Abstract
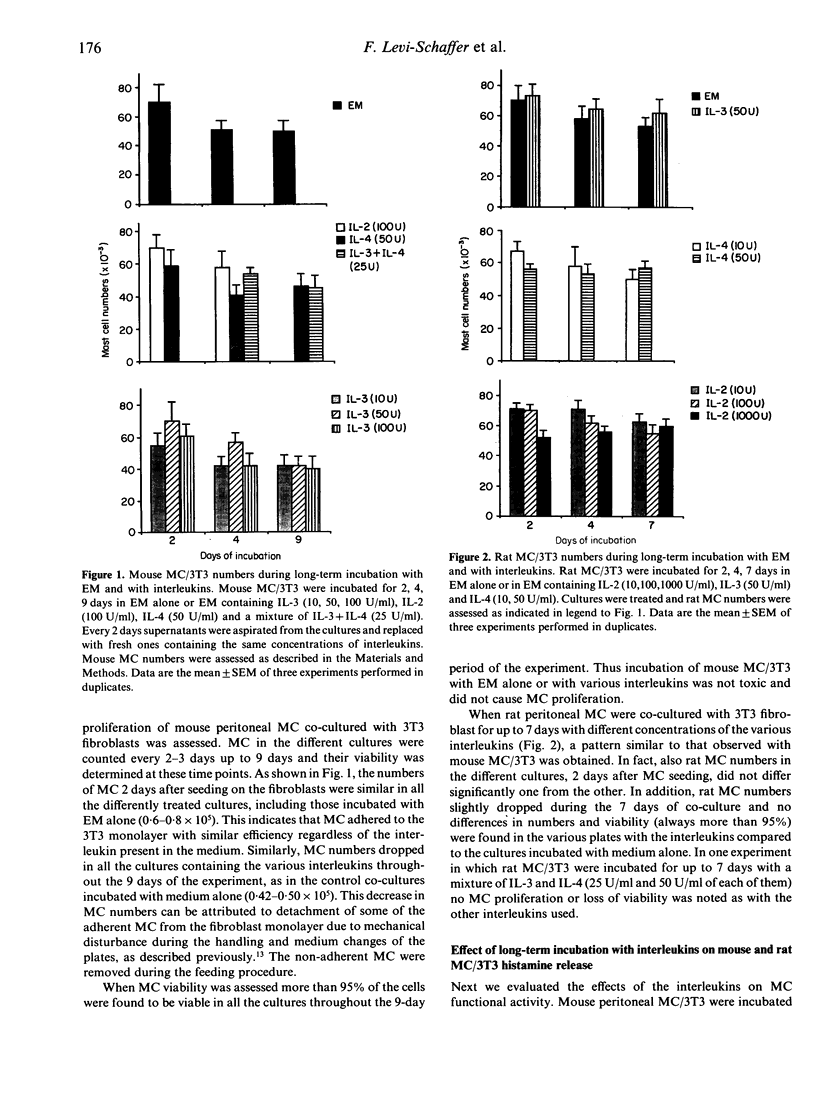
We investigated the effects of interleukin-2 (IL-2), interleukin-3 (IL-3) and interleukin-4 (IL-4) on mouse and rat peritoneal mast cells (MC) co-cultured with 3T3 fibroblasts (MC/3T3). The continuous presence of these cytokines for 7-9 days in the culture media was neither toxic nor caused proliferation of MC, as determined by the stability of MC numbers in culture. Long-term incubation of mouse MC/3T3 with IL-2 (100 U/ml), IL-3 (50 U/ml), IL-4 (50 U/ml) or a mixture of IL-3 and IL-4 (25 U/ml) induced an increase in basal histamine release of 79.3 +/- 19.0%, 41.0 +/- 17.3%, 25.2 +/- 10.4% and 30.2 +/- 3.2%, respectively, over control cells incubated with medium alone. When rat MC/3T3 were incubated for 7 days with the various interleukins an enhancement in histamine release similar to that observed with mouse MC/3T3 was found. Preincubation (1 hr) of rat MC/3T3 with interleukins prior to immunological activation with anti-IgE antibodies enhanced histamine release. The highest effect was observed with IL-3 + IL-4 (60.4 +/- 10.8% increase) followed by IL-2 (51.5 +/- 4.5%), IL-4 (28.6 +/- 10.3%) and IL-3 (13.2 +/- 4.2%). This study demonstrates that when mouse and rat peritoneal MC are cultured with fibroblasts in the presence of interleukins they do not proliferate, suggesting that they preserve their connective tissue type MC phenotype. Moreover, interleukins display a pro-inflammatory effect on these cells by enhancing both basal and anti-IgE-mediated histamine release.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alam R., Welter J. B., Forsythe P. A., Lett-Brown M. A., Grant J. A. Comparative effect of recombinant IL-1, -2, -3, -4, and -6, IFN-gamma, granulocyte-macrophage-colony-stimulating factor, tumor necrosis factor-alpha, and histamine-releasing factors on the secretion of histamine from basophils. J Immunol. 1989 May 15;142(10):3431–3435. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alam R., Wyczolkowska J. Action of the human lymphokine histamine releasing factor on mouse peritoneal mast cells. Immunol Lett. 1985;11(2):111–115. doi: 10.1016/0165-2478(85)90152-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ginsburg H., Nir I., Hammel I., Eren R., Weissman B. A., Naot Y. Differentiation and activity of mast cells following immunization in cultures of lymph-node cells. Immunology. 1978 Sep;35(3):485–502. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamaguchi Y., Kanakura Y., Fujita J., Takeda S., Nakano T., Tarui S., Honjo T., Kitamura Y. Interleukin 4 as an essential factor for in vitro clonal growth of murine connective tissue-type mast cells. J Exp Med. 1987 Jan 1;165(1):268–273. doi: 10.1084/jem.165.1.268. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirai K., Morita Y., Misaki Y., Ohta K., Takaishi T., Suzuki S., Motoyoshi K., Miyamoto T. Modulation of human basophil histamine release by hemopoietic growth factors. J Immunol. 1988 Dec 1;141(11):3958–3964. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huleihel M., Douvdevani A., Segal S., Apte R. N. Regulation of interleukin 1 generation in immune-activated fibroblasts. Eur J Immunol. 1990 Apr;20(4):731–738. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830200404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ida S., Hooks J. J., Siraganian R. P., Notkins A. L. Enhancement of IgE-mediated histamine release from human basophils by viruses: role of interferon. J Exp Med. 1977 Apr 1;145(4):892–906. doi: 10.1084/jem.145.4.892. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kedar E., Tsuberi B. Z., Landesberg A., Anafi M., Leshem B., Gillis S., Urdal D. L., Slavin S. In vitro and in vivo cytokine-induced facilitation of immunohematopoietic reconstitution in mice undergoing bone marrow transplantation. Bone Marrow Transplant. 1988 Jul;3(4):297–314. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobayashi T., Nakano T., Nakahata T., Asai H., Yagi Y., Tsuji K., Komiyama A., Akabane T., Kojima S., Kitamura Y. Formation of mast cell colonies in methylcellulose by mouse peritoneal cells and differentiation of these cloned cells in both the skin and the gastric mucosa of W/Wv mice: evidence that a common precursor can give rise to both "connective tissue-type" and "mucosal" mast cells. J Immunol. 1986 Feb 15;136(4):1378–1384. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel S. L., Chensue S. W., Phan S. H. Prostaglandins as endogenous mediators of interleukin 1 production. J Immunol. 1986 Jan;136(1):186–192. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levi-Schaffer F., Austen K. F., Caulfield J. P., Hein A., Bloes W. F., Stevens R. L. Fibroblasts maintain the phenotype and viability of the rat heparin-containing mast cell in vitro. J Immunol. 1985 Nov;135(5):3454–3462. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levi-Schaffer F., Austen K. F., Gravallese P. M., Stevens R. L. Coculture of interleukin 3-dependent mouse mast cells with fibroblasts results in a phenotypic change of the mast cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Sep;83(17):6485–6488. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.17.6485. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levi-Schaffer F., Dayton E. T., Austen K. F., Hein A., Caulfield J. P., Gravallese P. M., Liu F. T., Stevens R. L. Mouse bone marrow-derived mast cells cocultured with fibroblasts. Morphology and stimulation-induced release of histamine, leukotriene B4, leukotriene C4, and prostaglandin D2. J Immunol. 1987 Nov 15;139(10):3431–3441. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levi-Schaffer F., Mekori Y. A., Segal V., Claman H. N. Histamine release from mouse and rat mast cells cultured with supernatants from chronic murine graft-vs-host splenocytes. Cell Immunol. 1990 Apr 15;127(1):146–158. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(90)90121-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levi-Schaffer F., Riesel N. In vitro regeneration of activated rat peritoneal mast cells cocultured with 3T3 fibroblasts. Cell Immunol. 1989 Mar;119(1):30–40. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(89)90221-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacDonald S. M., Schleimer R. P., Kagey-Sobotka A., Gillis S., Lichtenstein L. M. Recombinant IL-3 induces histamine release from human basophils. J Immunol. 1989 May 15;142(10):3527–3532. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakano T., Kanakura Y., Asai H., Kitamura Y. Changing processes from bone marrow-derived cultured mast cells to connective tissue-type mast cells in the peritoneal cavity of mast cell-deficient w/wv mice: association of proliferation arrest and differentiation. J Immunol. 1987 Jan 15;138(2):544–549. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plaut M., Pierce J. H., Watson C. J., Hanley-Hyde J., Nordan R. P., Paul W. E. Mast cell lines produce lymphokines in response to cross-linkage of Fc epsilon RI or to calcium ionophores. Nature. 1989 May 4;339(6219):64–67. doi: 10.1038/339064a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Razin E., Ihle J. N., Seldin D., Mencia-Huerta J. M., Katz H. R., LeBlanc P. A., Hein A., Caulfield J. P., Austen K. F., Stevens R. L. Interleukin 3: A differentiation and growth factor for the mouse mast cell that contains chondroitin sulfate E proteoglycan. J Immunol. 1984 Mar;132(3):1479–1486. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salari H., Chan-Yeung M. Interleukin-1 potentiates antigen-mediated arachidonic acid metabolite formation in mast cells. Clin Exp Allergy. 1989 Nov;19(6):637–641. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2222.1989.tb02760.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaff R. E., Beaven M. A. Increased sensitivity of the enzymatic isotopic assay of histamine: measurement of histamine in plasma and serum. Anal Biochem. 1979 Apr 15;94(2):425–430. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(79)90385-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sonoda S., Sonoda T., Nakano T., Kanayama Y., Kanakura Y., Asai H., Yonezawa T., Kitamura Y. Development of mucosal mast cells after injection of a single connective tissue-type mast cell in the stomach mucosa of genetically mast cell-deficient W/Wv mice. J Immunol. 1986 Aug 15;137(4):1319–1322. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Subramanian N., Bray M. A. Interleukin 1 releases histamine from human basophils and mast cells in vitro. J Immunol. 1987 Jan 1;138(1):271–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsuji K., Nakahata T., Takagi M., Kobayashi T., Ishiguro A., Kikuchi T., Naganuma K., Koike K., Miyajima A., Arai K. Effects of interleukin-3 and interleukin-4 on the development of "connective tissue-type" mast cells: interleukin-3 supports their survival and interleukin-4 triggers and supports their proliferation synergistically with interleukin-3. Blood. 1990 Jan 15;75(2):421–427. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wodnar-Filipowicz A., Heusser C. H., Moroni C. Production of the haemopoietic growth factors GM-CSF and interleukin-3 by mast cells in response to IgE receptor-mediated activation. Nature. 1989 May 11;339(6220):150–152. doi: 10.1038/339150a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


