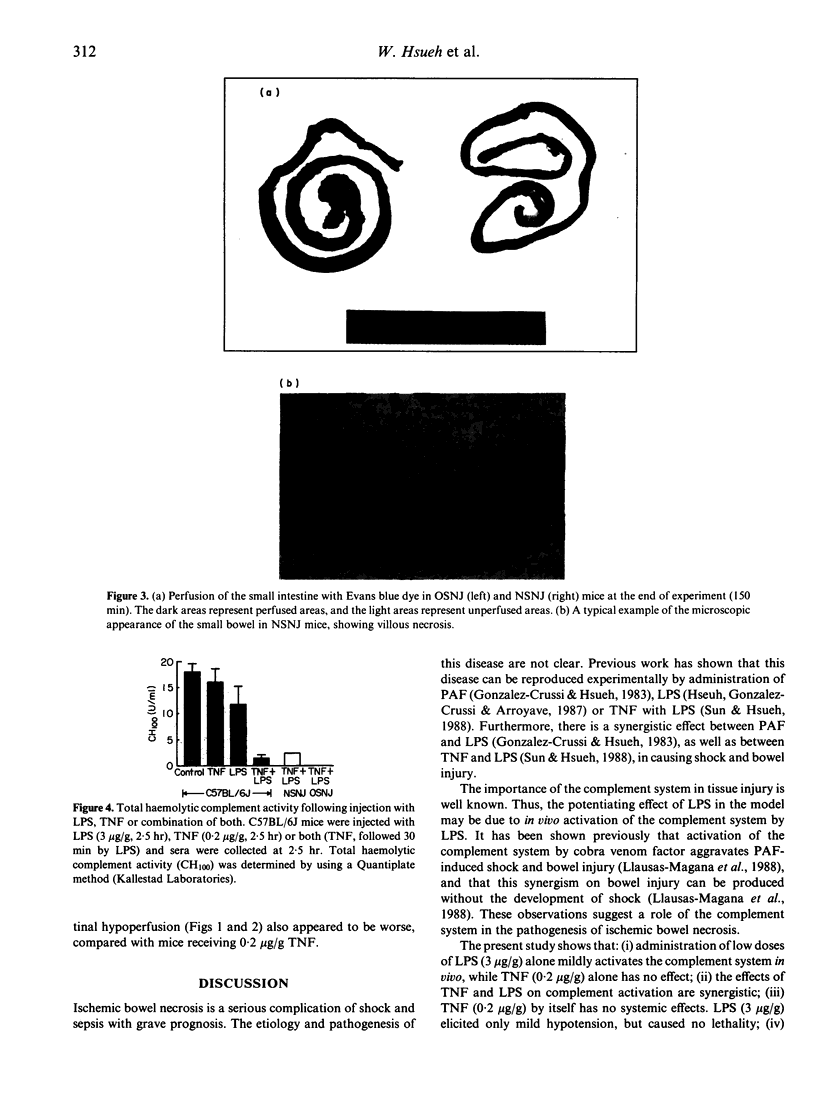
It has previously been shown that tumour necrosis factor-alpha (TNF), together with bacterial lipopolysaccharide (LPS), induces shock and bowel necrosis in the rat. Since the complement system plays an important role in inflammation and tissue injury, its role has been studied in a similar model in mice. In most of the present experiments, a low dose (0.2 micrograms/g) of TNF was used for priming, followed 30 min later by LPS (3 micrograms/g), and the experiment was terminated in 150 min. It is shown that: (i) TNF exerts no systemic effects by itself; LPS elicits only mild hypotension but causes no lethality; (ii) TNF-primed mice show exaggerated effects of shock, hypothermia, haemoconcentration and bowel injury after LPS; the majority of these mice died within 150 min; (iii) administration of LPS alone mildly activates the complement system in vivo, while TNF alone has no effect; (iv) the effects of TNF and LPS on complement activation are synergistic; (v) the acute development of shock and bowel injury in response to TNF-LPS is dependent on an intact complement system, more specifically C5, since C5-deficient mice were protected from TNF-LPS-induced shock and tissue injury; C5-deficient mice also showed less hypotension, hypothermia, haemoconcentration and better intestinal perfusion compared with C5-sufficient animals; (vi) however, when the priming dose of TNF was raised to 0.5 micrograms/g, most of the C5-deficient mice developed marked hypothermia, hypotension, haemoconcentration, bowel injury and died. Thus, it is concluded that TNF and LPS act synergistically in activating the complement system, which plays an important role in mediating the tissue injury and lethality induced by these agents.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beutler B., Milsark I. W., Cerami A. C. Passive immunization against cachectin/tumor necrosis factor protects mice from lethal effect of endotoxin. Science. 1985 Aug 30;229(4716):869–871. doi: 10.1126/science.3895437. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carswell E. A., Old L. J., Kassel R. L., Green S., Fiore N., Williamson B. An endotoxin-induced serum factor that causes necrosis of tumors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Sep;72(9):3666–3670. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.9.3666. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ERICKSON R. P., TACHIBANA D. K., HERZENBERG L. A., ROSENBERG L. T. A SINGLE GENE CONTROLLING HEMOLYTIC COMPLEMENT AND A SERUM ANTIGEN IN THE MOUSE. J Immunol. 1964 Apr;92:611–615. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferreira A., Nussenweig V. Control of C3 levels in mice during ontogeny by a gene in the central region of the H-2 complex. Nature. 1976 Apr 15;260(5552):613–615. doi: 10.1038/260613a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez-Crussi F., Hsueh W. Experimental model of ischemic bowel necrosis. The role of platelet-activating factor and endotoxin. Am J Pathol. 1983 Jul;112(1):127–135. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsueh W., Gonzalez-Crussi F., Arroyave J. L. Platelet-activating factor-induced ischemic bowel necrosis. An investigation of secondary mediators in its pathogenesis. Am J Pathol. 1986 Feb;122(2):231–239. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsueh W., González-Crussi F., Arroyave J. L. Platelet-activating factor: an endogenous mediator for bowel necrosis in endotoxemia. FASEB J. 1987 Nov;1(5):403–405. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.1.5.3678700. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson K. J., Ward P. A. Protective function of C6 in rabbits treated with bacterial endotoxin. J Immunol. 1971 Apr;106(4):1125–1127. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson K. J., Ward P. A. The requirement for serum complement in the detoxification of bacterial endotoxin. J Immunol. 1972 Mar;108(3):611–616. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laster S. M., Wood J. G., Gooding L. R. Tumor necrosis factor can induce both apoptic and necrotic forms of cell lysis. J Immunol. 1988 Oct 15;141(8):2629–2634. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathison J. C., Wolfson E., Ulevitch R. J. Participation of tumor necrosis factor in the mediation of gram negative bacterial lipopolysaccharide-induced injury in rabbits. J Clin Invest. 1988 Jun;81(6):1925–1937. doi: 10.1172/JCI113540. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothstein J. L., Lint T. F., Schreiber H. Tumor necrosis factor/cachectin. Induction of hemorrhagic necrosis in normal tissue requires the fifth component of complement (C5). J Exp Med. 1988 Dec 1;168(6):2007–2021. doi: 10.1084/jem.168.6.2007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sun X. M., Hsueh W. Bowel necrosis induced by tumor necrosis factor in rats is mediated by platelet-activating factor. J Clin Invest. 1988 May;81(5):1328–1331. doi: 10.1172/JCI113459. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tracey K. J., Beutler B., Lowry S. F., Merryweather J., Wolpe S., Milsark I. W., Hariri R. J., Fahey T. J., 3rd, Zentella A., Albert J. D. Shock and tissue injury induced by recombinant human cachectin. Science. 1986 Oct 24;234(4775):470–474. doi: 10.1126/science.3764421. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tracey K. J., Wei H., Manogue K. R., Fong Y., Hesse D. G., Nguyen H. T., Kuo G. C., Beutler B., Cotran R. S., Cerami A. Cachectin/tumor necrosis factor induces cachexia, anemia, and inflammation. J Exp Med. 1988 Mar 1;167(3):1211–1227. doi: 10.1084/jem.167.3.1211. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



