Abstract
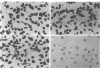
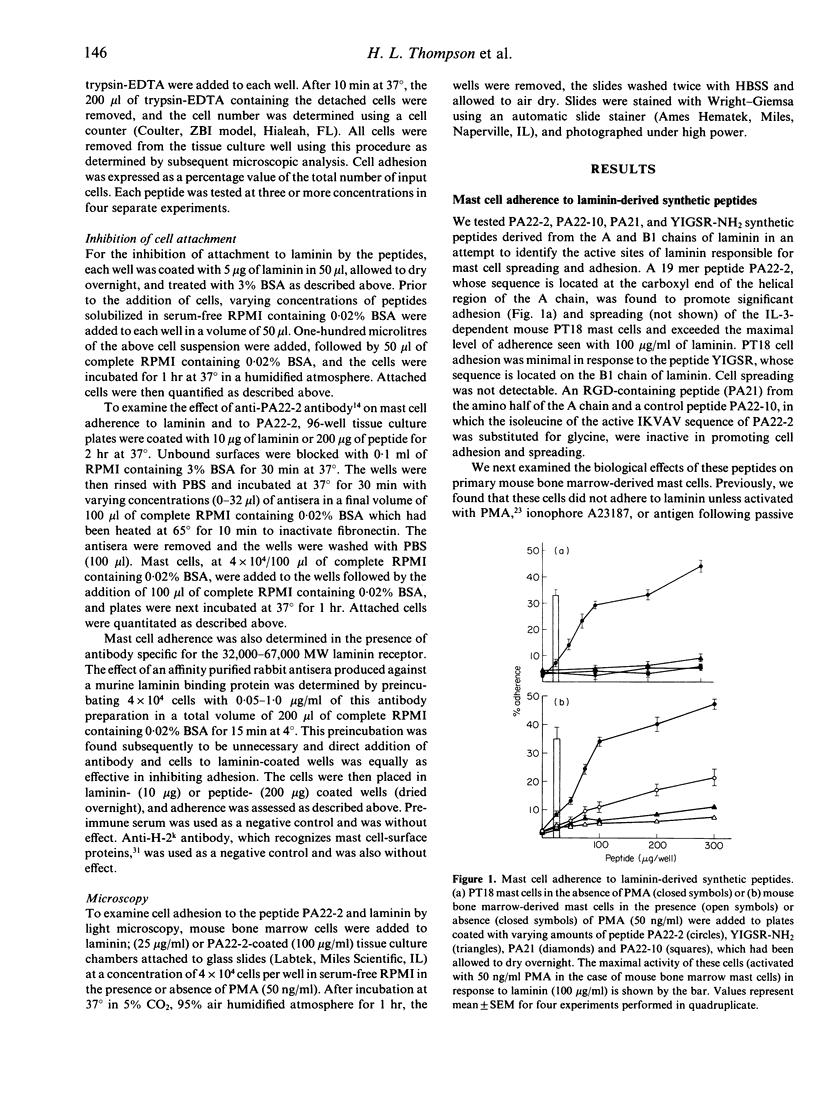
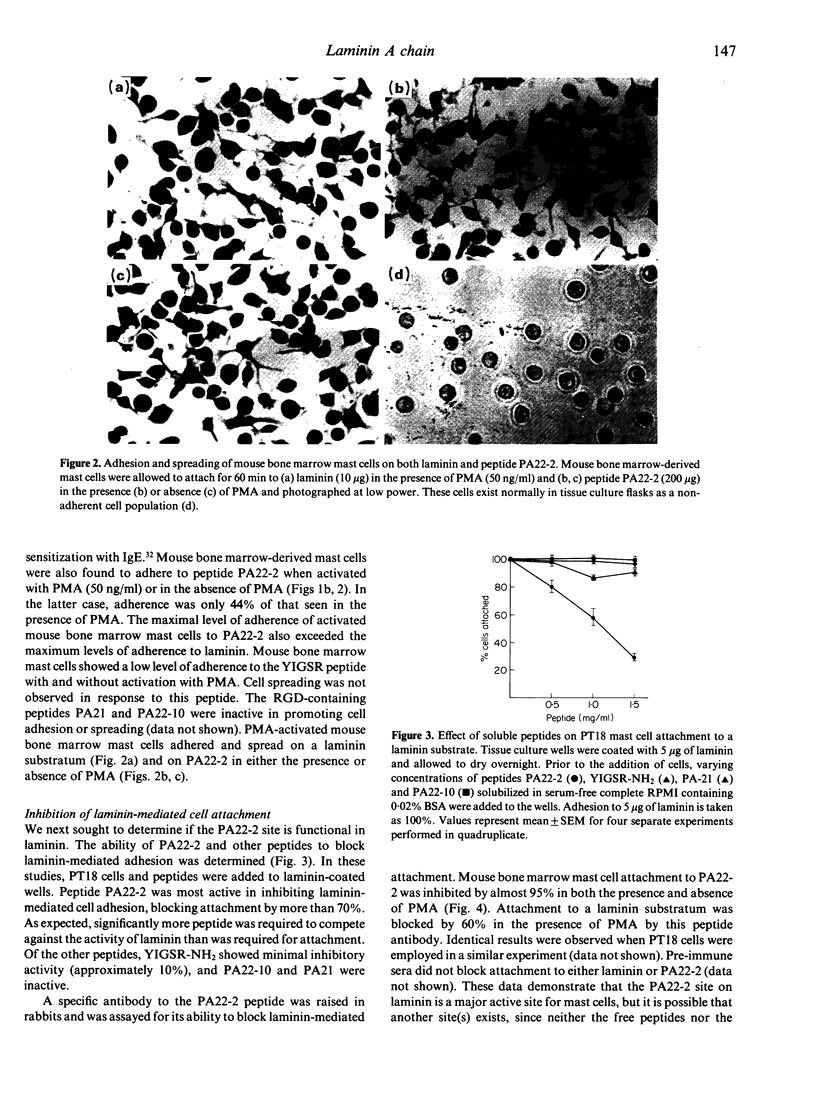
PT18 mast cells and mouse bone marrow-derived mast cells have been shown to adhere and spread when in contact with a laminin substratum. Mouse bone marrow cells, however, first require activation with phorbol myristate acetate (PMA), ionophore, or antigen-specific IgE with antigen in order to exhibit these phenomena. Here, we have studied the interaction of these cells with three active synthetic peptides derived from different domains of laminin. PT18 cells and mouse bone marrow mast cells attached and spread on the 19 amino acid synthetic laminin A chain-derived peptide PA22-2, containing the active five amino acid sequence IKVAV, and this attachment did not require prior activation of the mouse bone marrow mast cells with PMA or IgE plus antigen. These cells did not adhere to the B1 chain peptide YIGSR-NH2 or the RGD-containing peptide from the A chain. PT18 cell adherence to laminin was inhibited by soluble peptide PA22-2, but not by either YIGSR-NH2, the RGD-containing, or control peptides. Antisera to the PA22-2 peptide completely abolished adherence to PA22-2, but only partially inhibited mast cell adherence to laminin. Antibody to the 67,000-32,000 MW laminin-binding protein receptor blocked cell adhesion to laminin and to the active A chain peptide. Thus, mast cell adhesion and spreading on laminin may be mediated by an interaction with the IKVAV sequence on the laminin A chain.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aumailley M., Nurcombe V., Edgar D., Paulsson M., Timpl R. The cellular interactions of laminin fragments. Cell adhesion correlates with two fragment-specific high affinity binding sites. J Biol Chem. 1987 Aug 25;262(24):11532–11538. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barlow D. P., Green N. M., Kurkinen M., Hogan B. L. Sequencing of laminin B chain cDNAs reveals C-terminal regions of coiled-coil alpha-helix. EMBO J. 1984 Oct;3(10):2355–2362. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02140.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bender J. G., Van Epps D. E., Stewart C. C. Characterization of granulocytes and mast cells in cultures of mouse bone marrow stimulated with interleukin-3. J Cell Physiol. 1988 Apr;135(1):71–78. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041350110. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark-Lewis I., Schrader J. W. P cell-stimulating factor: biochemical characterization of a new T cell-derived factor. J Immunol. 1981 Nov;127(5):1941–1947. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clément B., Segui-Real B., Savagner P., Kleinman H. K., Yamada Y. Hepatocyte attachment to laminin is mediated through multiple receptors. J Cell Biol. 1990 Jan;110(1):185–192. doi: 10.1083/jcb.110.1.185. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engel J., Odermatt E., Engel A., Madri J. A., Furthmayr H., Rohde H., Timpl R. Shapes, domain organizations and flexibility of laminin and fibronectin, two multifunctional proteins of the extracellular matrix. J Mol Biol. 1981 Jul 25;150(1):97–120. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90326-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gehlsen K. R., Dillner L., Engvall E., Ruoslahti E. The human laminin receptor is a member of the integrin family of cell adhesion receptors. Science. 1988 Sep 2;241(4870):1228–1229. doi: 10.1126/science.2970671. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goding J. W., Burns G. F. Monoclonal antibody OKT-9 recognizes the receptor for transferrin on human acute lymphocytic leukemia cells. J Immunol. 1981 Sep;127(3):1256–1258. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodman S. L., Deutzmann R., von der Mark K. Two distinct cell-binding domains in laminin can independently promote nonneuronal cell adhesion and spreading. J Cell Biol. 1987 Jul;105(1):589–598. doi: 10.1083/jcb.105.1.589. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graf J., Iwamoto Y., Sasaki M., Martin G. R., Kleinman H. K., Robey F. A., Yamada Y. Identification of an amino acid sequence in laminin mediating cell attachment, chemotaxis, and receptor binding. Cell. 1987 Mar 27;48(6):989–996. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90707-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horwitz A., Duggan K., Greggs R., Decker C., Buck C. The cell substrate attachment (CSAT) antigen has properties of a receptor for laminin and fibronectin. J Cell Biol. 1985 Dec;101(6):2134–2144. doi: 10.1083/jcb.101.6.2134. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hynes R. O. Integrins: a family of cell surface receptors. Cell. 1987 Feb 27;48(4):549–554. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90233-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ihle J. N., Keller J., Oroszlan S., Henderson L. E., Copeland T. D., Fitch F., Prystowsky M. B., Goldwasser E., Schrader J. W., Palaszynski E. Biologic properties of homogeneous interleukin 3. I. Demonstration of WEHI-3 growth factor activity, mast cell growth factor activity, p cell-stimulating factor activity, colony-stimulating factor activity, and histamine-producing cell-stimulating factor activity. J Immunol. 1983 Jul;131(1):282–287. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iwamoto Y., Graf J., Sasaki M., Kleinman H. K., Greatorex D. R., Martin G. R., Robey F. A., Yamada Y. Synthetic pentapeptide from the B1 chain of laminin promotes B16F10 melanoma cell migration. J Cell Physiol. 1988 Feb;134(2):287–291. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041340216. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iwamoto Y., Robey F. A., Graf J., Sasaki M., Kleinman H. K., Yamada Y., Martin G. R. YIGSR, a synthetic laminin pentapeptide, inhibits experimental metastasis formation. Science. 1987 Nov 20;238(4830):1132–1134. doi: 10.1126/science.2961059. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanemoto T., Reich R., Royce L., Greatorex D., Adler S. H., Shiraishi N., Martin G. R., Yamada Y., Kleinman H. K. Identification of an amino acid sequence from the laminin A chain that stimulates metastasis and collagenase IV production. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Mar;87(6):2279–2283. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.6.2279. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kato S., Ben T. L., De Luca L. M. Phorbol esters enhance attachment of NIH/3T3 cells to laminin and type IV collagen substrates. Exp Cell Res. 1988 Nov;179(1):31–41. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(88)90345-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleinman H. K., Cannon F. B., Laurie G. W., Hassell J. R., Aumailley M., Terranova V. P., Martin G. R., DuBois-Dalcq M. Biological activities of laminin. J Cell Biochem. 1985;27(4):317–325. doi: 10.1002/jcb.240270402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleinman H. K., Ogle R. C., Cannon F. B., Little C. D., Sweeney T. M., Luckenbill-Edds L. Laminin receptors for neurite formation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Feb;85(4):1282–1286. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.4.1282. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mercurio A. M., Shaw L. M. Macrophage interactions with laminin: PMA selectively induces the adherence and spreading of mouse macrophages on a laminin substratum. J Cell Biol. 1988 Nov;107(5):1873–1880. doi: 10.1083/jcb.107.5.1873. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palm S. L., McCarthy J. B., Furcht L. T. Alternative model for the internal structure of laminin. Biochemistry. 1985 Dec 17;24(26):7753–7760. doi: 10.1021/bi00347a038. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paulsson M., Deutzmann R., Timpl R., Dalzoppo D., Odermatt E., Engel J. Evidence for coiled-coil alpha-helical regions in the long arm of laminin. EMBO J. 1985 Feb;4(2):309–316. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03630.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Razin E., Ihle J. N., Seldin D., Mencia-Huerta J. M., Katz H. R., LeBlanc P. A., Hein A., Caulfield J. P., Austen K. F., Stevens R. L. Interleukin 3: A differentiation and growth factor for the mouse mast cell that contains chondroitin sulfate E proteoglycan. J Immunol. 1984 Mar;132(3):1479–1486. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reich R., Thompson E. W., Iwamoto Y., Martin G. R., Deason J. R., Fuller G. C., Miskin R. Effects of inhibitors of plasminogen activator, serine proteinases, and collagenase IV on the invasion of basement membranes by metastatic cells. Cancer Res. 1988 Jun 15;48(12):3307–3312. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robey F. A., Fields R. L. Automated synthesis of N-bromoacetyl-modified peptides for the preparation of synthetic peptide polymers, peptide-protein conjugates, and cyclic peptides. Anal Biochem. 1989 Mar;177(2):373–377. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(89)90068-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sasaki M., Kleinman H. K., Huber H., Deutzmann R., Yamada Y. Laminin, a multidomain protein. The A chain has a unique globular domain and homology with the basement membrane proteoglycan and the laminin B chains. J Biol Chem. 1988 Nov 15;263(32):16536–16544. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tashiro K., Sephel G. C., Weeks B., Sasaki M., Martin G. R., Kleinman H. K., Yamada Y. A synthetic peptide containing the IKVAV sequence from the A chain of laminin mediates cell attachment, migration, and neurite outgrowth. J Biol Chem. 1989 Sep 25;264(27):16174–16182. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson H. L., Burbelo P. D., Metcalfe D. D. Regulation of adhesion of mouse bone marrow-derived mast cells to laminin. J Immunol. 1990 Nov 15;145(10):3425–3431. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson H. L., Burbelo P. D., Segui-Real B., Yamada Y., Metcalfe D. D. Laminin promotes mast cell attachment. J Immunol. 1989 Oct 1;143(7):2323–2327. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Timpl R., Johansson S., van Delden V., Oberbäumer I., Hök M. Characterization of protease-resistant fragments of laminin mediating attachment and spreading of rat hepatocytes. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jul 25;258(14):8922–8927. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Timpl R., Rohde H., Robey P. G., Rennard S. I., Foidart J. M., Martin G. R. Laminin--a glycoprotein from basement membranes. J Biol Chem. 1979 Oct 10;254(19):9933–9937. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamada K. M., Kennedy D. W. Dualistic nature of adhesive protein function: fibronectin and its biologically active peptide fragments can autoinhibit fibronectin function. J Cell Biol. 1984 Jul;99(1 Pt 1):29–36. doi: 10.1083/jcb.99.1.29. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yow H. K., Wong J. M., Chen H. S., Lee C. G., Davis S., Steele G. D., Jr, Chen L. B. Increased mRNA expression of a laminin-binding protein in human colon carcinoma: complete sequence of a full-length cDNA encoding the protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Sep;85(17):6394–6398. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.17.6394. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von der Mark K., Kühl U. Laminin and its receptor. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1985 Dec 17;823(2):147–160. doi: 10.1016/0304-419x(85)90010-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]