Abstract
Human-mouse hybridoma cell lines producing human monoclonal antibodies against the cardiac glycoside digoxin were established after in vitro immunization or direct immortalization of human peripheral blood lymphocytes with digoxin. Three antibodies, designated MO6, LH92 and LH1114, displayed different patterns of fine specificity against digoxin and several digoxin analogues, as elucidated by inhibition ELISA. All three monoclonal antibodies had mu heavy chains, two of them (MO6 and LH114) had kappa light chains and one (LH92) lambda light chains. DNA encoding the variable regions of both heavy and light chains of the three antibodies were amplified from cDNA using the polymerase chain reaction (PCR). The nucleotide sequences of the amplified DNA were determined after subcloning of PCR fragments in M13 vectors. The deduced amino acid sequences revealed considerable sequence differences in the complementarity determining regions between the three antibodies.
Full text
PDF
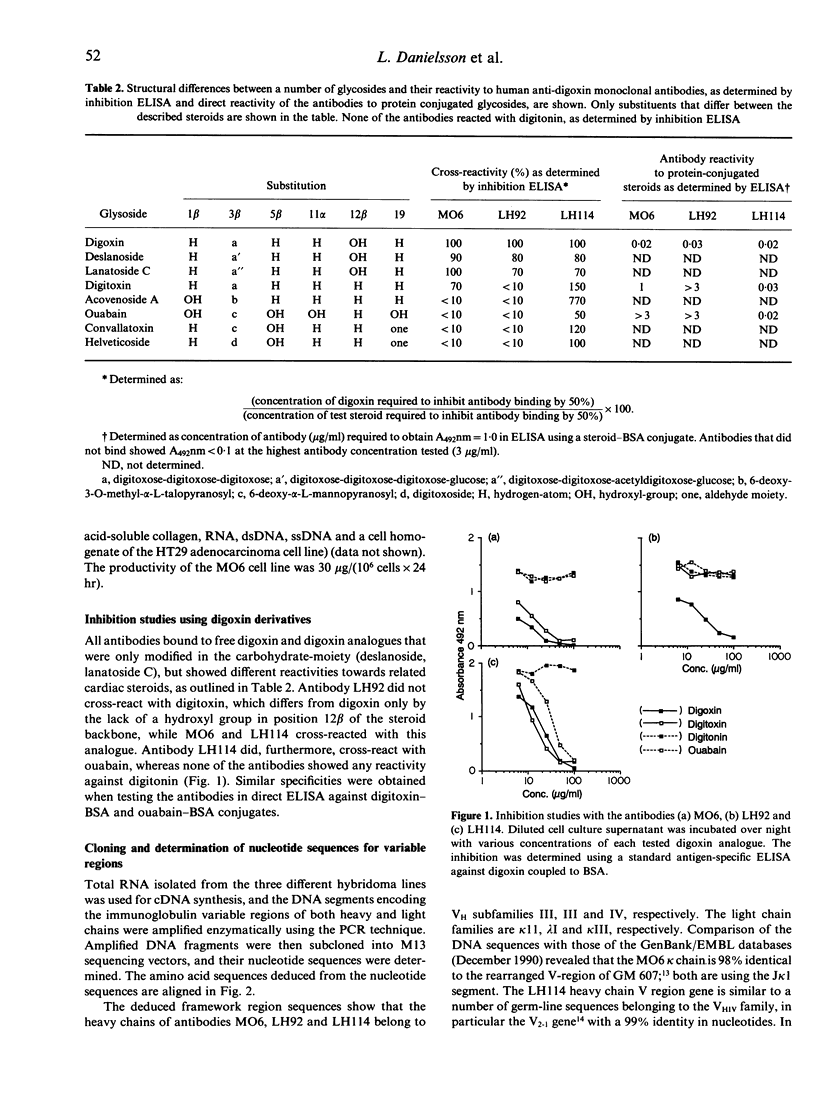


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bedzyk W. D., Johnson L. S., Riordan G. S., Voss E. W., Jr Comparison of variable region primary structures within an anti-fluorescein idiotype family. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jan 25;264(3):1565–1569. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biggin M. D., Gibson T. J., Hong G. F. Buffer gradient gels and 35S label as an aid to rapid DNA sequence determination. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jul;80(13):3963–3965. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.13.3963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borrebaeck C. A., Danielsson L., Möller S. A. Human monoclonal antibodies produced by primary in vitro immunization of peripheral blood lymphocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jun;85(11):3995–3999. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.11.3995. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen P. P., Albrandt K., Orida N. K., Radoux V., Chen E. Y., Schrantz R., Liu F. T., Carson D. A. Genetic basis for the cross-reactive idiotypes on the light chains of human IgM anti-IgG autoantibodies. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Nov;83(21):8318–8322. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.21.8318. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crews S., Griffin J., Huang H., Calame K., Hood L. A single VH gene segment encodes the immune response to phosphorylcholine: somatic mutation is correlated with the class of the antibody. Cell. 1981 Jul;25(1):59–66. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90231-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devereux J., Haeberli P., Smithies O. A comprehensive set of sequence analysis programs for the VAX. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 11;12(1 Pt 1):387–395. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.1part1.387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friguet B., Chaffotte A. F., Djavadi-Ohaniance L., Goldberg M. E. Measurements of the true affinity constant in solution of antigen-antibody complexes by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. J Immunol Methods. 1985 Mar 18;77(2):305–319. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(85)90044-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter M. M., Margolies M. N., Ju A., Haber E. High-affinity monoclonal antibodies to the cardiac glycoside, digoxin. J Immunol. 1982 Sep;129(3):1165–1172. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kabat E. A. The nature of an antigenic determinant. J Immunol. 1966 Jul;97(1):1–11. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klobeck H. G., Solomon A., Zachau H. G. Contribution of human V kappa II germ-line genes to light-chain diversity. Nature. 1984 May 3;309(5963):73–76. doi: 10.1038/309073a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larrick J. W., Danielsson L., Brenner C. A., Abrahamson M., Fry K. E., Borrebaeck C. A. Rapid cloning of rearranged immunoglobulin genes from human hybridoma cells using mixed primers and the polymerase chain reaction. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989 May 15;160(3):1250–1256. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(89)80138-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee K. H., Matsuda F., Kinashi T., Kodaira M., Honjo T. A novel family of variable region genes of the human immunoglobulin heavy chain. J Mol Biol. 1987 Jun 20;195(4):761–768. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90482-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mudgett-Hunter M., Anderson W., Haber E., Margolies M. N. Binding and structural diversity among high-affinity monoclonal anti-digoxin antibodies. Mol Immunol. 1985 Apr;22(4):477–488. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(85)90132-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Near R. I., Haber E. Characterization of the heavy and light chain immunoglobulin variable region genes used in a set of anti-digoxin antibodies. Mol Immunol. 1989 Apr;26(4):371–382. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(89)90126-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohlin M., Broliden P. A., Danielsson L., Wahren B., Rosen J., Jondal M., Borrebaeck C. A. Human monoclonal antibodies against a recombinant HIV envelope antigen produced by primary in vitro immunization. Characterization and epitope mapping. Immunology. 1989 Nov;68(3):325–331. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohlin M., Danielsson L., Carlsson R., Borrebaeck C. A. The effect of leucyl-leucine methyl ester on proliferation and Ig secretion of EBV-transformed human B lymphocytes. Immunology. 1989 Apr;66(4):485–490. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Panka D. J., Margolies M. N. Complete variable region sequences of five homologous high affinity anti-digoxin antibodies. J Immunol. 1987 Oct 1;139(7):2385–2391. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Panka D. J., Mudgett-Hunter M., Parks D. R., Peterson L. L., Herzenberg L. A., Haber E., Margolies M. N. Variable region framework differences result in decreased or increased affinity of variant anti-digoxin antibodies. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 May;85(9):3080–3084. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.9.3080. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


