Abstract
Non-major histocompatibility complex (MHC) restricted cytotoxicity is an important part of the immune reaction mounted in response to bovine herpes virus type 1 (BHV-1) infection. In this study, we evaluated the effect of BHV-1 infection on the ability of lung parenchyma leucocytes (LPL), cranial tracheobronchial lymph node cells (BLNC) and peripheral blood mononuclear leucocytes (PBML) to mediate this function. While LPL from non-infected calves mediated cytotoxicity against BHV-1-infected cells, a similar activity could not be detected in PBML or BLNC. In contrast, both LPL and PBML from naive calves could mediate cytotoxicity against K562 target cells but only after activation with interleukin-2 (IL-2). BLNC were unable to kill K562 cells. Infection of calves with BHV-1 enhanced the ability of LPL and PBML to kill BHV-1-infected cells. This enhancement was detected as early as Day 1 after infection in LPL whereas it could only be detected in PBML 8 days after infection. The results demonstrate that the leucocyte population present at the site of infection was able to mediate a potentially important antiviral function and that this function was enhanced rapidly in response to infection. Thus LPL-mediated cytotoxicity may be an important mechanism for the recovery from BHV-1 infection.
Full text
PDF

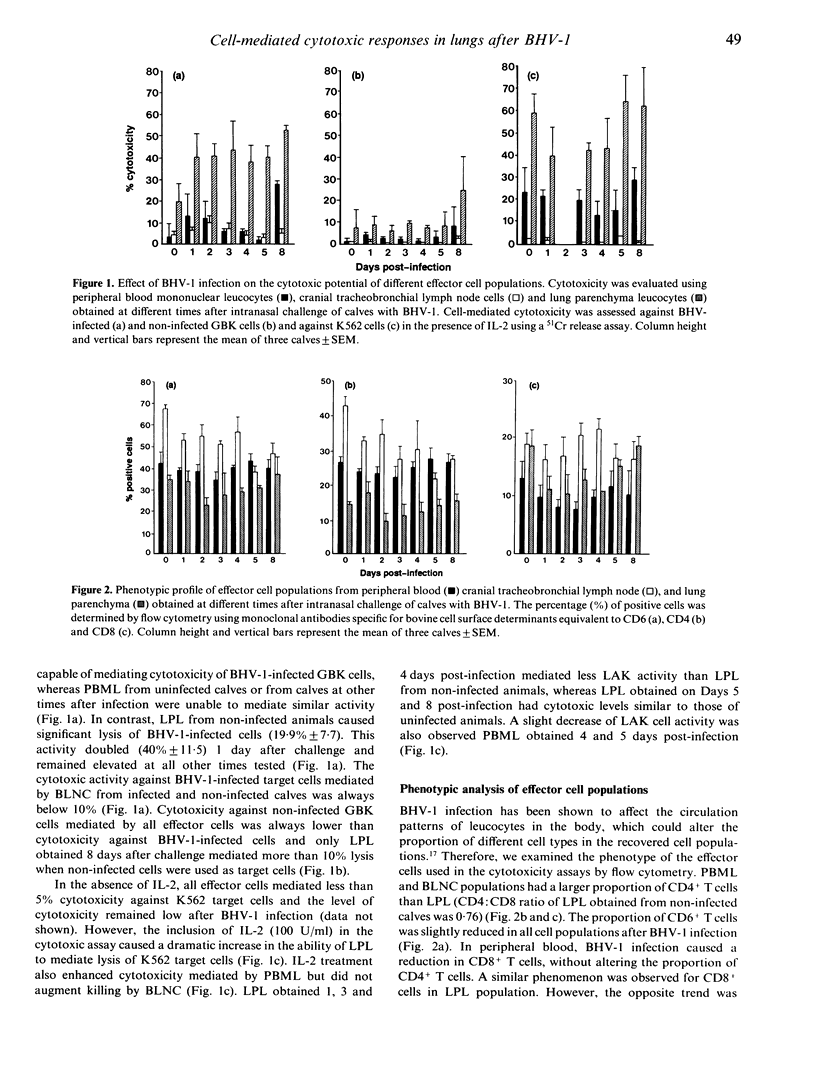
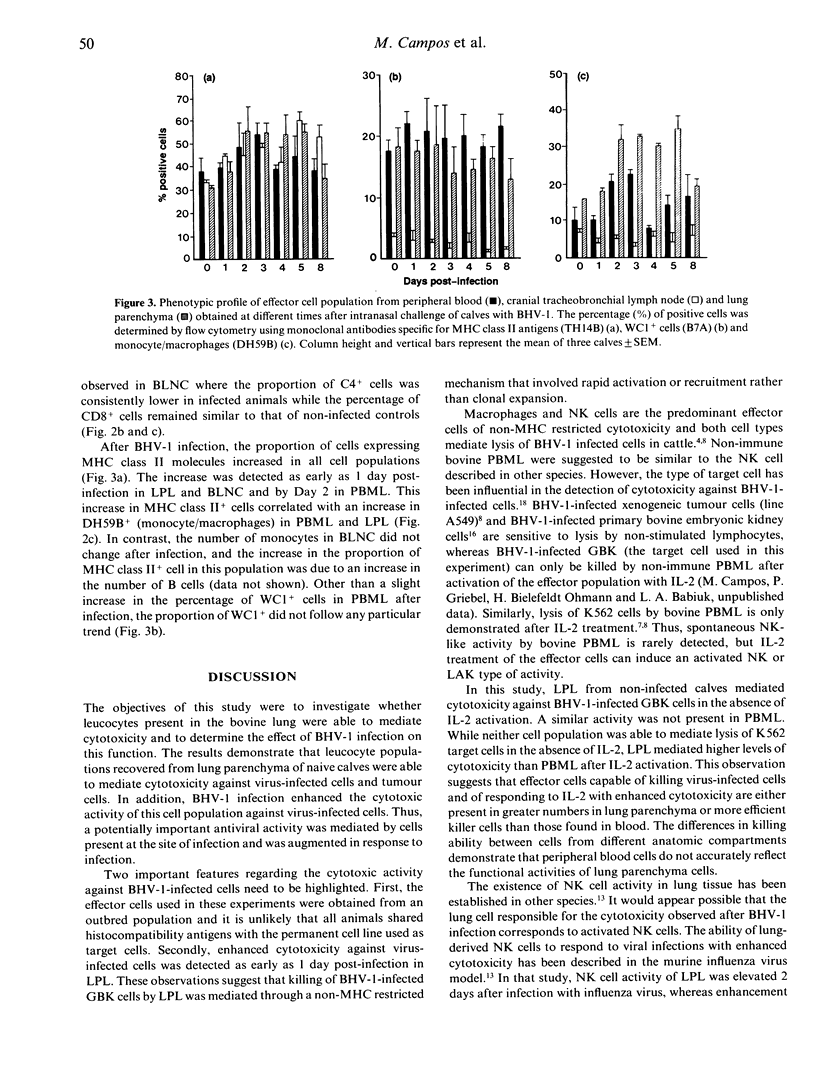


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abraham E., Freitas A. A., Coutinho A. A. Purification and characterization of intraparenchymal lung lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1990 Mar 15;144(6):2117–2122. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campos M., Ohmann H. B., Hutchings D., Rapin N., Babiuk L. A., Lawman M. J. Role of interferon-gamma in inducing cytotoxicity of peripheral blood mononuclear leukocytes to bovine herpesvirus type 1 (BHV-1)-infected cells. Cell Immunol. 1989 Apr 15;120(1):259–269. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(89)90193-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campos M., Rossi C. R. Cell-mediated cytotoxicity of bovine mononuclear cells to IBRV-infected cells: dependence on Sephadex G-10 adherent cells. Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 1985 Apr;8(4):363–375. doi: 10.1016/0165-2427(85)90006-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campos M., Rossi C. R. Cytotoxicity of bovine lymphocytes after treatment with lymphokines. Am J Vet Res. 1986 Jul;47(7):1524–1528. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campos M., Rossi C. R. In vitro induction of cytotoxic lymphocytes from infectious bovine rhinotracheitis virus hyperimmune cattle. Am J Vet Res. 1986 Nov;47(11):2411–2414. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cook C. G., Splitter G. A. Characterization of bovine mononuclear cell populations with natural cytolytic activity against bovine herpesvirus 1-infected cells. Cell Immunol. 1989 Apr 15;120(1):240–249. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(89)90191-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fitzgerald-Bocarsly P., Feldman M., Curl S., Schnell J., Denny T. Positively selected Leu-11a (CD16+) cells require the presence of accessory cells or factors for the lysis of herpes simplex virus-infected fibroblasts but not herpes simplex virus-infected Raji. J Immunol. 1989 Aug 15;143(4):1318–1326. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fitzgerald P. A., Evans R., Kirkpatrick D., Lopez C. Heterogeneity of human NK cells: comparison of effectors that lyse HSV-1-infected fibroblasts and K562 erythroleukemia targets. J Immunol. 1983 Apr;130(4):1663–1667. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grewal A. S., Rouse B. T., Babiuk L. A. Mechanisms of resistant of herpesviruses: comparison of the effectiveness of different cell types in mediating antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity. Infect Immun. 1977 Mar;15(3):698–703. doi: 10.1128/iai.15.3.698-703.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griebel P. J., Qualtiere L., Davis W. C., Lawman M. J., Babiuk L. A. Bovine peripheral blood leukocyte subpopulation dynamics following a primary bovine herpesvirus-1 infection. Viral Immunol. 1987;1(4):267–286. doi: 10.1089/vim.1987.1.267. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holt P. G., Kees U. R., Shon-Hegrad M. A., Rose A., Ford J., Bilyk N., Bowman R., Robinson B. W. Limiting-dilution analysis of T cells extracted from solid human lung tissue: comparison of precursor frequencies for proliferative responses and lymphokine production between lung and blood T cells from individual donors. Immunology. 1988 Aug;64(4):649–654. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holt P. G., Robinson B. W., Reid M., Kees U. R., Warton A., Dawson V. H., Rose A., Schon-Hegrad M., Papadimitriou J. M. Extraction of immune and inflammatory cells from human lung parenchyma: evaluation of an enzymatic digestion procedure. Clin Exp Immunol. 1986 Oct;66(1):188–200. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howell D. M., Fitzgerald-Bocarsly P. Natural killer-mediated lysis of some but not all HSV-1- or VSV-infected targets requires the participation of HLA-DR-positive accessory cells. Immunology. 1991 Mar;72(3):443–447. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jericho K. W., Yates W. D., Babiuk L. A. Bovine herpesvirus-1 vaccination against experimental bovine herpesvirus-1 and Pasteurella haemolytica respiratory tract infection: onset of protection. Am J Vet Res. 1982 Oct;43(10):1776–1780. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawman M. J., Griebel P., Hutchings D. L., Davis W. C., Heise J., Qualtiere L., Babiuk L. A. Generation of IL-2 dependent bovine cytotoxic T lymphocyte clones reactive against BHV-1 infected target cells: loss of genetic restriction and virus specificity. Viral Immunol. 1987;1(3):163–176. doi: 10.1089/vim.1987.1.163. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paya C. V., Schoon R. A., Leibson P. J. Alternative mechanisms of natural killer cell activation during herpes simplex virus infection. J Immunol. 1990 Jun 1;144(11):4370–4375. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rouse B. T., Babiuk L. A. The direct antiviral cytotoxicity by bovine lymphocytes is not restricted by genetic incompatibility of lymphocytes and target cells. J Immunol. 1977 Feb;118(2):618–624. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rouse B. T., Wardley R. C., Babiuk L. A. Antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity in cows: comparison of effector cell activity against heterologous erthrocyte and herpesvirus-infected bovine target cells. Infect Immun. 1976 May;13(5):1433–1441. doi: 10.1128/iai.13.5.1433-1441.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Splitter G. A., Eskra L., Abruzzini A. F. Cloned bovine cytolytic T cells recognize bovine herpes virus-1 in a genetically restricted, antigen-specific manner. Immunology. 1988 Jan;63(1):145–150. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein-Streilein J., Bennett M., Mann D., Kumar V. Natural killer cells in mouse lung: surface phenotype, target preference, and response to local influenza virus infection. J Immunol. 1983 Dec;131(6):2699–2704. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


