Abstract
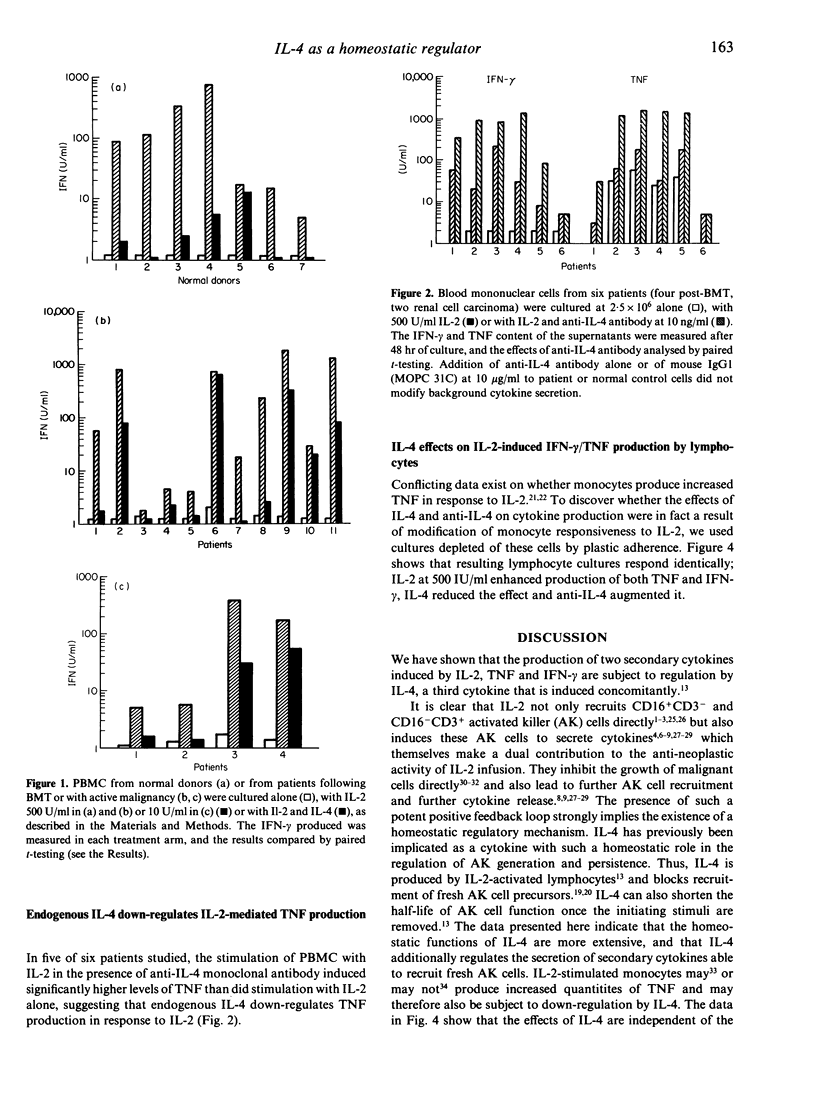
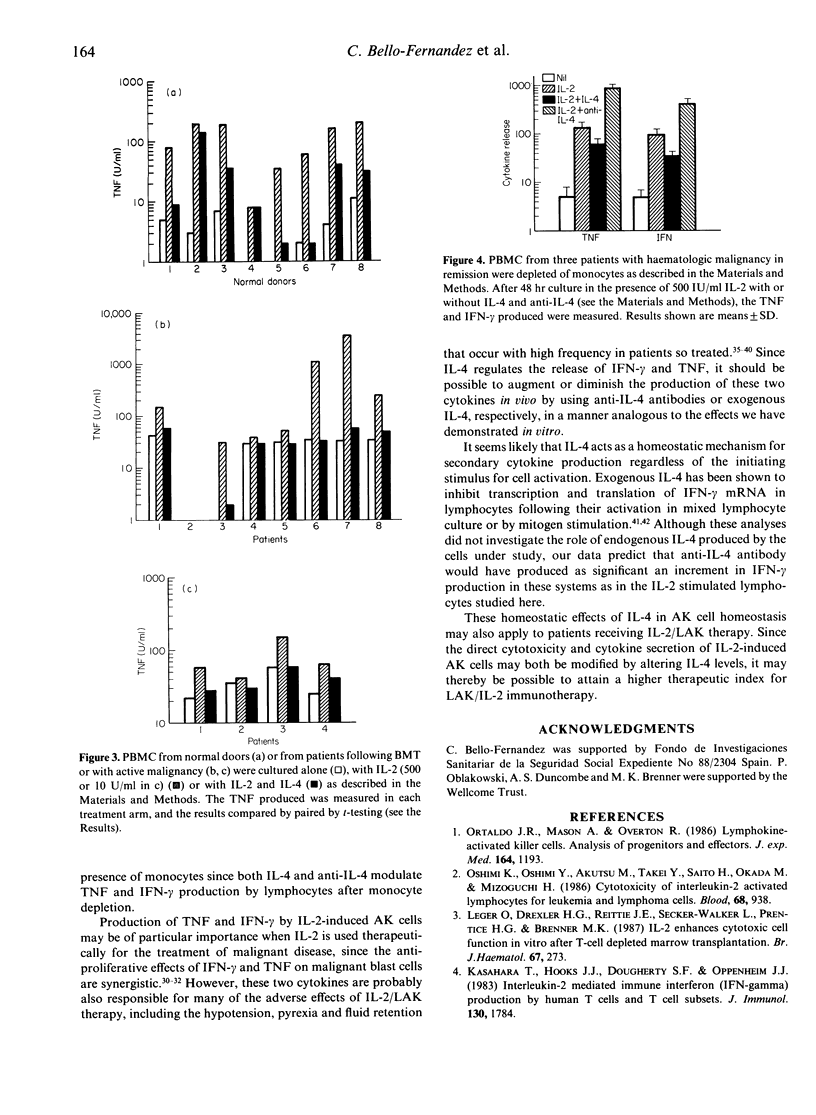
Interleukin-4 (IL-4) is a cytokine secreted by interleukin-2 (IL-2)-activated lymphocytes. IL-2-stimulated lymphocytes also secrete two cytokines, tumour necrosis factor (TNF) and gamma-interferon (IFN-gamma), which contribute to effector function and which may themselves recruit fresh, cytokine-secreting effector cells. We have now investigated whether the IL-4 induced is able to homeostatically regulate secretion of the TNF and IFN-gamma. Peripheral blood mononuclear cells or lymphocytes from normal donors and from patients with neoplastic disease were cultured in the presence of IL-2 alone, IL-4 alone or with both cytokines. IL-2 induced high levels of TNF and IFN-gamma secretion in both groups. The addition of recombinant IL-4 to these IL-2-stimulated cultures lead to significant inhibition of IFN-gamma and TNF production. IFN-gamma secretion was reduced by 50-99% in normal donors and by between 11% and 99% in patients (P less than 0.001). TNF levels induced by IL-2 were similarly reduced by IL-4 both in normal donors (P less than 0.003) and in patients (P less than 0.01). These inhibitory effects were produced by IL-4 at doses of IL-2 attainable in vivo. Inhibition appears to represent a homeostatic regulatory mechanism which may limit recruitment of fresh activated killer (AK) cells. When endogenous IL-4 activity in IL-2-activated lymphocytes was blocked by anti-IL-4 antibody, significantly higher levels of IFN-gamma and TNF were secreted (P less than 0.05). Since both TNF and IFN-gamma may contribute to the anti-neoplastic action of IL-2, manipulating the level of IL-4 activity in vivo could augment the benefits of IL-2 immunotherapy.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Broxmeyer H. E., Williams D. E., Lu L., Cooper S., Anderson S. L., Beyer G. S., Hoffman R., Rubin B. Y. The suppressive influences of human tumor necrosis factors on bone marrow hematopoietic progenitor cells from normal donors and patients with leukemia: synergism of tumor necrosis factor and interferon-gamma. J Immunol. 1986 Jun 15;136(12):4487–4495. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chouaib S., Bertoglio J., Blay J. Y., Marchiol-Fournigault C., Fradelizi D. Generation of lymphokine-activated killer cells: synergy between tumor necrosis factor and interleukin 2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Sep;85(18):6875–6879. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.18.6875. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Economou J. S., McBride W. H., Essner R., Rhoades K., Golub S., Holmes E. C., Morton D. L. Tumour necrosis factor production by IL-2-activated macrophages in vitro and in vivo. Immunology. 1989 Aug;67(4):514–519. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farrant J., Newton C. A., North M. E., Weyman C., Brenner M. K. Production of antibody by human B cells under serum-free conditions. J Immunol Methods. 1984 Mar 30;68(1-2):25–34. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(84)90133-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaynor E. R., Vitek L., Sticklin L., Creekmore S. P., Ferraro M. E., Thomas J. X., Jr, Fisher S. G., Fisher R. I. The hemodynamic effects of treatment with interleukin-2 and lymphokine-activated killer cells. Ann Intern Med. 1988 Dec 15;109(12):953–958. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-109-12-953. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gemlo B. T., Palladino M. A., Jr, Jaffe H. S., Espevik T. P., Rayner A. A. Circulating cytokines in patients with metastatic cancer treated with recombinant interleukin 2 and lymphokine-activated killer cells. Cancer Res. 1988 Oct 15;48(20):5864–5867. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gottlieb D. J., Brenner M. K., Heslop H. E., Bianchi A. C., Bello-Fernandez C., Mehta A. B., Newland A. C., Galazka A. R., Scott E. M., Hoffbrand A. V. A phase I clinical trial of recombinant interleukin 2 following high dose chemo-radiotherapy for haematological malignancy: applicability to the elimination of minimal residual disease. Br J Cancer. 1989 Oct;60(4):610–615. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1989.324. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gottlieb D. J., Prentice H. G., Heslop H. E., Bello-Fernandez C., Bianchi A. C., Galazka A. R., Brenner M. K. Effects of recombinant interleukin-2 administration on cytotoxic function following high-dose chemo-radiotherapy for hematological malignancy. Blood. 1989 Nov 15;74(7):2335–2342. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heslop H. E., Gottlieb D. J., Bianchi A. C., Meager A., Prentice H. G., Mehta A. B., Hoffbrand A. V., Brenner M. K. In vivo induction of gamma interferon and tumor necrosis factor by interleukin-2 infusion following intensive chemotherapy or autologous marrow transplantation. Blood. 1989 Sep;74(4):1374–1380. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heslop H. E., Gottlieb D. J., Reittie J. E., Bello-Fernandez C., Meager A., Prentice H. G., Brenner M. K. Spontaneous and interleukin 2 induced secretion of tumour necrosis factor and gamma interferon following autologous marrow transplantation or chemotherapy. Br J Haematol. 1989 Jun;72(2):122–126. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1989.tb07671.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howard M., Farrar J., Hilfiker M., Johnson B., Takatsu K., Hamaoka T., Paul W. E. Identification of a T cell-derived b cell growth factor distinct from interleukin 2. J Exp Med. 1982 Mar 1;155(3):914–923. doi: 10.1084/jem.155.3.914. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kasahara T., Hooks J. J., Dougherty S. F., Oppenheim J. J. Interleukin 2-mediated immune interferon (IFN-gamma) production by human T cells and T cell subsets. J Immunol. 1983 Apr;130(4):1784–1789. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kasid A., Director E. P., Rosenberg S. A. Induction of endogenous cytokine-mRNA in circulating peripheral blood mononuclear cells by IL-2 administration to cancer patients. J Immunol. 1989 Jul 15;143(2):736–739. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kovacs E. J., Beckner S. K., Longo D. L., Varesio L., Young H. A. Cytokine gene expression during the generation of human lymphokine-activated killer cells: early induction of interleukin 1 beta by interleukin 2. Cancer Res. 1989 Feb 15;49(4):940–944. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leger O., Drexler H. G., Reittie J. E., Secker-Walker L., Prentice H. G., Brenner M. K. Interleukin 2 enhances cytotoxic cell function in vitro after T-cell depleted marrow transplantation. Br J Haematol. 1987 Nov;67(3):273–279. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1987.tb02347.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Limb G. A., Meager A., Woolley J., Wadhwa M., Biggerstaff J., Brown K. A., Wolstencroft R. A. Release of cytokines during generation of lymphokine-activated killer (LAK) cells by IL-2. Immunology. 1989 Dec;68(4):514–519. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lotze M. T., Matory Y. L., Ettinghausen S. E., Rayner A. A., Sharrow S. O., Seipp C. A., Custer M. C., Rosenberg S. A. In vivo administration of purified human interleukin 2. II. Half life, immunologic effects, and expansion of peripheral lymphoid cells in vivo with recombinant IL 2. J Immunol. 1985 Oct;135(4):2865–2875. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meager A., Parti S., Leung H., Peil E., Mahon B. Preparation and characterization of monoclonal antibodies directed against antigenic determinants of recombinant human tumour necrosis factor (rTNF). Hybridoma. 1987 Jun;6(3):305–311. doi: 10.1089/hyb.1987.6.305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munker R., Koeffler P. In vitro action of tumor necrosis factor on myeloid leukemia cells. Blood. 1987 Apr;69(4):1102–1108. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nedwin G. E., Svedersky L. P., Bringman T. S., Palladino M. A., Jr, Goeddel D. V. Effect of interleukin 2, interferon-gamma, and mitogens on the production of tumor necrosis factors alpha and beta. J Immunol. 1985 Oct;135(4):2492–2497. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ortaldo J. R., Mason A., Overton R. Lymphokine-activated killer cells. Analysis of progenitors and effectors. J Exp Med. 1986 Oct 1;164(4):1193–1205. doi: 10.1084/jem.164.4.1193. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oshimi K., Oshimi Y., Akutsu M., Takei Y., Saito H., Okada M., Mizoguchi H. Cytotoxicity of interleukin 2-activated lymphocytes for leukemia and lymphoma cells. Blood. 1986 Oct;68(4):938–948. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ostensen M. E., Thiele D. L., Lipsky P. E. Tumor necrosis factor-alpha enhances cytolytic activity of human natural killer cells. J Immunol. 1987 Jun 15;138(12):4185–4191. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peleman R., Wu J., Fargeas C., Delespesse G. Recombinant interleukin 4 suppresses the production of interferon gamma by human mononuclear cells. J Exp Med. 1989 Nov 1;170(5):1751–1756. doi: 10.1084/jem.170.5.1751. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peschel C., Paul W. E., Ohara J., Green I. Effects of B cell stimulatory factor-1/interleukin 4 on hematopoietic progenitor cells. Blood. 1987 Jul;70(1):254–263. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Price G., Brenner M. K., Prentice H. G., Hoffbrand A. V., Newland A. C. Cytotoxic effects of tumour necrosis factor and gamma-interferon on acute myeloid leukaemia blasts. Br J Cancer. 1987 Mar;55(3):287–290. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1987.55. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reittie J. E., Gottlieb D., Heslop H. E., Leger O., Drexler H. G., Hazlehurst G., Hoffbrand A. V., Prentice H. G., Brenner M. K. Endogenously generated activated killer cells circulate after autologous and allogeneic marrow transplantation but not after chemotherapy. Blood. 1989 Apr;73(5):1351–1358. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rooney C. M., Wimperis J. Z., Brenner M. K., Patterson J., Hoffbrand A. V., Prentice H. G. Natural killer cell activity following T-cell depleted allogeneic bone marrow transplantation. Br J Haematol. 1986 Mar;62(3):413–420. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1986.tb02952.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg S. A., Lotze M. T., Muul L. M., Chang A. E., Avis F. P., Leitman S., Linehan W. M., Robertson C. N., Lee R. E., Rubin J. T. A progress report on the treatment of 157 patients with advanced cancer using lymphokine-activated killer cells and interleukin-2 or high-dose interleukin-2 alone. N Engl J Med. 1987 Apr 9;316(15):889–897. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198704093161501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spits H., Yssel H., Paliard X., Kastelein R., Figdor C., de Vries J. E. IL-4 inhibits IL-2-mediated induction of human lymphokine-activated killer cells, but not the generation of antigen-specific cytotoxic T lymphocytes in mixed leukocyte cultures. J Immunol. 1988 Jul 1;141(1):29–36. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spits H., Yssel H., Takebe Y., Arai N., Yokota T., Lee F., Arai K., Banchereau J., de Vries J. E. Recombinant interleukin 4 promotes the growth of human T cells. J Immunol. 1987 Aug 15;139(4):1142–1147. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson J. A., Lee D. J., Lindgren C. G., Benz L. A., Collins C., Levitt D., Fefer A. Influence of dose and duration of infusion of interleukin-2 on toxicity and immunomodulation. J Clin Oncol. 1988 Apr;6(4):669–678. doi: 10.1200/JCO.1988.6.4.669. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vercelli D., Jabara H. H., Lauener R. P., Geha R. S. IL-4 inhibits the synthesis of IFN-gamma and induces the synthesis of IgE in human mixed lymphocyte cultures. J Immunol. 1990 Jan 15;144(2):570–573. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vilcek J., Henriksen-Destefano D., Siegel D., Klion A., Robb R. J., Le J. Regulation of IFN-gamma induction in human peripheral blood cells by exogenous and endogenously produced interleukin 2. J Immunol. 1985 Sep;135(3):1851–1856. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- West W. H., Tauer K. W., Yannelli J. R., Marshall G. D., Orr D. W., Thurman G. B., Oldham R. K. Constant-infusion recombinant interleukin-2 in adoptive immunotherapy of advanced cancer. N Engl J Med. 1987 Apr 9;316(15):898–905. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198704093161502. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Widmer M. B., Acres R. B., Sassenfeld H. M., Grabstein K. H. Regulation of cytolytic cell populations from human peripheral blood by B cell stimulatory factor 1 (interleukin 4). J Exp Med. 1987 Nov 1;166(5):1447–1455. doi: 10.1084/jem.166.5.1447. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yokota T., Otsuka T., Mosmann T., Banchereau J., DeFrance T., Blanchard D., De Vries J. E., Lee F., Arai K. Isolation and characterization of a human interleukin cDNA clone, homologous to mouse B-cell stimulatory factor 1, that expresses B-cell- and T-cell-stimulating activities. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Aug;83(16):5894–5898. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.16.5894. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- te Velde A. A., Klomp J. P., Yard B. A., de Vries J. E., Figdor C. G. Modulation of phenotypic and functional properties of human peripheral blood monocytes by IL-4. J Immunol. 1988 Mar 1;140(5):1548–1554. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


