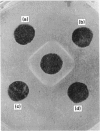
Abstract
Polyclonal antibodies to a purified neurotoxic phospholipase A2 (PLA2), VRV PL-VIIIa, from Vipera russelli venom were raised in rabbits. Anti-PL-VIIIa-Ig (gamma-globulin fraction of rabbit antiserum injected with VRV PL-VIIIa) selectively neutralized the neurotoxicity of VRV PL-VIIIa, VRV PL-V, VRV PL-VI (neurotoxic PLA2 of V. russelli venom) and whole V. russelli venom without affecting their PLA2 activity, which clearly demonstrates that the catalytic site and the neurotoxic site (the site through which the PLA2 binds to the nervous system) are distinct on a PLA2 molecule. Anti-PL-VIIIa Ig did not have any effect on the oedema-inducing activity and indirect haemolytic activity of VRV PL-VIIIa, VRV PL-V and VRV PL-VI, which are attributed to the PLA2 activity of the peptide, but inhibited their anti-coagulant potency.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cotman C., Brown D. H., Harrell B. W., Anderson N. G. Analytical differential centrifugation: an analysis of the sedimentation properties of synaptosomes, mitochondria and lysosomes from rat brain homogenates. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1970 Feb;136(2):436–447. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(70)90215-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jayanthi G. P., Kasturi S., Gowda T. V. Dissociation of catalytic activity and neurotoxicity of a basic phospholipase A2 from Russell's viper (Vipera russelli) venom. Toxicon. 1989;27(8):875–885. doi: 10.1016/0041-0101(89)90099-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kasturi S., Gowda T. V. Purification and characterization of a major phospholipase A2 from Russell's viper (Vipera russelli) venom. Toxicon. 1989;27(2):229–237. doi: 10.1016/0041-0101(89)90136-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kini R. M., Evans H. J. A model to explain the pharmacological effects of snake venom phospholipases A2. Toxicon. 1989;27(6):613–635. doi: 10.1016/0041-0101(89)90013-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kini R. M., Haar N. C., Evans H. J. Non-enzymatic inhibitors of coagulation and platelet aggregation from Naja nigricollis venom are cardiotoxins. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Feb 15;150(3):1012–1016. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(88)90729-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kini R. M., Iwanaga S. Structure-function relationships of phospholipases. I: Prediction of presynaptic neurotoxicity. Toxicon. 1986;24(6):527–541. doi: 10.1016/0041-0101(86)90173-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kini R. M., Iwanaga S. Structure-function relationships of phospholipases. II: Charge density distribution and the myotoxicity of presynaptically neurotoxic phospholipases. Toxicon. 1986;24(9):895–905. doi: 10.1016/0041-0101(86)90090-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ownby C. L., Colberg T. R., Odell G. V. A new method for quantitating hemorrhage induced by rattlesnake venoms: ability of polyvalent antivenom to neutralize hemorrhagic activity. Toxicon. 1984;22(2):227–233. doi: 10.1016/0041-0101(84)90023-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vishwanath B. S., Fawzy A. A., Franson R. C. Edema-inducing activity of phospholipase A2 purified from human synovial fluid and inhibition by aristolochic acid. Inflammation. 1988 Dec;12(6):549–561. doi: 10.1007/BF00914317. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vishwanath B. S., Kini R. M., Gowda T. V. Characterization of three edema-inducing phospholipase A2 enzymes from habu (Trimeresurus flavoviridis) venom and their interaction with the alkaloid aristolochic acid. Toxicon. 1987;25(5):501–515. doi: 10.1016/0041-0101(87)90286-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]