Abstract
Defined lines of primary human renal epithelial cells were established and their expression of class II major histocompatibility (MHC) antigens was up-regulated by culture with interferon-gamma (IFN-gamma). The ability of these cells to stimulate the proliferation of allogeneic peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMC) was compared with that of endothelial cells and splenic mononuclear cells. It was found that both endothelial and splenic cells stimulated lympho-proliferation but that cultured renal epithelial cells were non-stimulatory. The failure of proliferation by allogeneic lymphocytes in culture with epithelial cells was not overcome by treatment with interleukin-1 (IL-1) or indomethacin. However, addition of IL-2 to mixed cultures of allogeneic PBMC and renal epithelial cells stimulated lympho-proliferation and allowed the generation of lymphoid cell lines which mediated non-specific lysis of renal epithelial cell lines. Stimulation of PBMC by mixed lymphocyte culture yielded an allospecific T-cell line which was added either to renal epithelial cells from the same donor as the stimulator cells used in the priming reaction or from a third-party donor; lympho-proliferation was observed in the specific secondary reaction but not in the non-specific reaction. These findings indicate that class II MHC antigen-expressing epithelial cells within a renal allograft may not initially stimulate the proliferation of resting allospecific recipient lymphocytes. However, within a rejecting graft it is likely that high local concentrations of IL-2 are present and that many of the infiltrating allospecific lymphocytes will be primed by previous contact with donor antigen-presenting cells, such as vascular endothelial cells or dendritic cells. Therefore, expression of class II MHC antigens by epithelial cells within the microenvironment of a renal allograft may render such cells immunogenic and able to play a direct role in the lymphocyte-mediated intragraft rejection process.
Full text
PDF

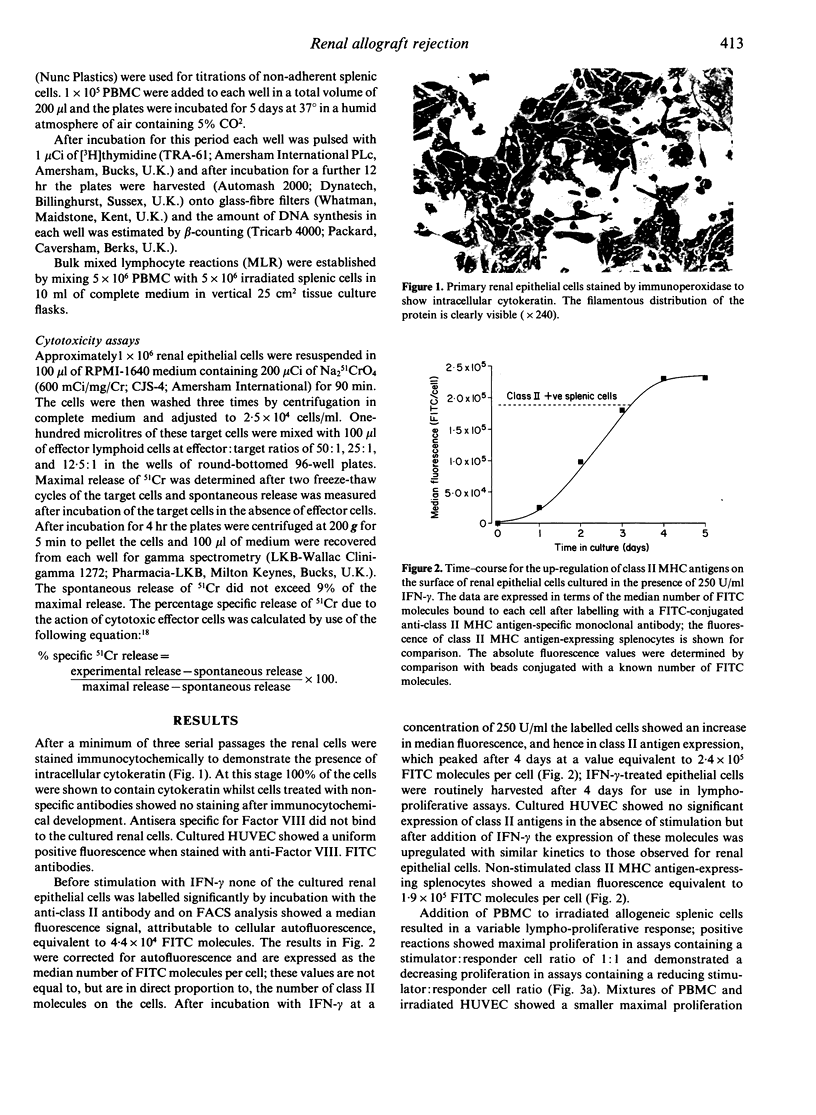
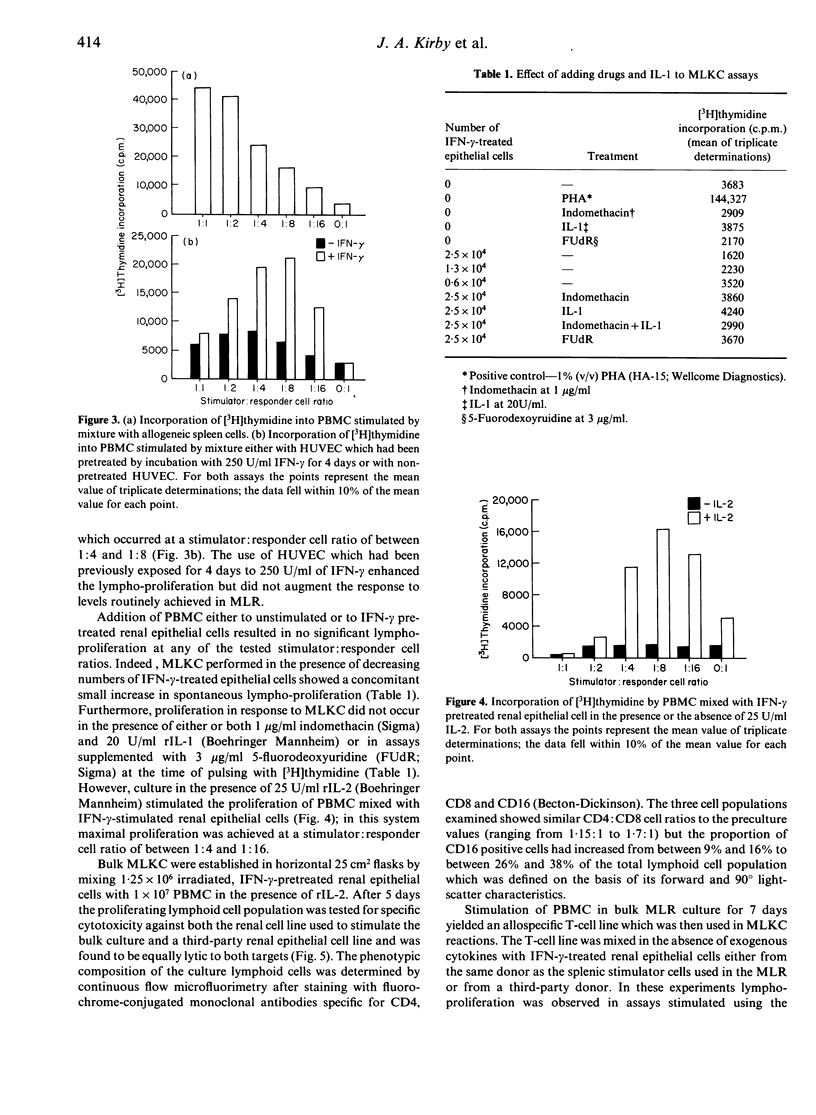


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bishop G. A., Hall B. M., Suranyi M. G., Tiller D. J., Horvath J. S., Duggin G. G. Expression of HLA antigens on renal tubular cells in culture. I. Evidence that mixed lymphocyte culture supernatants and gamma interferon increase both class I and class II HLA antigens. Transplantation. 1986 Dec;42(6):671–679. doi: 10.1097/00007890-198612000-00018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bishop G. A., Waugh J. A., Hall B. M. Expression of HLA antigens on renal tubular cells in culture. II. Effect of increased HLA antigen expression on tubular cell stimulation of lymphocyte activation and on their vulnerability to cell-mediated lysis. Transplantation. 1988 Aug;46(2):303–310. doi: 10.1097/00007890-198808000-00022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brunner K. T., Mauel J., Cerottini J. C., Chapuis B. Quantitative assay of the lytic action of immune lymphoid cells on 51-Cr-labelled allogeneic target cells in vitro; inhibition by isoantibody and by drugs. Immunology. 1968 Feb;14(2):181–196. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esquenazi V., Fuller L., Pardo V., Roth D., Milgrom M., Miller J. In vivo and in vitro induction of class II molecules on canine renal cells and their effect on the mixed lymphocyte kidney cell culture. Transplantation. 1987 Nov;44(5):680–692. doi: 10.1097/00007890-198711000-00017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franke W. W., Weber K., Osborn M., Schmid E., Freudenstein C. Antibody to prekeratin. Decoration of tonofilament like arrays in various cells of epithelial character. Exp Cell Res. 1978 Oct 15;116(2):429–445. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(78)90466-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frohman M., Cowing C. Presentation of antigen by B cells: functional dependence on radiation dose, interleukins, cellular activation, and differential glycosylation. J Immunol. 1985 Apr;134(4):2269–2275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geppert T. D., Lipsky P. E. Antigen presentation by interferon-gamma-treated endothelial cells and fibroblasts: differential ability to function as antigen-presenting cells despite comparable Ia expression. J Immunol. 1985 Dec;135(6):3750–3762. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilbert S. F., Migeon B. R. D-valine as a selective agent for normal human and rodent epithelial cells in culture. Cell. 1975 May;5(1):11–17. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(75)90086-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall B. M., Bishop G. A., Duggin G. G., Horvath J. S., Philips J., Tiller D. J. Increased expression of HLA-DR antigens on renal tubular cells in renal transplants: relevance to the rejection response. Lancet. 1984 Aug 4;2(8397):247–251. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(84)90297-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halloran P. F., Wadgymar A., Autenried P. The regulation of expression of major histocompatibility complex products. Transplantation. 1986 Apr;41(4):413–420. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harding C. V., Unanue E. R. Quantitation of antigen-presenting cell MHC class II/peptide complexes necessary for T-cell stimulation. Nature. 1990 Aug 9;346(6284):574–576. doi: 10.1038/346574a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirschberg H., Evensen S. A., Henriksen T., Thorsby E. The human mixed lymphocyte-endothelium culture interaction. Transplantation. 1975 Jun;19(6):495–504. doi: 10.1097/00007890-197506000-00008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jenkins M. K., Schwartz R. H. Antigen presentation by chemically modified splenocytes induces antigen-specific T cell unresponsiveness in vitro and in vivo. J Exp Med. 1987 Feb 1;165(2):302–319. doi: 10.1084/jem.165.2.302. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirby J. A., Forsythe J. L., Proud G., Taylor R. M. Renal allograft rejection: possible involvement of lymphokine-activated killer cells. Immunology. 1989 May;67(1):62–67. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirby J. A., Forsythe J. L., Simm A., Proud G., Taylor R. M. Renal allograft rejection: protection of renal tubular epithelial cells from lymphokine activated killer cell mediated lysis by pretreatment with cytokines. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 1989;4(9):824–828. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lechler R. I., Lombardi G., Batchelor J. R., Reinsmoen N., Bach F. H. The molecular basis of alloreactivity. Immunol Today. 1990 Mar;11(3):83–88. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(90)90033-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Markmann J., Lo D., Naji A., Palmiter R. D., Brinster R. L., Heber-Katz E. Antigen presenting function of class II MHC expressing pancreatic beta cells. Nature. 1988 Dec 1;336(6198):476–479. doi: 10.1038/336476a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miltenburg A. M., Meijer-Paape M. E., Daha M. R., Paul L. C. Lymphokine-activated killer cells lyse human renal cancer cell lines and cultured normal kidney cells. Immunology. 1988 Apr;63(4):729–731. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morahan G., Brennan F. E., Bhathal P. S., Allison J., Cox K. O., Miller J. F. Expression in transgenic mice of class I histocompatibility antigens controlled by the metallothionein promoter. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 May;86(10):3782–3786. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.10.3782. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mukherji B., Guha A., Loomis R., Ergin M. T. Cell-mediated amplification and down regulation of cytotoxic immune response against autologous human cancer. J Immunol. 1987 Mar 15;138(6):1987–1991. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy K. M., Weaver C. T., Elish M., Allen P. M., Loh D. Y. Peripheral tolerance to allogeneic class II histocompatibility antigens expressed in transgenic mice: evidence against a clonal-deletion mechanism. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Dec;86(24):10034–10038. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.24.10034. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pober J. S., Collins T., Gimbrone M. A., Jr, Cotran R. S., Gitlin J. D., Fiers W., Clayberger C., Krensky A. M., Burakoff S. J., Reiss C. S. Lymphocytes recognize human vascular endothelial and dermal fibroblast Ia antigens induced by recombinant immune interferon. Nature. 1983 Oct 20;305(5936):726–729. doi: 10.1038/305726a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Romaniuk A., Prop J., Petersen A. H., Wildevuur C. R., Nieuwenhuis P. Expression of class II major histocompatibility complex antigens by bronchial epithelium in rat lung allografts. Transplantation. 1987 Aug;44(2):209–214. doi: 10.1097/00007890-198708000-00007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rose M. L., Coles M. I., Griffin R. J., Pomerance A., Yacoub M. H. Expression of class I and class II major histocompatibility antigens in normal and transplanted human heart. Transplantation. 1986 Jun;41(6):776–780. doi: 10.1097/00007890-198606000-00021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth D., Fuller L., Esquenazi V., Kyriakides G. K., Pardo V., Miller J. The biologic significance of the mixed lymphocyte kidney culture in humans. Transplantation. 1985 Oct;40(4):376–383. doi: 10.1097/00007890-198510000-00007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scala G., Oppenheim J. J. Antigen presentation by human monocytes: evidence for stimulant processing and requirement for interleukin 1. J Immunol. 1983 Sep;131(3):1160–1166. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vegt P. A., van der Linden C. J., Daemen A. J., Jeekel J., Buurman W. A. Lymphocyte stimulation by canine kidney cells. Transplantation. 1982 Sep;34(3):134–139. doi: 10.1097/00007890-198209000-00004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



