Abstract
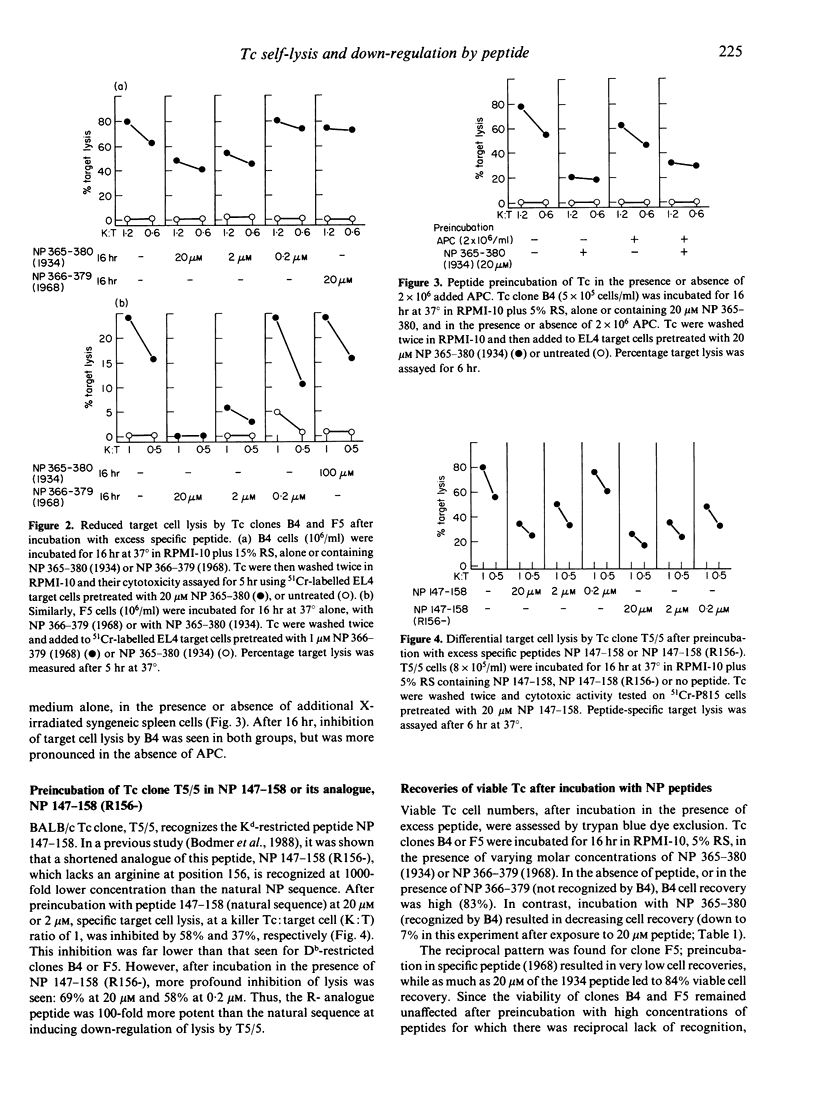
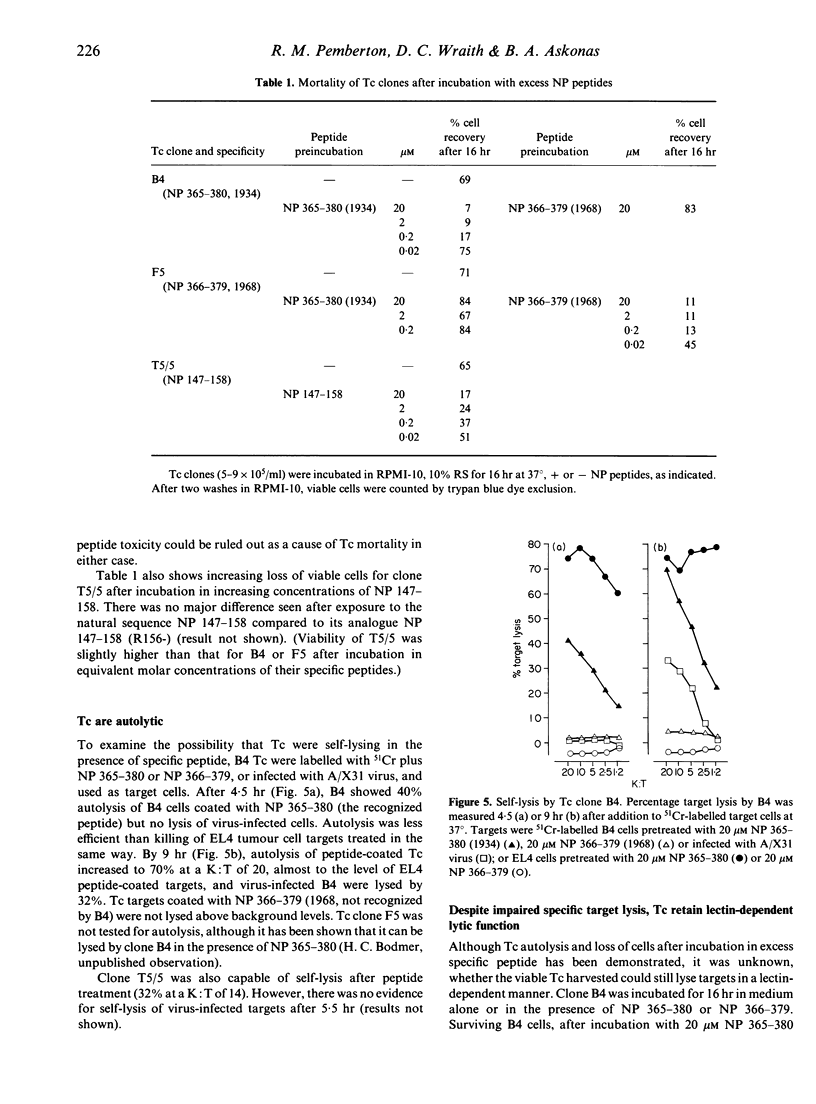
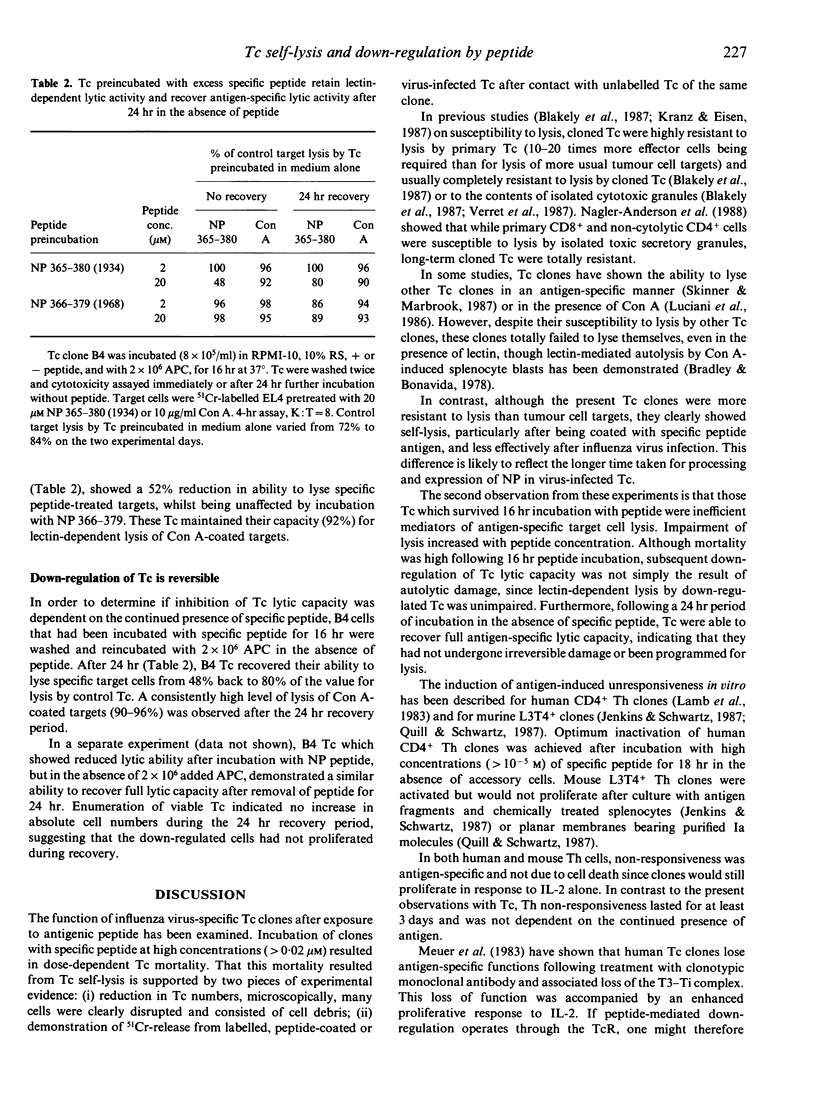
Virus-specific cytotoxic T-cell (Tc) clones can lyse target cells in vitro in the presence of their specific peptide epitopes. The lytic potency of murine influenza nucleoprotein (NP)-specific Tc clones was investigated after observing that target cell killing was reduced in the presence of high (greater than 0.2 microM) concentrations of specific NP peptide antigen. Following incubation of Tc for 16 hr in the presence of a range of peptide concentrations, two effects were observed; (i) a peptide dose-dependent mortality of Tc, which has been attributed to self-lysis by clonal Tc in the presence of specific peptide; (ii) and a reduced ability to specifically lyse NP-expressing target cells whilst retaining lectin-dependent lytic activity in the surviving Tc. This functional down-regulation was reversible after 24 hr incubation in the absence of peptide. Toxic effects were excluded, since inhibition of specific target lysis by Tc was mediated only be pretreatment with specifically recognized peptide.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berke G., Sullivan K. A., Amos D. B. Tumor immunity in vitro: destruction of a mouse ascites tumor through a cycling pathway. Science. 1972 Aug 4;177(4047):433–434. doi: 10.1126/science.177.4047.433. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blakely A., Gorman K., Ostergaard H., Svoboda K., Liu C. C., Young J. D., Clark W. R. Resistance of cloned cytotoxic T lymphocytes to cell-mediated cytotoxicity. J Exp Med. 1987 Oct 1;166(4):1070–1083. doi: 10.1084/jem.166.4.1070. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bodmer H. C., Pemberton R. M., Rothbard J. B., Askonas B. A. Enhanced recognition of a modified peptide antigen by cytotoxic T cells specific for influenza nucleoprotein. Cell. 1988 Jan 29;52(2):253–258. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90514-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradley T. P., Bonavida B. Studies on the induction and expression of T cell-mediated immunity. VII. Inactivation of autologous cytotoxic T lymphocytes when used as both effectors and targets in a lectin-dependent cellular cytotoxic reaction. Transplantation. 1978 Oct;26(4):212–217. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clayberger C., Parham P., Rothbard J., Ludwig D. S., Schoolnik G. K., Krensky A. M. HLA-A2 peptides can regulate cytolysis by human allogeneic T lymphocytes. Nature. 1987 Dec 24;330(6150):763–765. doi: 10.1038/330763a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Claësson M. H. Veto cell H-2 antigens: veto cell activity is restricted by determinants encoded by K, D, and I MHC regions. Cell Immunol. 1987 Oct 15;109(2):360–370. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(87)90319-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Essery G., Feldmann M., Lamb J. R. Interleukin-2 can prevent and reverse antigen-induced unresponsiveness in cloned human T lymphocytes. Immunology. 1988 Jul;64(3):413–417. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman K., Liu C. C., Blakely A., Young J. D., Torbett B. E., Clark W. R. Cloned cytotoxic T lymphocytes as target cells. II. Polarity of lysis revisited. J Immunol. 1988 Oct 1;141(7):2211–2215. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gotch F., McMichael A., Rothbard J. Recognition of influenza A matrix protein by HLA-A2-restricted cytotoxic T lymphocytes. Use of analogues to orientate the matrix peptide in the HLA-A2 binding site. J Exp Med. 1988 Dec 1;168(6):2045–2057. doi: 10.1084/jem.168.6.2045. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Günther J., Haas W., Von Boehmer H. Suppression of T cell responses through competition for T cell growth factor (interleukin 2). Eur J Immunol. 1982 Mar;12(3):247–249. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830120315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hodes R. J., Nadler L. M., Hathcock K. S. Regulatory mechanisms in cell-mediated immune responses. III. Antigen-specific and nonspecific suppressor activities generated during MLC. J Immunol. 1977 Sep;119(3):961–967. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jenkins M. K., Schwartz R. H. Antigen presentation by chemically modified splenocytes induces antigen-specific T cell unresponsiveness in vitro and in vivo. J Exp Med. 1987 Feb 1;165(2):302–319. doi: 10.1084/jem.165.2.302. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koren H. S., Ax W., Freund-Moelbert E. Morphological observations on the contact-induced lysis of target cells. Eur J Immunol. 1973 Jan;3(1):32–37. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830030108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kranz D. M., Eisen H. N. Resistance of cytotoxic T lymphocytes to lysis by a clone of cytotoxic T lymphocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 May;84(10):3375–3379. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.10.3375. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuppers R. C., Henney C. S. Evidence for direct linkage between antigen recognition and lytic expression in effector T cells. J Exp Med. 1976 Mar 1;143(3):684–689. doi: 10.1084/jem.143.3.684. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamb J. R., Skidmore B. J., Green N., Chiller J. M., Feldmann M. Induction of tolerance in influenza virus-immune T lymphocyte clones with synthetic peptides of influenza hemagglutinin. J Exp Med. 1983 May 1;157(5):1434–1447. doi: 10.1084/jem.157.5.1434. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luciani M. F., Brunet J. F., Suzan M., Denizot F., Golstein P. Self-sparing of long-term in vitro-cloned or uncloned cytotoxic T lymphocytes. J Exp Med. 1986 Sep 1;164(3):962–967. doi: 10.1084/jem.164.3.962. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maryanski J. L., Pala P., Corradin G., Jordan B. R., Cerottini J. C. H-2-restricted cytolytic T cells specific for HLA can recognize a synthetic HLA peptide. Nature. 1986 Dec 11;324(6097):578–579. doi: 10.1038/324578a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meuer S. C., Fitzgerald K. A., Hussey R. E., Hodgdon J. C., Schlossman S. F., Reinherz E. L. Clonotypic structures involved in antigen-specific human T cell function. Relationship to the T3 molecular complex. J Exp Med. 1983 Feb 1;157(2):705–719. doi: 10.1084/jem.157.2.705. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller R. G. An immunological suppressor cell inactivating cytotoxic T-lymphocyte precursor cells recognizing it. Nature. 1980 Oct 9;287(5782):544–546. doi: 10.1038/287544a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagler-Anderson C., Verret C. R., Firmenich A. A., Berne M., Eisen H. N. Resistance of primary CD8+ cytotoxic T lymphocytes to lysis by cytotoxic granules from cloned T cell lines. J Immunol. 1988 Nov 15;141(10):3299–3305. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ostergaard H., Gorman K., Clark W. R. Cloned cytotoxic T lymphocyte target cells fail to induce early activation events in effector cytotoxic T lymphocytes. Cell Immunol. 1988 Jun;114(1):188–197. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(88)90265-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pala P., Bodmer H. C., Pemberton R. M., Cerottini J. C., Maryanski J. L., Askonas B. A. Competition between unrelated peptides recognized by H-2-Kd restricted T cells. J Immunol. 1988 Oct 1;141(7):2289–2294. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quill H., Schwartz R. H. Stimulation of normal inducer T cell clones with antigen presented by purified Ia molecules in planar lipid membranes: specific induction of a long-lived state of proliferative nonresponsiveness. J Immunol. 1987 Jun 1;138(11):3704–3712. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds J. D., Morris B. The effect of antigen on the development of Peyer's patches in sheep. Eur J Immunol. 1984 Jan;14(1):1–6. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830140102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimonkevitz R., Colon S., Kappler J. W., Marrack P., Grey H. M. Antigen recognition by H-2-restricted T cells. II. A tryptic ovalbumin peptide that substitutes for processed antigen. J Immunol. 1984 Oct;133(4):2067–2074. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skinner M., Marbrook J. The most efficient cytotoxic T lymphocytes are the least susceptible to lysis. J Immunol. 1987 Aug 15;139(4):985–987. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor P. M., Davey J., Howland K., Rothbard J. B., Askonas B. A. Class I MHC molecules rather than other mouse genes dictate influenza epitope recognition by cytotoxic T cells. Immunogenetics. 1987;26(4-5):267–272. doi: 10.1007/BF00346521. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Townsend A. R., Rothbard J., Gotch F. M., Bahadur G., Wraith D., McMichael A. J. The epitopes of influenza nucleoprotein recognized by cytotoxic T lymphocytes can be defined with short synthetic peptides. Cell. 1986 Mar 28;44(6):959–968. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90019-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unanue E. R., Beller D. I., Lu C. Y., Allen P. M. Antigen presentation: comments on its regulation and mechanism. J Immunol. 1984 Jan;132(1):1–5. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verret C. R., Firmenich A. A., Kranz D. M., Eisen H. N. Resistance of cytotoxic T lymphocytes to the lytic effects of their toxic granules. J Exp Med. 1987 Nov 1;166(5):1536–1547. doi: 10.1084/jem.166.5.1536. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wraith D. C., Vessey A. E. Influenza virus-specific cytotoxic T-cell recognition: stimulation of nucleoprotein-specific clones with intact antigen. Immunology. 1986 Oct;59(2):173–180. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zweerink H. J., Courtneidge S. A., Skehel J. J., Crumpton M. J., Askonas B. A. Cytotoxic T cells kill influenza virus infected cells but do not distinguish between serologically distinct type A viruses. Nature. 1977 May 26;267(5609):354–356. doi: 10.1038/267354a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


