Abstract
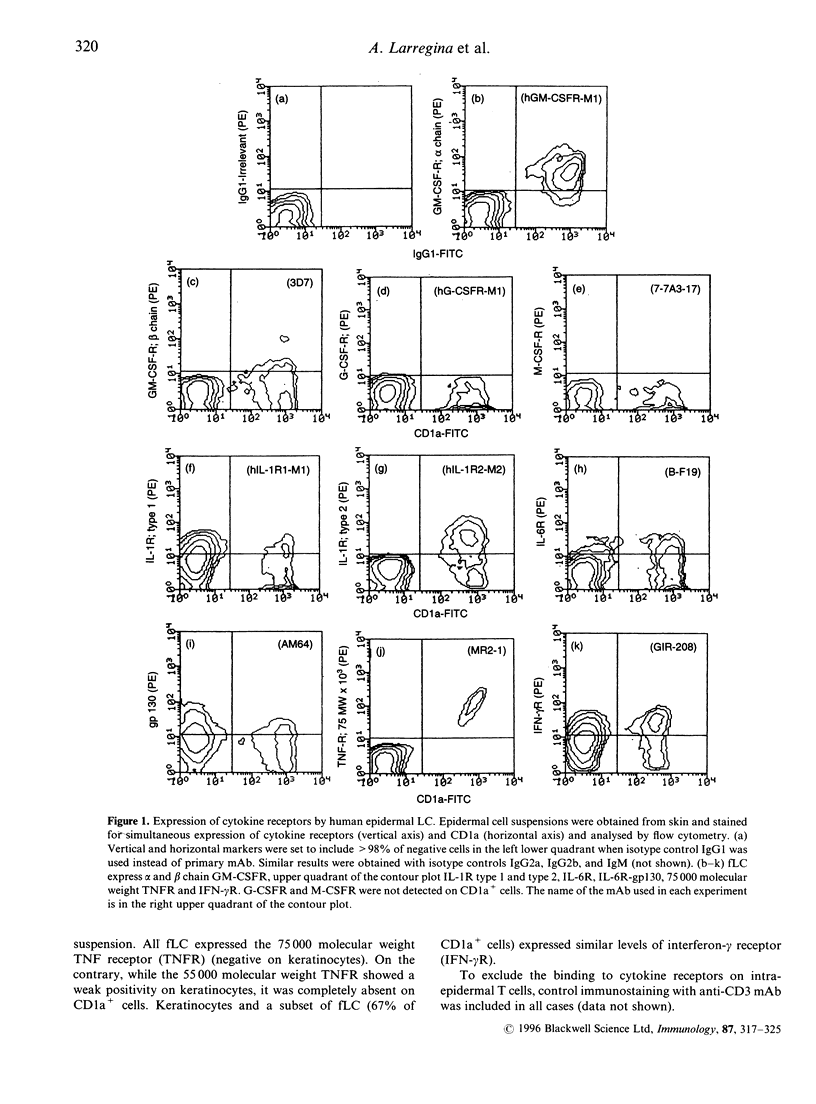
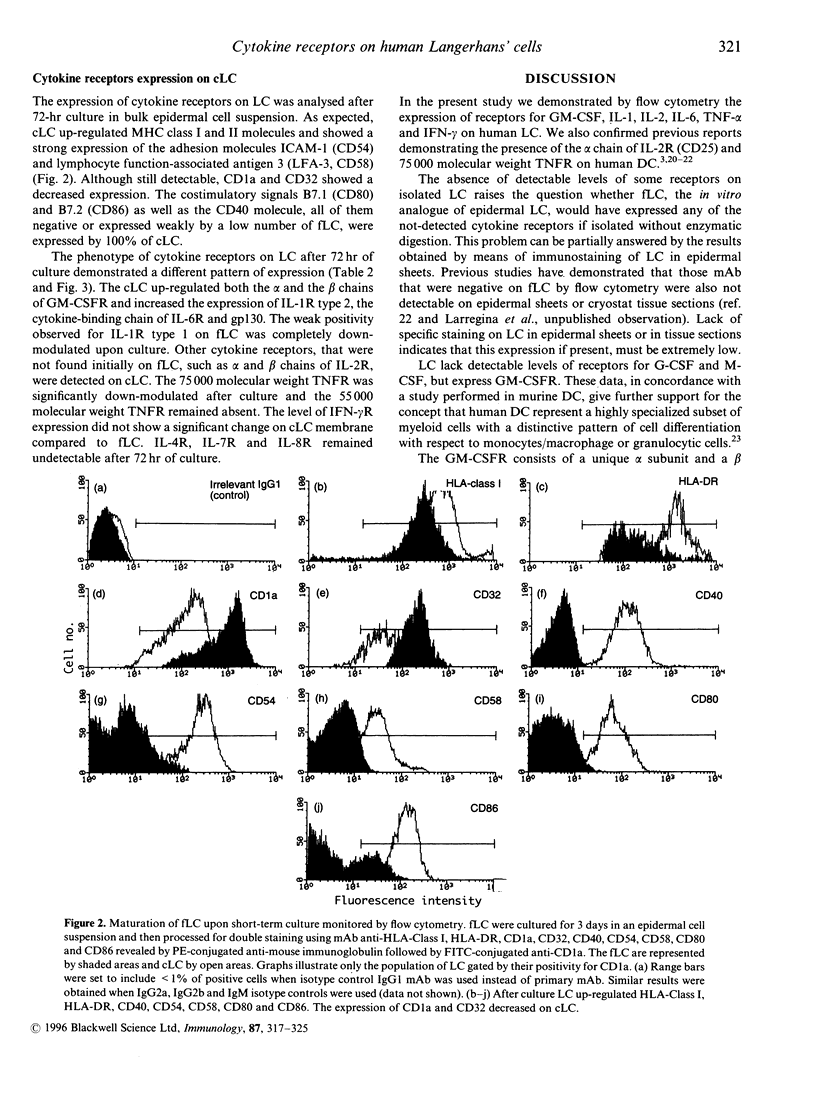
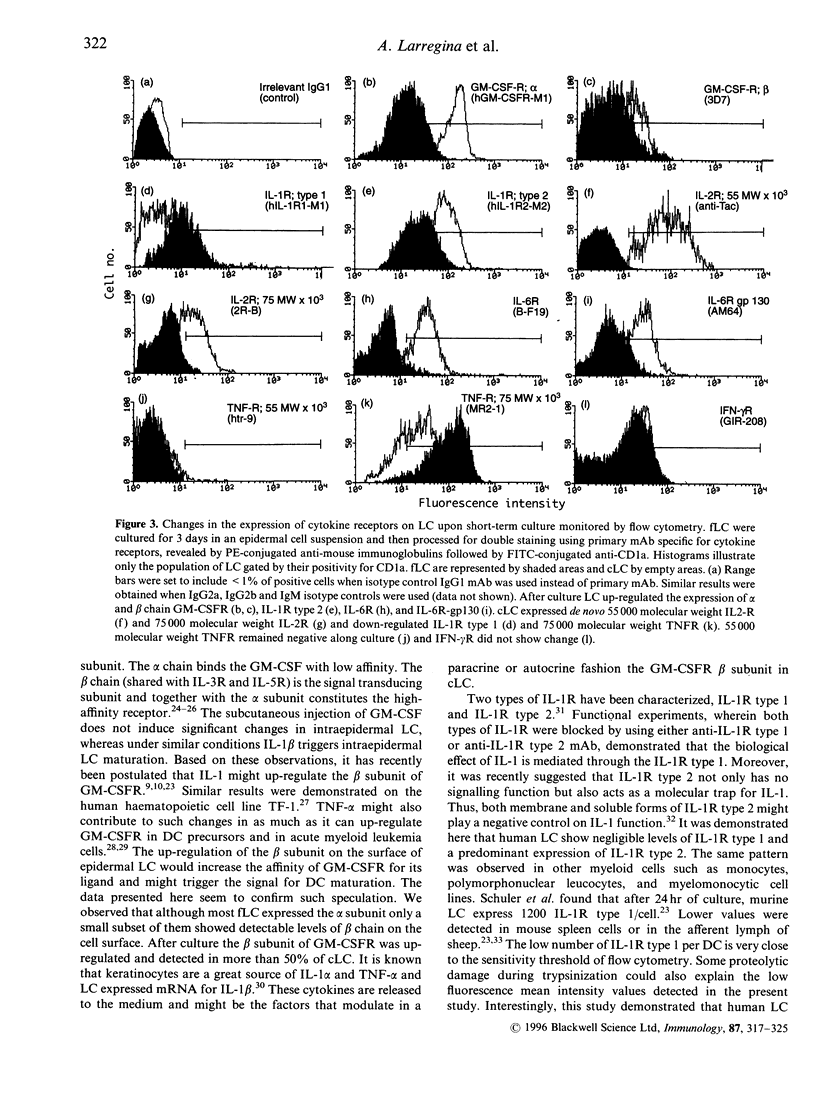
It is well established that granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor (GM-CSF), interleukin (IL)-1 and tumour necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-alpha) are involved in Langerhans' cell (LC) development and dendritic cell traffic. However, little is known about the pattern of cytokine receptors on human LC and their modulation during different stages of maturation. The expression of cytokine receptors was studied by flow cytometry on both freshly isolated LC (fLC) and 72-hr cultured LC (cLC). Epidermal cell suspensions enriched in LC were obtained after skin trypsinization and Ficoll-Hypaque gradient. LC were identified by their CD1a positivity. Although the majority of fLC were positive for the alpha chain of GM-CSF receptor (GM-CSFR), the beta chain of GM-CSFR was detected only on 15% of CD1a+ cells. fLC were also positive for IL-1 receptor (IL-1R) type 1, IL-1R type 2, 75,000 molecular weight TNF receptor (TNFR) and interferon-gamma receptor (IFN-gamma R). IL-6R and its transducing signal gp130 were present in a subset of fLC. Granulocyte colony-stimulating factor receptor (G-CSFR), macrophage colony-stimulating factor receptor (M-CSFR), the alpha and beta chain of IL-2R, IL-4R, IL-7R, IL-8R and 55,000 molecular weight TNFR were not detected on fLC. After culture, LC up-regulated the expression of both the alpha and beta chains of GM-CSFR, IL-1R type 2, alpha and beta chains of IL-2R, IL-6R and gp130. In contrast, IL-1R type 1 and 75,000 molecular weight TNFR were down-modulated and the expression of IFN-gamma R was not affected by culture. These results suggest that LC undergo changes in the cytokine receptor repertory during in vitro maturation.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aiba S., Katz S. I. The ability of cultured Langerhans cells to process and present protein antigens is MHC-dependent. J Immunol. 1991 Apr 15;146(8):2479–2487. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brockhaus M., Schoenfeld H. J., Schlaeger E. J., Hunziker W., Lesslauer W., Loetscher H. Identification of two types of tumor necrosis factor receptors on human cell lines by monoclonal antibodies. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Apr;87(8):3127–3131. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.8.3127. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caux C., Dezutter-Dambuyant C., Schmitt D., Banchereau J. GM-CSF and TNF-alpha cooperate in the generation of dendritic Langerhans cells. Nature. 1992 Nov 19;360(6401):258–261. doi: 10.1038/360258a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang C. H., Furue M., Tamaki K. Selective regulation of ICAM-1 and major histocompatibility complex class I and II molecule expression on epidermal Langerhans cells by some of the cytokines released by keratinocytes and T cells. Eur J Immunol. 1994 Nov;24(11):2889–2895. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830241146. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colotta F., Re F., Muzio M., Bertini R., Polentarutti N., Sironi M., Giri J. G., Dower S. K., Sims J. E., Mantovani A. Interleukin-1 type II receptor: a decoy target for IL-1 that is regulated by IL-4. Science. 1993 Jul 23;261(5120):472–475. doi: 10.1126/science.8332913. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crowe P. D., VanArsdale T. L., Goodwin R. G., Ware C. F. Specific induction of 80-kDa tumor necrosis factor receptor shedding in T lymphocytes involves the cytoplasmic domain and phosphorylation. J Immunol. 1993 Dec 15;151(12):6882–6890. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cumberbatch M., Fielding I., Kimber I. Modulation of epidermal Langerhans' cell frequency by tumour necrosis factor-alpha. Immunology. 1994 Mar;81(3):395–401. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cumberbatch M., Kimber I. Dermal tumour necrosis factor-alpha induces dendritic cell migration to draining lymph nodes, and possibly provides one stimulus for Langerhans' cell migration. Immunology. 1992 Feb;75(2):257–263. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dinarello C. A. Interleukin-1 and interleukin-1 antagonism. Blood. 1991 Apr 15;77(8):1627–1652. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drapier J. C., Wietzerbin J. IFN-gamma reduces specific binding of tumor necrosis factor on murine macrophages. J Immunol. 1991 Feb 15;146(4):1198–1203. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elbaz O., Budel L. M., Hoogerbrugge H., Touw I. P., Delwel R., Mahmoud L. A., Löwenberg B. Tumor necrosis factor regulates the expression of granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor and interleukin-3 receptors on human acute myeloid leukemia cells. Blood. 1991 Mar 1;77(5):989–995. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Enk A. H., Angeloni V. L., Udey M. C., Katz S. I. An essential role for Langerhans cell-derived IL-1 beta in the initiation of primary immune responses in skin. J Immunol. 1993 May 1;150(9):3698–3704. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fiskerstrand C. E., Hopkins J., Sargan D. R. Interleukin-1 receptor expression by ovine afferent lymph dendritic cells: response to secondary antigen challenge. Eur J Immunol. 1994 Oct;24(10):2351–2356. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830241014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gearing D. P., King J. A., Gough N. M., Nicola N. A. Expression cloning of a receptor for human granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor. EMBO J. 1989 Dec 1;8(12):3667–3676. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08541.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayashida K., Kitamura T., Gorman D. M., Arai K., Yokota T., Miyajima A. Molecular cloning of a second subunit of the receptor for human granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor (GM-CSF): reconstitution of a high-affinity GM-CSF receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Dec;87(24):9655–9659. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.24.9655. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heufler C., Koch F., Schuler G. Granulocyte/macrophage colony-stimulating factor and interleukin 1 mediate the maturation of murine epidermal Langerhans cells into potent immunostimulatory dendritic cells. J Exp Med. 1988 Feb 1;167(2):700–705. doi: 10.1084/jem.167.2.700. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ioffreda M. D., Whitaker D., Murphy G. F. Mast cell degranulation upregulates alpha 6 integrins on epidermal Langerhans cells. J Invest Dermatol. 1993 Aug;101(2):150–154. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12363632. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan G., Walsh G., Guido L. S., Meyn P., Burkhardt R. A., Abalos R. M., Barker J., Frindt P. A., Fajardo T. T., Celona R. Novel responses of human skin to intradermal recombinant granulocyte/macrophage-colony-stimulating factor: Langerhans cell recruitment, keratinocyte growth, and enhanced wound healing. J Exp Med. 1992 Jun 1;175(6):1717–1728. doi: 10.1084/jem.175.6.1717. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knight S. C., Stagg A. J. Antigen-presenting cell types. Curr Opin Immunol. 1993 Jun;5(3):374–382. doi: 10.1016/0952-7915(93)90056-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koch F., Heufler C., Kämpgen E., Schneeweiss D., Böck G., Schuler G. Tumor necrosis factor alpha maintains the viability of murine epidermal Langerhans cells in culture, but in contrast to granulocyte/macrophage colony-stimulating factor, without inducing their functional maturation. J Exp Med. 1990 Jan 1;171(1):159–171. doi: 10.1084/jem.171.1.159. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kämpgen E., Koch F., Heufler C., Eggert A., Gill L. L., Gillis S., Dower S. K., Romani N., Schuler G. Understanding the dendritic cell lineage through a study of cytokine receptors. J Exp Med. 1994 Jun 1;179(6):1767–1776. doi: 10.1084/jem.179.6.1767. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loetscher H., Pan Y. C., Lahm H. W., Gentz R., Brockhaus M., Tabuchi H., Lesslauer W. Molecular cloning and expression of the human 55 kd tumor necrosis factor receptor. Cell. 1990 Apr 20;61(2):351–359. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90815-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lundqvist E. N., Bäck O. Interleukin-1 decreases the number of Ia+ epidermal dendritic cells but increases their expression of Ia antigen. Acta Derm Venereol. 1990;70(5):391–394. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacPherson G. G., Fossum S., Harrison B. Properties of lymph-borne (veiled) dendritic cells in culture. II. Expression of the IL-2 receptor: role of GM-CSF. Immunology. 1989 Sep;68(1):108–113. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsue H., Cruz P. D., Jr, Bergstresser P. R., Takashima A. Langerhans cells are the major source of mRNA for IL-1 beta and MIP-1 alpha among unstimulated mouse epidermal cells. J Invest Dermatol. 1992 Nov;99(5):537–541. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12667296. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyajima A., Kitamura T., Harada N., Yokota T., Arai K. Cytokine receptors and signal transduction. Annu Rev Immunol. 1992;10:295–331. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.10.040192.001455. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porteu F., Nathan C. Shedding of tumor necrosis factor receptors by activated human neutrophils. J Exp Med. 1990 Aug 1;172(2):599–607. doi: 10.1084/jem.172.2.599. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Romani N., Lenz A., Glassel H., Stössel H., Stanzl U., Majdic O., Fritsch P., Schuler G. Cultured human Langerhans cells resemble lymphoid dendritic cells in phenotype and function. J Invest Dermatol. 1989 Nov;93(5):600–609. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12319727. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryffel B., Brockhaus M., Greiner B., Mihatsch M. J., Gudat F. Tumour necrosis factor receptor distribution in human lymphoid tissue. Immunology. 1991 Nov;74(3):446–452. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Santiago-Schwarz F., Divaris N., Kay C., Carsons S. E. Mechanisms of tumor necrosis factor-granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor-induced dendritic cell development. Blood. 1993 Nov 15;82(10):3019–3028. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schall T. J., Lewis M., Koller K. J., Lee A., Rice G. C., Wong G. H., Gatanaga T., Granger G. A., Lentz R., Raab H. Molecular cloning and expression of a receptor for human tumor necrosis factor. Cell. 1990 Apr 20;61(2):361–370. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90816-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith C. A., Davis T., Anderson D., Solam L., Beckmann M. P., Jerzy R., Dower S. K., Cosman D., Goodwin R. G. A receptor for tumor necrosis factor defines an unusual family of cellular and viral proteins. Science. 1990 May 25;248(4958):1019–1023. doi: 10.1126/science.2160731. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steiner G., Tschachler E., Tani M., Malek T. R., Shevach E. M., Holter W., Knapp W., Wolff K., Stingl G. Interleukin 2 receptors on cultured murine epidermal Langerhans cells. J Immunol. 1986 Jul 1;137(1):155–159. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeshita T., Asao H., Ohtani K., Ishii N., Kumaki S., Tanaka N., Munakata H., Nakamura M., Sugamura K. Cloning of the gamma chain of the human IL-2 receptor. Science. 1992 Jul 17;257(5068):379–382. doi: 10.1126/science.1631559. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tartaglia L. A., Goeddel D. V. Two TNF receptors. Immunol Today. 1992 May;13(5):151–153. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(92)90116-O. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tazi A., Bouchonnet F., Grandsaigne M., Boumsell L., Hance A. J., Soler P. Evidence that granulocyte macrophage-colony-stimulating factor regulates the distribution and differentiated state of dendritic cells/Langerhans cells in human lung and lung cancers. J Clin Invest. 1993 Feb;91(2):566–576. doi: 10.1172/JCI116236. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teunissen M. B., Wormmeester J., Krieg S. R., Peters P. J., Vogels I. M., Kapsenberg M. L., Bos J. D. Human epidermal Langerhans cells undergo profound morphologic and phenotypical changes during in vitro culture. J Invest Dermatol. 1990 Feb;94(2):166–173. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12874439. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vermeer M., Streilein J. W. Ultraviolet B light-induced alterations in epidermal Langerhans cells are mediated in part by tumor necrosis factor-alpha. Photodermatol Photoimmunol Photomed. 1990 Dec;7(6):258–265. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ware C. F., Crowe P. D., Vanarsdale T. L., Andrews J. L., Grayson M. H., Jerzy R., Smith C. A., Goodwin R. G. Tumor necrosis factor (TNF) receptor expression in T lymphocytes. Differential regulation of the type I TNF receptor during activation of resting and effector T cells. J Immunol. 1991 Dec 15;147(12):4229–4238. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe Y., Kitamura T., Hayashida K., Miyajima A. Monoclonal antibody against the common beta subunit (beta c) of the human interleukin-3 (IL-3), IL-5, and granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor receptors shows upregulation of beta c by IL-1 and tumor necrosis factor-alpha. Blood. 1992 Nov 1;80(9):2215–2220. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Witmer-Pack M. D., Olivier W., Valinsky J., Schuler G., Steinman R. M. Granulocyte/macrophage colony-stimulating factor is essential for the viability and function of cultured murine epidermal Langerhans cells. J Exp Med. 1987 Nov 1;166(5):1484–1498. doi: 10.1084/jem.166.5.1484. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


