Abstract
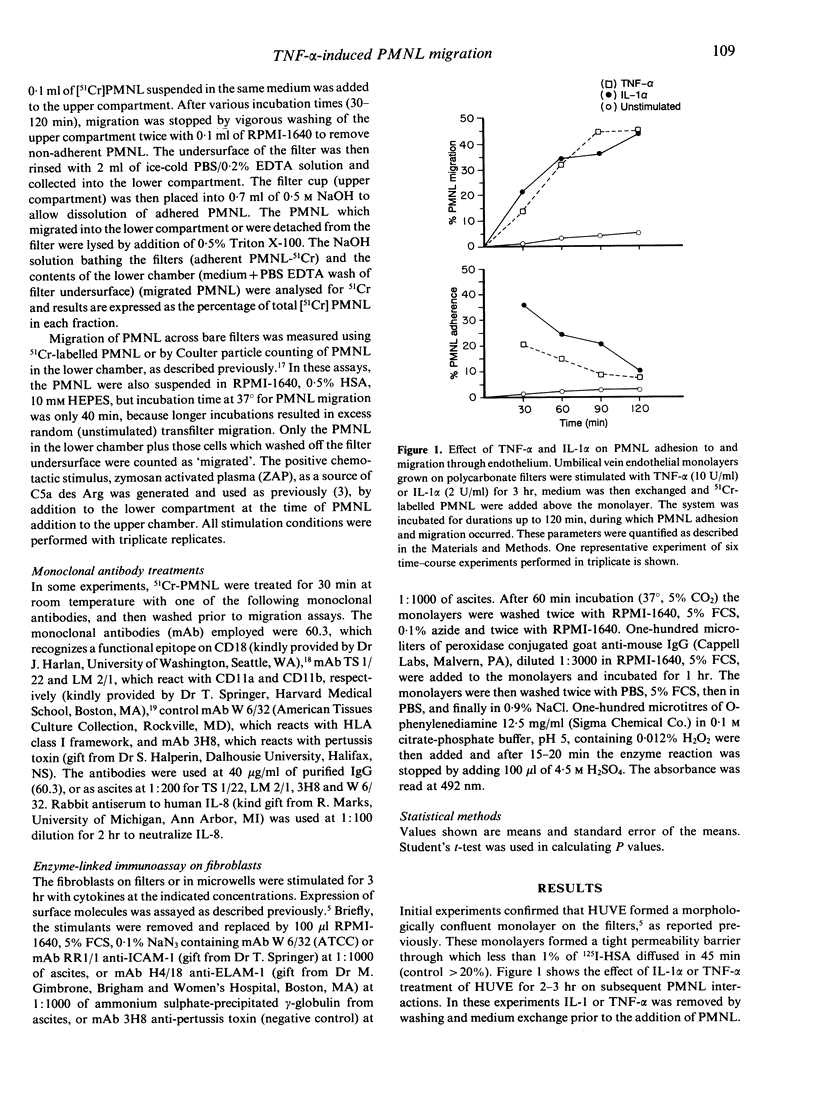
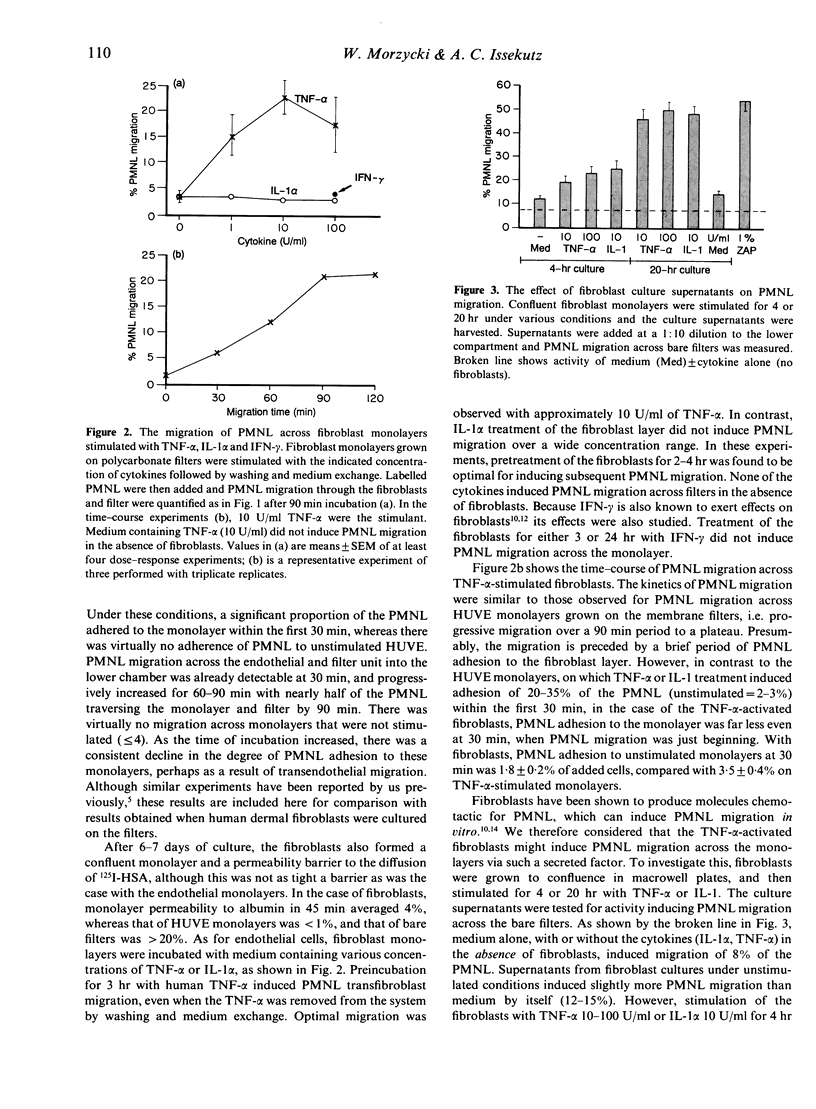
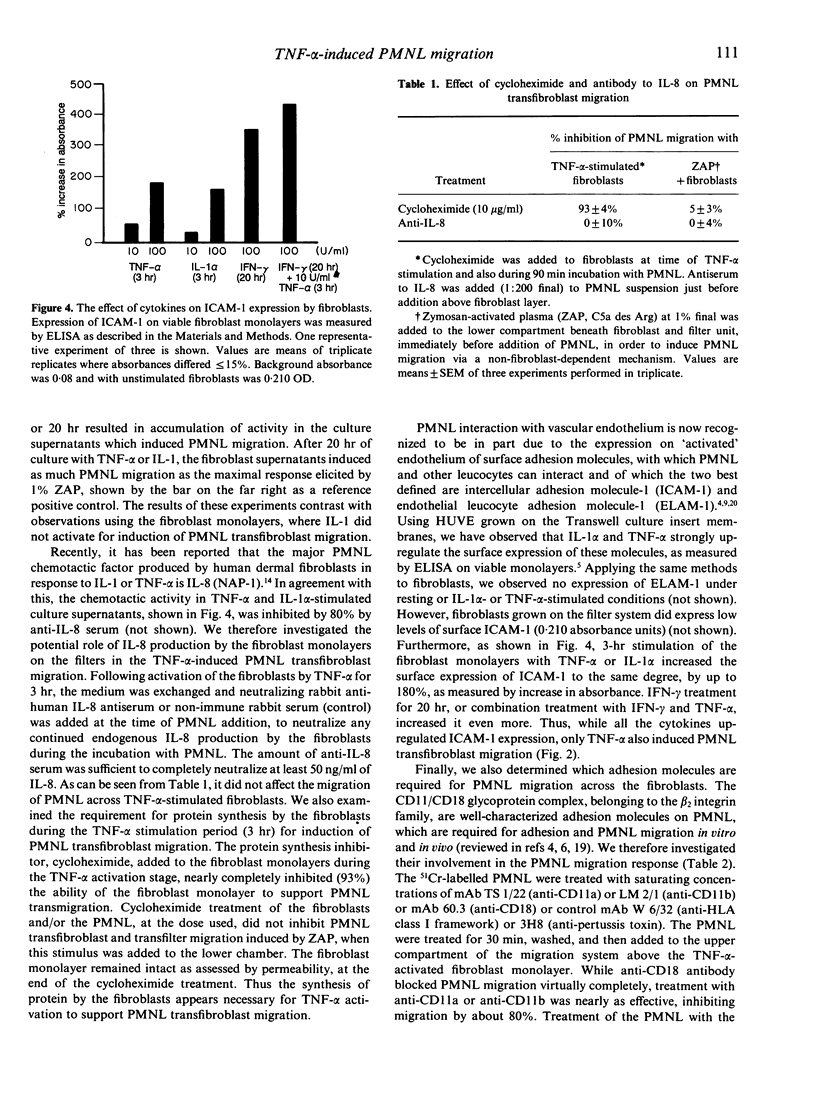
Interleukin-1 (IL-1) and tumour necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-alpha) both induce polymorphonuclear leucocyte (PMNL) infiltration into tissues and they have a synergistic action in this respect. We and others have observed that IL-1 alpha and TNF-alpha induce 51Cr-labelled PMNL migration across monolayers of umbilical vein endothelium via an endothelial cell-dependent mechanism. Here we investigated the interaction of PMNL with fibroblasts, since PMNL probably encounter such cells in many tissues once they traverse the vascular wall. TNF-alpha, but not IL-1 alpha, was found to activate fibroblast monolayers, grown on polycarbonate filters, to stimulate PMNL transfibroblast migration. This was a time- and fibroblast-dependent process which required fibroblast protein synthesis, as indicated by inhibition with cycloheximide. The effect of TNF-alpha was not related to fibroblast chemotactic factor production (primarily IL-8), or to ICAM-1 up-regulation, since IL-1 was as active as TNF-alpha in this respect, without activating fibroblasts to support PMNL transfibroblast migration. Antiserum to IL-8, present during the assay, did not inhibit PMNL migration across the monolayers. The PMNL migration was highly dependent on the function of both CD11a (LFA-1) and CD11b (MAC-1) PMNL adhesion molecules, since monoclonal antibodies to either inhibited migration by about 80%. The results suggest a distinct activation by TNF-alpha of fibroblasts to facilitate PMNL migration through fibroblast barriers. These findings may in part account for the synergistic action of IL-1 and TNF-alpha in inducing extravascular accumulation of PMNL during inflammation.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson D. C., Miller L. J., Schmalstieg F. C., Rothlein R., Springer T. A. Contributions of the Mac-1 glycoprotein family to adherence-dependent granulocyte functions: structure-function assessments employing subunit-specific monoclonal antibodies. J Immunol. 1986 Jul 1;137(1):15–27. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beatty P. G., Ledbetter J. A., Martin P. J., Price T. H., Hansen J. A. Definition of a common leukocyte cell-surface antigen (Lp95-150) associated with diverse cell-mediated immune functions. J Immunol. 1983 Dec;131(6):2913–2918. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bevilacqua M. P., Stengelin S., Gimbrone M. A., Jr, Seed B. Endothelial leukocyte adhesion molecule 1: an inducible receptor for neutrophils related to complement regulatory proteins and lectins. Science. 1989 Mar 3;243(4895):1160–1165. doi: 10.1126/science.2466335. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dayer J. M., Beutler B., Cerami A. Cachectin/tumor necrosis factor stimulates collagenase and prostaglandin E2 production by human synovial cells and dermal fibroblasts. J Exp Med. 1985 Dec 1;162(6):2163–2168. doi: 10.1084/jem.162.6.2163. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dustin M. L., Rothlein R., Bhan A. K., Dinarello C. A., Springer T. A. Induction by IL 1 and interferon-gamma: tissue distribution, biochemistry, and function of a natural adherence molecule (ICAM-1). J Immunol. 1986 Jul 1;137(1):245–254. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dustin M. L., Staunton D. E., Springer T. A. Supergene families meet in the immune system. Immunol Today. 1988 Jul-Aug;9(7-8):213–215. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(88)91216-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elias J. A., Freundlich B., Kern J. A., Rosenbloom J. Cytokine networks in the regulation of inflammation and fibrosis in the lung. Chest. 1990 Jun;97(6):1439–1445. doi: 10.1378/chest.97.6.1439. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elias J. A., Lentz V. IL-1 and tumor necrosis factor synergistically stimulate fibroblast IL-6 production and stabilize IL-6 messenger RNA. J Immunol. 1990 Jul 1;145(1):161–166. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furie M. B., McHugh D. D. Migration of neutrophils across endothelial monolayers is stimulated by treatment of the monolayers with interleukin-1 or tumor necrosis factor-alpha. J Immunol. 1989 Nov 15;143(10):3309–3317. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaffe E. A., Nachman R. L., Becker C. G., Minick C. R. Culture of human endothelial cells derived from umbilical veins. Identification by morphologic and immunologic criteria. J Clin Invest. 1973 Nov;52(11):2745–2756. doi: 10.1172/JCI107470. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee T. H., Lee G. W., Ziff E. B., Vilcek J. Isolation and characterization of eight tumor necrosis factor-induced gene sequences from human fibroblasts. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 May;10(5):1982–1988. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.5.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lo S. K., Van Seventer G. A., Levin S. M., Wright S. D. Two leukocyte receptors (CD11a/CD18 and CD11b/CD18) mediate transient adhesion to endothelium by binding to different ligands. J Immunol. 1989 Nov 15;143(10):3325–3329. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Megyeri P., Sadowska J., Issekutz T. B., Issekutz A. C. Endotoxin-stimulated human macrophages produce a factor that induces polymorphonuclear leucocyte infiltration and is distinct from interleukin-1, tumour necrosis factor alpha and chemotactic factors. Immunology. 1990 Jan;69(1):155–161. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morzycki W., Sadowska J., Issekutz A. C. Interleukin-1 and tumour necrosis factor alpha induced polymorphonuclear leukocyte-endothelial cell adhesion and transendothelial migration in vitro: the effect of apical versus basal monolayer stimulation. Immunol Lett. 1990 Sep;25(4):331–340. doi: 10.1016/0165-2478(90)90204-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moser R., Schleiffenbaum B., Groscurth P., Fehr J. Interleukin 1 and tumor necrosis factor stimulate human vascular endothelial cells to promote transendothelial neutrophil passage. J Clin Invest. 1989 Feb;83(2):444–455. doi: 10.1172/JCI113903. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Movat H. Z., Burrowes C. E., Cybulsky M. I., Dinarello C. A. Acute inflammation and a Shwartzman-like reaction induced by interleukin-1 and tumor necrosis factor. Synergistic action of the cytokines in the induction of inflammation and microvascular injury. Am J Pathol. 1987 Dec;129(3):463–476. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pober J. S., Cotran R. S. The role of endothelial cells in inflammation. Transplantation. 1990 Oct;50(4):537–544. doi: 10.1097/00007890-199010000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rampart M., De Smet W., Fiers W., Herman A. G. Inflammatory properties of recombinant tumor necrosis factor in rabbit skin in vivo. J Exp Med. 1989 Jun 1;169(6):2227–2232. doi: 10.1084/jem.169.6.2227. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schröder J. M., Sticherling M., Henneicke H. H., Preissner W. C., Christophers E. IL-1 alpha or tumor necrosis factor-alpha stimulate release of three NAP-1/IL-8-related neutrophil chemotactic proteins in human dermal fibroblasts. J Immunol. 1990 Mar 15;144(6):2223–2232. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seelentag W., Mermod J. J., Vassalli P. Interleukin 1 and tumor necrosis factor-alpha additively increase the levels of granulocyte-macrophage and granulocyte colony-stimulating factor (CSF) mRNA in human fibroblasts. Eur J Immunol. 1989 Jan;19(1):209–212. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830190135. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith C. W., Marlin S. D., Rothlein R., Toman C., Anderson D. C. Cooperative interactions of LFA-1 and Mac-1 with intercellular adhesion molecule-1 in facilitating adherence and transendothelial migration of human neutrophils in vitro. J Clin Invest. 1989 Jun;83(6):2008–2017. doi: 10.1172/JCI114111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tonnesen M. G., Smedly L. A., Henson P. M. Neutrophil-endothelial cell interactions. Modulation of neutrophil adhesiveness induced by complement fragments C5a and C5a des arg and formyl-methionyl-leucyl-phenylalanine in vitro. J Clin Invest. 1984 Nov;74(5):1581–1592. doi: 10.1172/JCI111574. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wankowicz Z., Megyeri P., Issekutz A. Synergy between tumour necrosis factor alpha and interleukin-1 in the induction of polymorphonuclear leukocyte migration during inflammation. J Leukoc Biol. 1988 Apr;43(4):349–356. doi: 10.1002/jlb.43.4.349. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


