Abstract
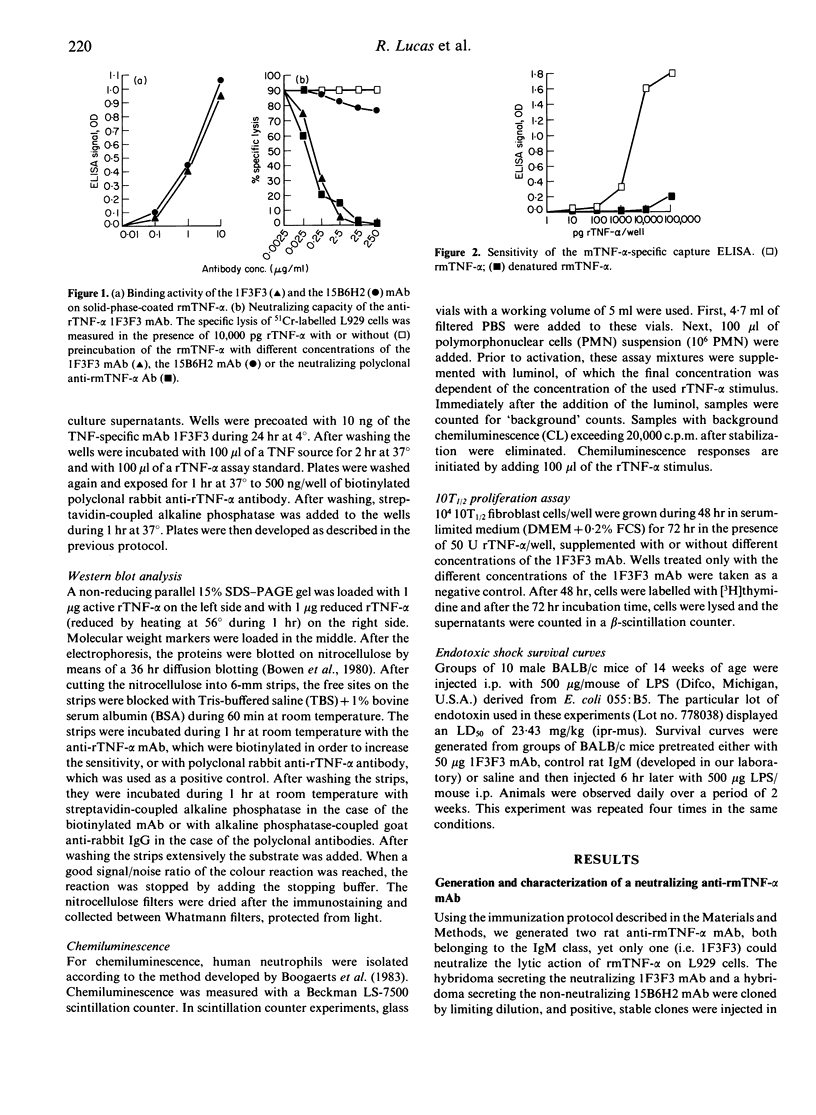
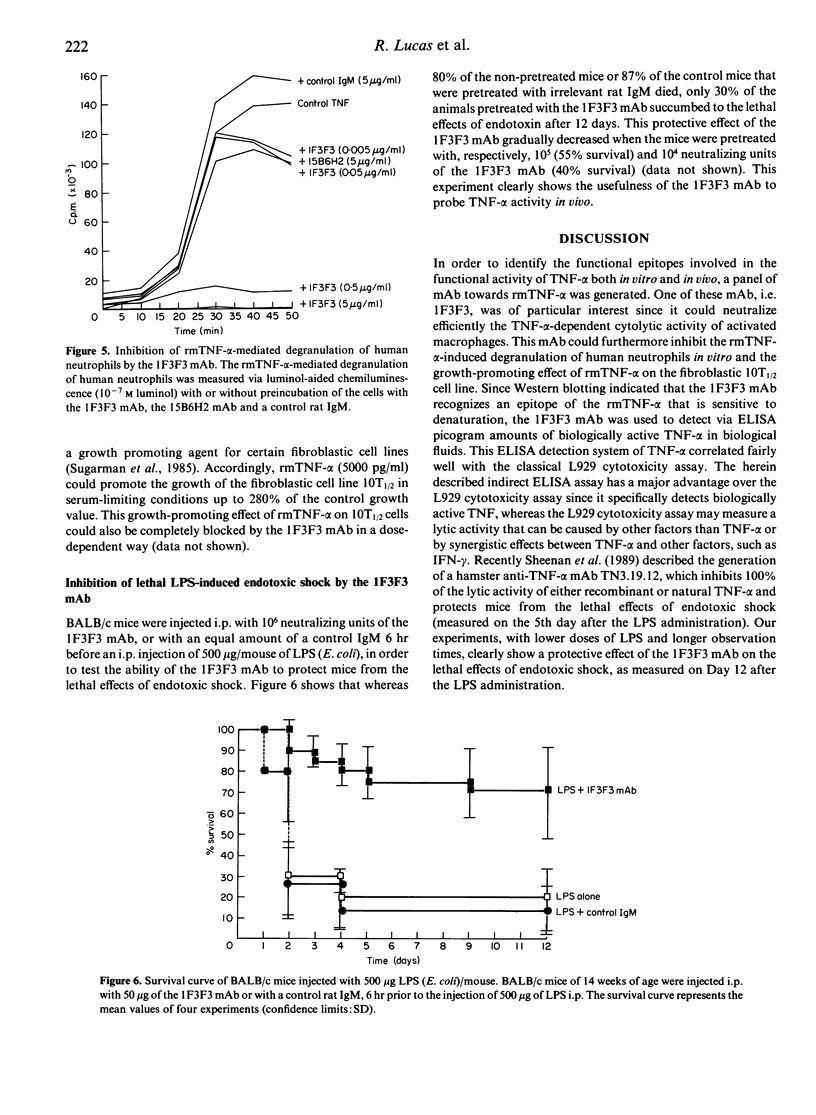
A rat anti-recombinant mouse tumour necrosis factor-alpha (rmTNF-alpha) monoclonal IgM antibody (1F3F3) with high specific binding activity for rmTNF-alpha was generated. The 1F3F3 monoclonal antibody (mAb) neutralizes the cytotoxic activity in vitro of rmTNF-alpha on L929 cells and inhibits the binding of radiolabelled rmTNF-alpha to its putative receptor on L929 cells. The 1F3F3 mAb binds to monomeric, dimeric and trimeric rmTNF-alpha and does not bind to reduced rmTNF-alpha, indicating that the recognized epitope is sensitive to denaturation. Using the 1F3F3 mAb as a capturing antibody and a biotinylated anti-rTNF-alpha as a detecting antibody, we have developed a sandwich ELISA that can specifically detect biologically active mTNF-alpha with a detection limit of 10 pg mTNF-alpha/well. This assay correlates well with the classical L929 cristal violet assay for the detection of bioactive rmTNF-alpha in biological fluids. The 1F3F3 mAb inhibits various in vitro biological activities of the rmTNF-alpha, such as the TNF-alpha-mediated tumoricidal activity of activated macrophages, the rmTNF-alpha-dependent stimulation of neutrophil degranulation and the growth-promoting effect of rmTNF-alpha. In vivo the 1F3F3 mAb inhibits lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced endotoxic shock. In conclusion, the 1F3F3 mAb is a useful tool to probe rmTNF-alpha activity both in vitro and in vivo.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bertolini D. R., Nedwin G. E., Bringman T. S., Smith D. D., Mundy G. R. Stimulation of bone resorption and inhibition of bone formation in vitro by human tumour necrosis factors. Nature. 1986 Feb 6;319(6053):516–518. doi: 10.1038/319516a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowen B., Steinberg J., Laemmli U. K., Weintraub H. The detection of DNA-binding proteins by protein blotting. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Jan 11;8(1):1–20. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carswell E. A., Old L. J., Kassel R. L., Green S., Fiore N., Williamson B. An endotoxin-induced serum factor that causes necrosis of tumors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Sep;72(9):3666–3670. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.9.3666. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaushansky K., Broudy V. C., Harlan J. M., Adamson J. W. Tumor necrosis factor-alpha and tumor necrosis factor-beta (lymphotoxin) stimulate the production of granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor, macrophage colony-stimulating factor, and IL-1 in vivo. J Immunol. 1988 Nov 15;141(10):3410–3415. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirstein M., Baglioni C. Tumor necrosis factor stimulates proliferation of human osteosarcoma cells and accumulation of c-myc messenger RNA. J Cell Physiol. 1988 Mar;134(3):479–484. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041340321. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leibovich S. J., Polverini P. J., Shepard H. M., Wiseman D. M., Shively V., Nuseir N. Macrophage-induced angiogenesis is mediated by tumour necrosis factor-alpha. Nature. 1987 Oct 15;329(6140):630–632. doi: 10.1038/329630a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Markwell M. A., Fox C. F. Surface-specific iodination of membrane proteins of viruses and eucaryotic cells using 1,3,4,6-tetrachloro-3alpha,6alpha-diphenylglycoluril. Biochemistry. 1978 Oct 31;17(22):4807–4817. doi: 10.1021/bi00615a031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Medcalf R. L., Kruithof E. K., Schleuning W. D. Plasminogen activator inhibitor 1 and 2 are tumor necrosis factor/cachectin-responsive genes. J Exp Med. 1988 Aug 1;168(2):751–759. doi: 10.1084/jem.168.2.751. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Remels L. M., De Baetselier P. C. Characterization of 3LL-tumor variants generated by in vitro macrophage-mediated selection. Int J Cancer. 1987 Mar 15;39(3):343–352. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910390313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schreiber R. D., Hicks L. J., Celada A., Buchmeier N. A., Gray P. W. Monoclonal antibodies to murine gamma-interferon which differentially modulate macrophage activation and antiviral activity. J Immunol. 1985 Mar;134(3):1609–1618. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheehan K. C., Ruddle N. H., Schreiber R. D. Generation and characterization of hamster monoclonal antibodies that neutralize murine tumor necrosis factors. J Immunol. 1989 Jun 1;142(11):3884–3893. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugarman B. J., Aggarwal B. B., Hass P. E., Figari I. S., Palladino M. A., Jr, Shepard H. M. Recombinant human tumor necrosis factor-alpha: effects on proliferation of normal and transformed cells in vitro. Science. 1985 Nov 22;230(4728):943–945. doi: 10.1126/science.3933111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Torti F. M., Dieckmann B., Beutler B., Cerami A., Ringold G. M. A macrophage factor inhibits adipocyte gene expression: an in vitro model of cachexia. Science. 1985 Aug 30;229(4716):867–869. doi: 10.1126/science.3839597. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tracey K. J., Beutler B., Lowry S. F., Merryweather J., Wolpe S., Milsark I. W., Hariri R. J., Fahey T. J., 3rd, Zentella A., Albert J. D. Shock and tissue injury induced by recombinant human cachectin. Science. 1986 Oct 24;234(4775):470–474. doi: 10.1126/science.3764421. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Urban J. L., Shepard H. M., Rothstein J. L., Sugarman B. J., Schreiber H. Tumor necrosis factor: a potent effector molecule for tumor cell killing by activated macrophages. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jul;83(14):5233–5237. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.14.5233. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


