Abstract
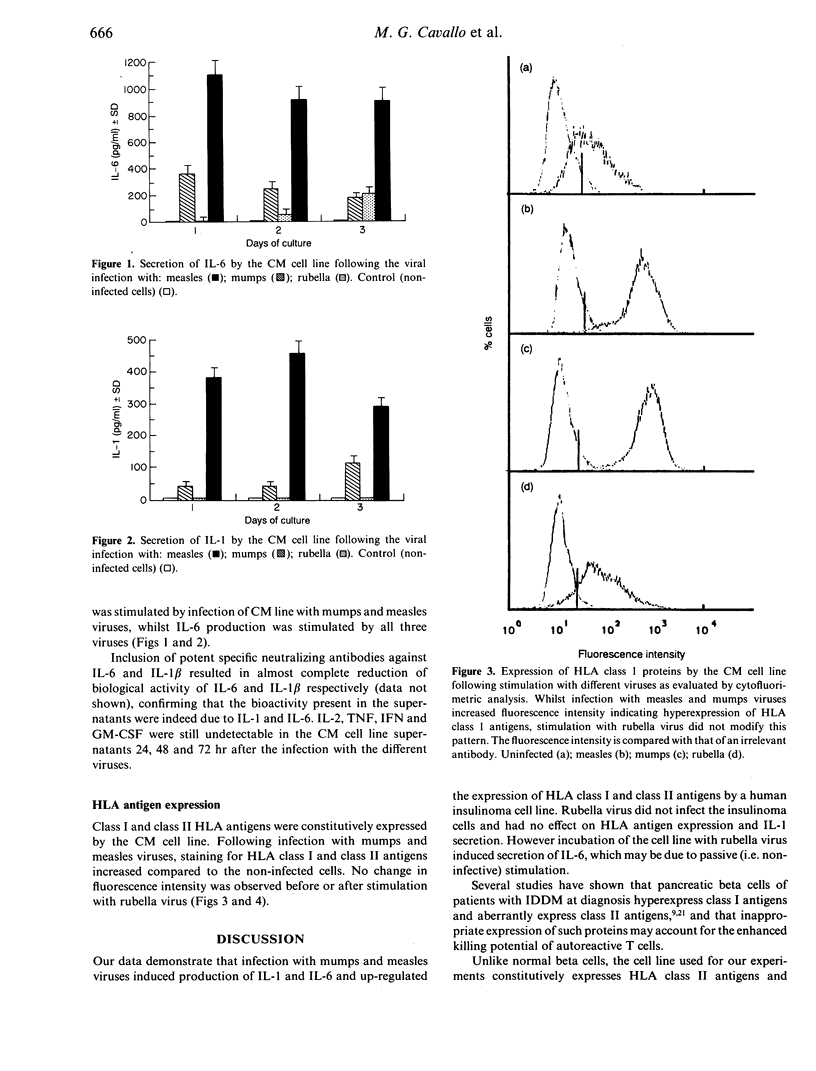
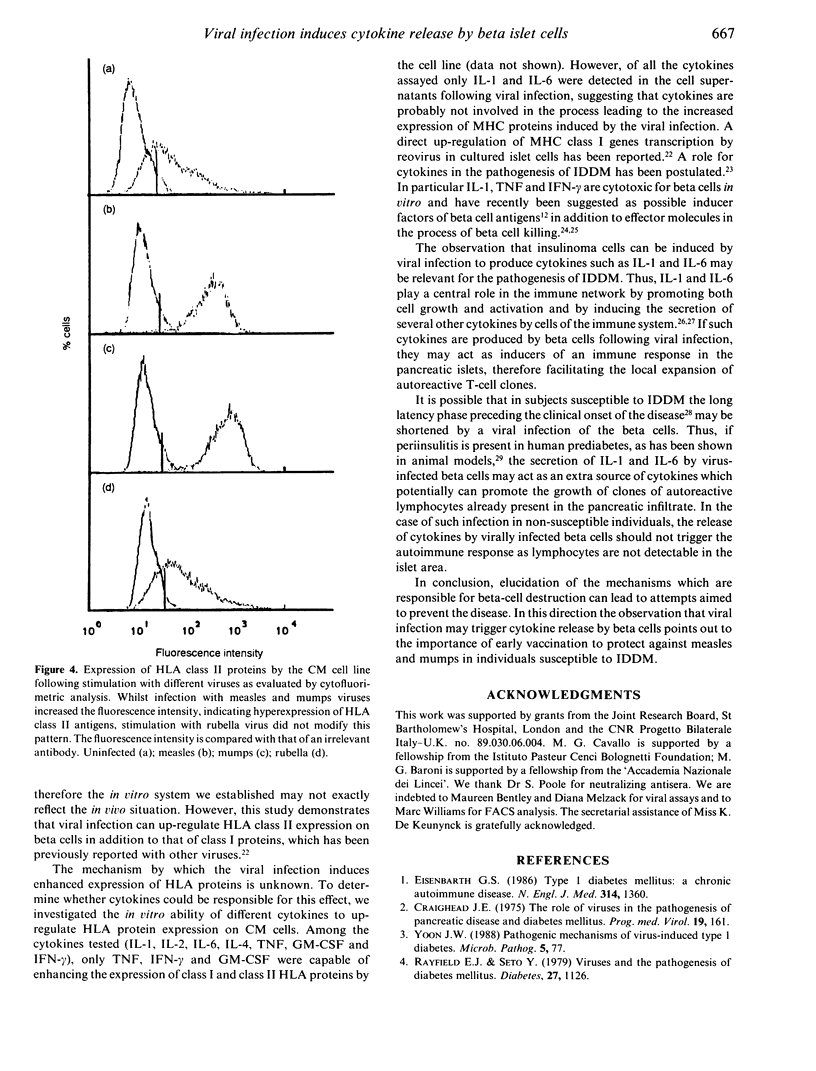
Viral infection has been suggested to play a triggering role in the pancreatic beta cell destruction which occurs in insulin-dependent diabetes (IDDM). However, the underlying mechanism of this phenomenon is unknown. In this study a human insulinoma cell line has been infected with measles, mumps and rubella viruses since a temporal association is reported between the clinical onset of IDDM and diseases caused by these viruses. The infection with measles and mumps viruses induced the release of interleukin-1 (IL-1) and interleukin-6 (IL-6) by the cell line as assessed by a bioassay and up-regulated the expression of human leucocyte antigen (HLA) class I and class II antigens as evaluated by cytofluorimetric analysis. Stimulation with rubella virus induced the release of IL-6 only and had no effect on HLA antigen expression. These data show for the first time that IL-1 and IL-6 secretion by an insulinoma cell line may occur after viral infection and suggest that cytokine release and increased expression of HLA molecules by beta cells may act to induce the immune response towards beta cells in IDDM.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bottazzo G. F., Dean B. M., McNally J. M., MacKay E. H., Swift P. G., Gamble D. R. In situ characterization of autoimmune phenomena and expression of HLA molecules in the pancreas in diabetic insulitis. N Engl J Med. 1985 Aug 8;313(6):353–360. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198508083130604. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell I. L., Cutri A., Wilson A., Harrison L. C. Evidence for IL-6 production by and effects on the pancreatic beta-cell. J Immunol. 1989 Aug 15;143(4):1188–1191. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell I. L., Harrison L. C., Ashcroft R. G., Jack I. Reovirus infection enhances expression of class I MHC proteins on human beta-cell and rat RINm5F cell. Diabetes. 1988 Mar;37(3):362–365. doi: 10.2337/diab.37.3.362. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell I. L., Iscaro A., Harrison L. C. IFN-gamma and tumor necrosis factor-alpha. Cytotoxicity to murine islets of Langerhans. J Immunol. 1988 Oct 1;141(7):2325–2329. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cebon J., Dempsey P., Fox R., Kannourakis G., Bonnem E., Burgess A. W., Morstyn G. Pharmacokinetics of human granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor using a sensitive immunoassay. Blood. 1988 Oct;72(4):1340–1347. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craighead J. E. The role of viruses in the pathogenesis of pancreatic disease and diabetes mellitus. Prog Med Virol. 1975;19:161–214. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenbarth G. S. Type I diabetes mellitus. A chronic autoimmune disease. N Engl J Med. 1986 May 22;314(21):1360–1368. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198605223142106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foulis A. K., Farquharson M. A. Aberrant expression of HLA-DR antigens by insulin-containing beta-cells in recent-onset type I diabetes mellitus. Diabetes. 1986 Nov;35(11):1215–1224. doi: 10.2337/diab.35.11.1215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foulis A. K., Farquharson M. A., Hardman R. Aberrant expression of class II major histocompatibility complex molecules by B cells and hyperexpression of class I major histocompatibility complex molecules by insulin containing islets in type 1 (insulin-dependent) diabetes mellitus. Diabetologia. 1987 May;30(5):333–343. doi: 10.1007/BF00299027. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gearing A. J., Bird C. R., Bristow A., Poole S., Thorpe R. A simple sensitive bioassay for interleukin-1 which is unresponsive to 10(3) U/ml of interleukin-2. J Immunol Methods. 1987 May 4;99(1):7–11. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(87)90025-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillis S., Ferm M. M., Ou W., Smith K. A. T cell growth factor: parameters of production and a quantitative microassay for activity. J Immunol. 1978 Jun;120(6):2027–2032. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helle M., Boeije L., Aarden L. A. Functional discrimination between interleukin 6 and interleukin 1. Eur J Immunol. 1988 Oct;18(10):1535–1540. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830181010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones D. B., Hunter N. R., Duff G. W. Heat-shock protein 65 as a beta cell antigen of insulin-dependent diabetes. Lancet. 1990 Sep 8;336(8715):583–585. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(90)93390-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lampeter E. F., Signore A., Gale E. A., Pozzilli P. Lessons from the NOD mouse for the pathogenesis and immunotherapy of human type 1 (insulin-dependent) diabetes mellitus. Diabetologia. 1989 Oct;32(10):703–708. doi: 10.1007/BF00274528. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le J., Vilcek J. Tumor necrosis factor and interleukin 1: cytokines with multiple overlapping biological activities. Lab Invest. 1987 Mar;56(3):234–248. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Londei M., Lamb J. R., Bottazzo G. F., Feldmann M. Epithelial cells expressing aberrant MHC class II determinants can present antigen to cloned human T cells. Nature. 1984 Dec 13;312(5995):639–641. doi: 10.1038/312639a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandrup-Poulsen T., Bendtzen K., Nerup J., Egeberg J., Nielsen J. H. Mechanisms of pancreatic islet cell destruction. Dose-dependent cytotoxic effect of soluble blood mononuclear cell mediators on isolated islets of Langerhans. Allergy. 1986 May;41(4):250–259. doi: 10.1111/j.1398-9995.1986.tb02025.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandrup-Poulsen T., Helqvist S., Mølvig J., Wogensen L. D., Nerup J. Cytokines as immune effector molecules in autoimmune endocrine diseases with special reference to insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Autoimmunity. 1989;4(3):191–234. doi: 10.3109/08916938909003049. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meager A., Parti S., Leung H., Peil E., Mahon B. Preparation and characterization of monoclonal antibodies directed against antigenic determinants of recombinant human tumour necrosis factor (rTNF). Hybridoma. 1987 Jun;6(3):305–311. doi: 10.1089/hyb.1987.6.305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Onodera T., Jenson A. B., Yoon J. W., Notkins A. L. Virus-induced diabetes mellitus: reovirus infection of pancreatic beta cells in mice. Science. 1978 Aug 11;201(4355):529–531. doi: 10.1126/science.208156. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rayfield E. J., Seto Y. Viruses and the pathogenesis of diabetes mellitus. Diabetes. 1978 Nov;27(11):1126–1140. doi: 10.2337/diab.27.11.1126. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tarn A. C., Thomas J. M., Dean B. M., Ingram D., Schwarz G., Bottazzo G. F., Gale E. A. Predicting insulin-dependent diabetes. Lancet. 1988 Apr 16;1(8590):845–850. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(88)91601-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong G. G., Clark S. C. Multiple actions of interleukin 6 within a cytokine network. Immunol Today. 1988 May;9(5):137–139. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(88)91200-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoon J. W., Austin M., Onodera T., Notkins A. L. Isolation of a virus from the pancreas of a child with diabetic ketoacidosis. N Engl J Med. 1979 May 24;300(21):1173–1179. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197905243002102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoon J. W., Onodera T., Notkins A. L. Virus-induced diabetes mellitus. XV. Beta cell damage and insulin-dependent hyperglycemia in mice infected with coxsackie virus B4. J Exp Med. 1978 Oct 1;148(4):1068–1080. doi: 10.1084/jem.148.4.1068. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoon J. W. Pathogenic mechanisms of virus-induced type 1 diabetes. Microb Pathog. 1988 Aug;5(2):77–86. doi: 10.1016/0882-4010(88)90010-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



