Abstract
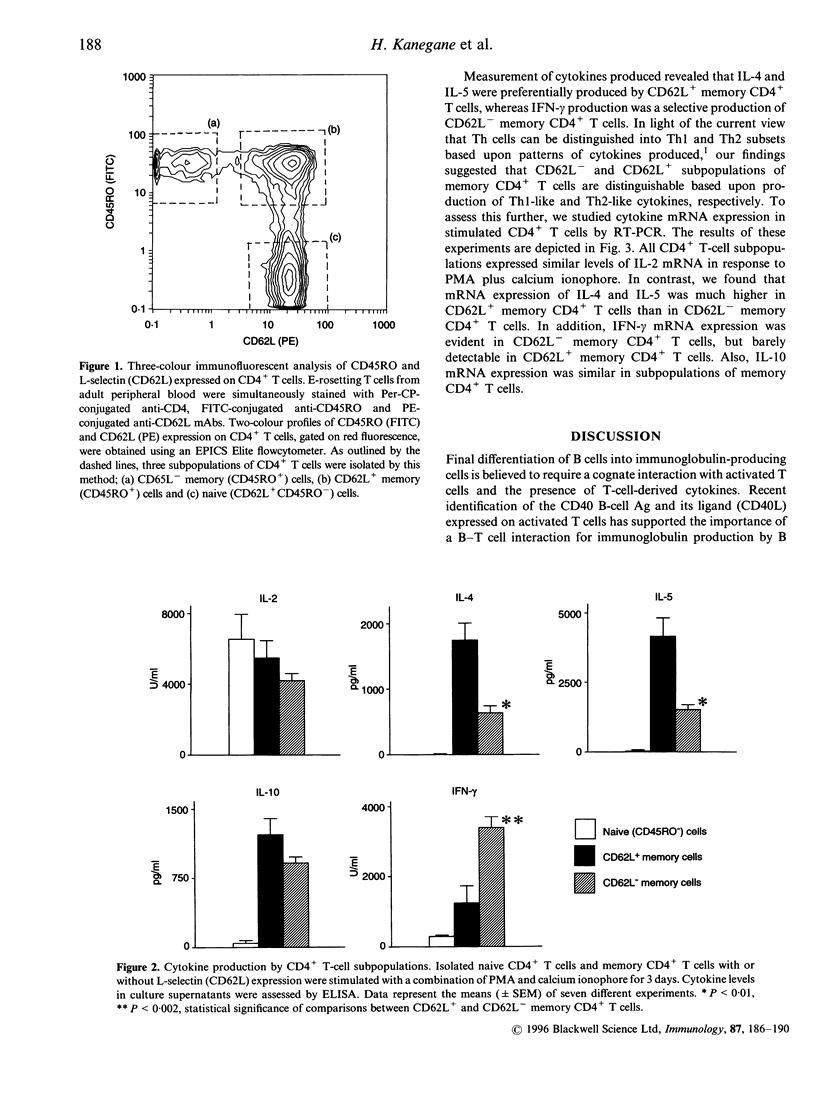
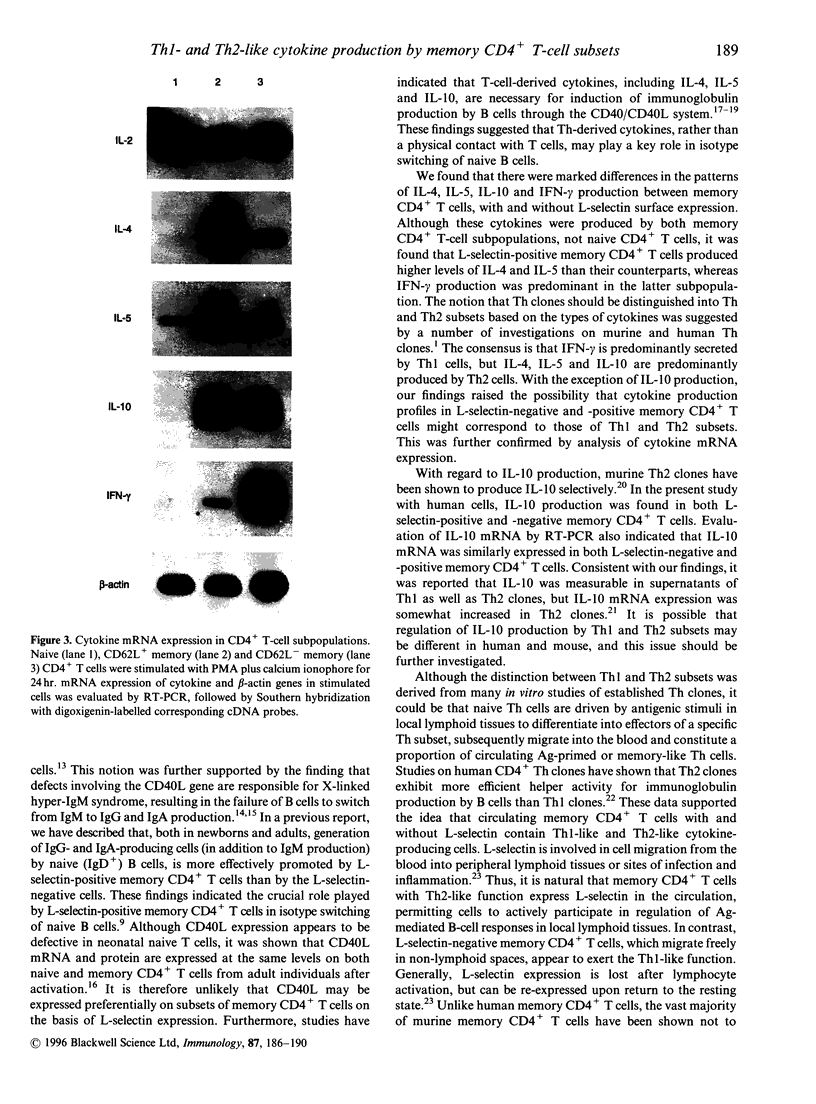
Human memory (CD45RO+) CD4+ T cells can be distinguished into two subpopulations on the basis of expression of the lymph node homing receptor, L-selectin (CD62L). In a prior study we showed that human L-selectin-positive memory T-helper (Th) cells promote the maturation of IgG- and IgA-producing cells by naive B cells. To further elucidate the contribution of memory CD4+ T cells to B-cell differentiation, human memory CD4+ T cells with or without L-selectin expression were evaluated for production of cytokines that participate in regulation of immunoglobulin production. It was found that L-selectin-positive human memory CD4+ T cells produce mainly interleukin (IL)-4 and IL-5, whereas L-selectin-negative CD4+ T cells produce mainly interferon-gamma (IFN-gamma). This profile of cytokine expression coincides with the profile that distinguishes Th1 and Th2 subsets. In contrast to the murine system, IL-10 production was similarly contributed by human L-selectin-positive and -negative memory CD4+ T-cell subpopulations. These results suggest that the human L-selectin-negative and -positive subpopulations of human memory CD4+ T cells contain Th1-like and Th2-like cytokine-producing cells, respectively.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akbar A. N., Terry L., Timms A., Beverley P. C., Janossy G. Loss of CD45R and gain of UCHL1 reactivity is a feature of primed T cells. J Immunol. 1988 Apr 1;140(7):2171–2178. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allen R. C., Armitage R. J., Conley M. E., Rosenblatt H., Jenkins N. A., Copeland N. G., Bedell M. A., Edelhoff S., Disteche C. M., Simoneaux D. K. CD40 ligand gene defects responsible for X-linked hyper-IgM syndrome. Science. 1993 Feb 12;259(5097):990–993. doi: 10.1126/science.7679801. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Banchereau J., de Paoli P., Vallé A., Garcia E., Rousset F. Long-term human B cell lines dependent on interleukin-4 and antibody to CD40. Science. 1991 Jan 4;251(4989):70–72. doi: 10.1126/science.1702555. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradley L. M., Atkins G. G., Swain S. L. Long-term CD4+ memory T cells from the spleen lack MEL-14, the lymph node homing receptor. J Immunol. 1992 Jan 15;148(2):324–331. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Defrance T., Vanbervliet B., Brière F., Durand I., Rousset F., Banchereau J. Interleukin 10 and transforming growth factor beta cooperate to induce anti-CD40-activated naive human B cells to secrete immunoglobulin A. J Exp Med. 1992 Mar 1;175(3):671–682. doi: 10.1084/jem.175.3.671. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Del Prete G. F., De Carli M., Ricci M., Romagnani S. Helper activity for immunoglobulin synthesis of T helper type 1 (Th1) and Th2 human T cell clones: the help of Th1 clones is limited by their cytolytic capacity. J Exp Med. 1991 Oct 1;174(4):809–813. doi: 10.1084/jem.174.4.809. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Del Prete G., De Carli M., Almerigogna F., Giudizi M. G., Biagiotti R., Romagnani S. Human IL-10 is produced by both type 1 helper (Th1) and type 2 helper (Th2) T cell clones and inhibits their antigen-specific proliferation and cytokine production. J Immunol. 1993 Jan 15;150(2):353–360. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiSanto J. P., Bonnefoy J. Y., Gauchat J. F., Fischer A., de Saint Basile G. CD40 ligand mutations in x-linked immunodeficiency with hyper-IgM. Nature. 1993 Feb 11;361(6412):541–543. doi: 10.1038/361541a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ehlers S., Smith K. A. Differentiation of T cell lymphokine gene expression: the in vitro acquisition of T cell memory. J Exp Med. 1991 Jan 1;173(1):25–36. doi: 10.1084/jem.173.1.25. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallatin M., St John T. P., Siegelman M., Reichert R., Butcher E. C., Weissman I. L. Lymphocyte homing receptors. Cell. 1986 Mar 14;44(5):673–680. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90832-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanegane H., Miyawaki T., Kato K., Yokoi T., Uehara T., Yachie A., Taniguchi N. A novel subpopulation of CD45RA+ CD4+ T cells expressing IL-2 receptor alpha-chain (CD25) and having a functionally transitional nature into memory cells. Int Immunol. 1991 Dec;3(12):1349–1356. doi: 10.1093/intimm/3.12.1349. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maliszewski C. R., Grabstein K., Fanslow W. C., Armitage R., Spriggs M. K., Sato T. A. Recombinant CD40 ligand stimulation of murine B cell growth and differentiation: cooperative effects of cytokines. Eur J Immunol. 1993 May;23(5):1044–1049. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830230510. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manetti R., Annunziato F., Biagiotti R., Giudizi M. G., Piccinni M. P., Giannarini L., Sampognaro S., Parronchi P., Vinante F., Pizzolo G. CD30 expression by CD8+ T cells producing type 2 helper cytokines. Evidence for large numbers of CD8+CD30+ T cell clones in human immunodeficiency virus infection. J Exp Med. 1994 Dec 1;180(6):2407–2411. doi: 10.1084/jem.180.6.2407. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyawaki T., Kasahara Y., Taga K., Yachie A., Taniguchi N. Differential expression of CD45RO (UCHL1) and its functional relevance in two subpopulations of circulating TCR-gamma/delta+ lymphocytes. J Exp Med. 1990 May 1;171(5):1833–1838. doi: 10.1084/jem.171.5.1833. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyawaki T., Kubagawa H., Butler J. L., Cooper M. D. Ig isotypes produced by EBV-transformed B cells as a function of age and tissue distribution. J Immunol. 1988 Jun 1;140(11):3887–3892. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore K. W., Vieira P., Fiorentino D. F., Trounstine M. L., Khan T. A., Mosmann T. R. Homology of cytokine synthesis inhibitory factor (IL-10) to the Epstein-Barr virus gene BCRFI. Science. 1990 Jun 8;248(4960):1230–1234. doi: 10.1126/science.2161559. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noelle R. J., Ledbetter J. A., Aruffo A. CD40 and its ligand, an essential ligand-receptor pair for thymus-dependent B-cell activation. Immunol Today. 1992 Nov;13(11):431–433. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(92)90068-I. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nonoyama S., Penix L. A., Edwards C. P., Lewis D. B., Ito S., Aruffo A., Wilson C. B., Ochs H. D. Diminished expression of CD40 ligand by activated neonatal T cells. J Clin Invest. 1995 Jan;95(1):66–75. doi: 10.1172/JCI117677. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paul W. E., Seder R. A. Lymphocyte responses and cytokines. Cell. 1994 Jan 28;76(2):241–251. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90332-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Picker L. J., Treer J. R., Ferguson-Darnell B., Collins P. A., Buck D., Terstappen L. W. Control of lymphocyte recirculation in man. I. Differential regulation of the peripheral lymph node homing receptor L-selectin on T cells during the virgin to memory cell transition. J Immunol. 1993 Feb 1;150(3):1105–1121. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanders M. E., Makgoba M. W., Shaw S. Human naive and memory T cells: reinterpretation of helper-inducer and suppressor-inducer subsets. Immunol Today. 1988 Jul-Aug;9(7-8):195–199. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(88)91212-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Semnani R. T., Nutman T. B., Hochman P., Shaw S., van Seventer G. A. Costimulation by purified intercellular adhesion molecule 1 and lymphocyte function-associated antigen 3 induces distinct proliferation, cytokine and cell surface antigen profiles in human "naive" and "memory" CD4+ T cells. J Exp Med. 1994 Dec 1;180(6):2125–2135. doi: 10.1084/jem.180.6.2125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tedder T. F., Matsuyama T., Rothstein D., Schlossman S. F., Morimoto C. Human antigen-specific memory T cells express the homing receptor (LAM-1) necessary for lymphocyte recirculation. Eur J Immunol. 1990 Jun;20(6):1351–1355. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830200622. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tominaga A., Takaki S., Koyama N., Katoh S., Matsumoto R., Migita M., Hitoshi Y., Hosoya Y., Yamauchi S., Kanai Y. Transgenic mice expressing a B cell growth and differentiation factor gene (interleukin 5) develop eosinophilia and autoantibody production. J Exp Med. 1991 Feb 1;173(2):429–437. doi: 10.1084/jem.173.2.429. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsuji T., Nibu R., Iwai K., Kanegane H., Yachie A., Seki H., Miyawaki T., Taniguchi N. Efficient induction of immunoglobulin production in neonatal naive B cells by memory CD4+ T cell subset expressing homing receptor L-selectin. J Immunol. 1994 May 1;152(9):4417–4424. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yssel H., De Waal Malefyt R., Roncarolo M. G., Abrams J. S., Lahesmaa R., Spits H., de Vries J. E. IL-10 is produced by subsets of human CD4+ T cell clones and peripheral blood T cells. J Immunol. 1992 Oct 1;149(7):2378–2384. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



