Abstract
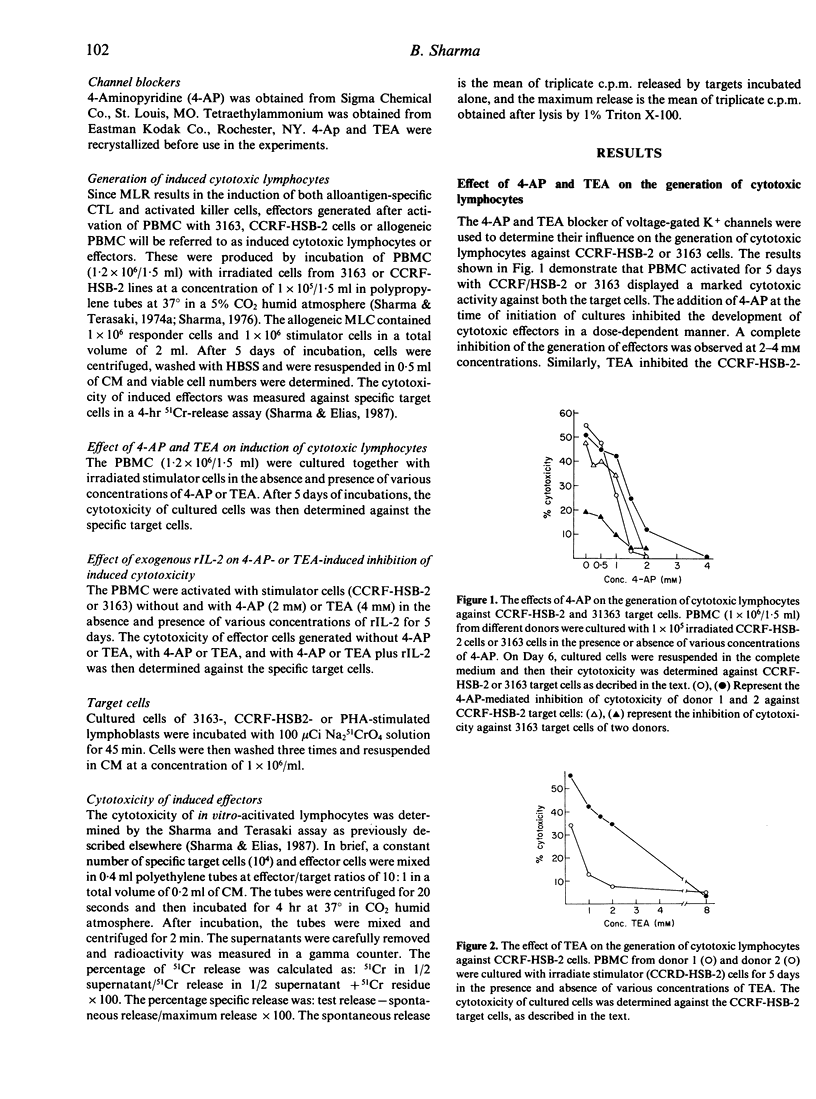
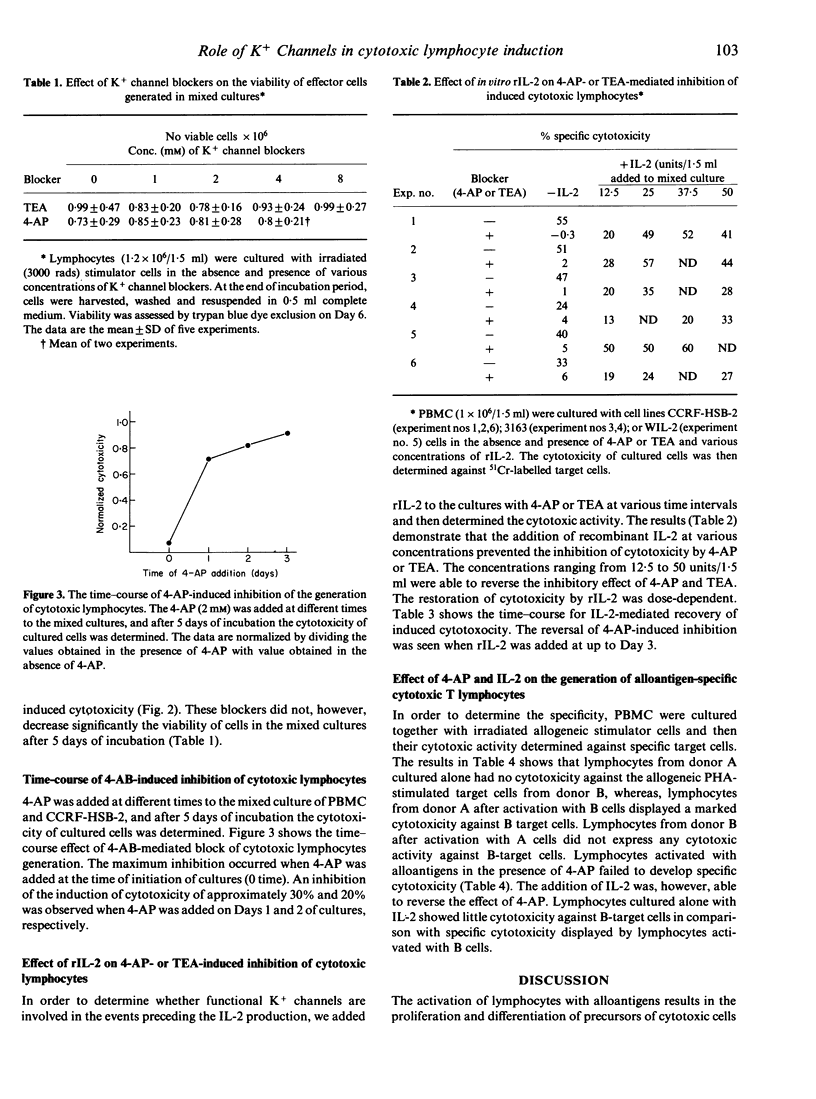
Recent studies with patch-clamp technique have shown the presence of voltage-gated K+ channels in human T lymphocytes and natural killer cells. Blockers of voltage-gated K+ channel currents (4-Aminopyridine, 4-AP, and tetraethylammonium, TEA), were used here in a pharmacological approach to examine a role of K+ channels in the differentiation of precursors of cytotoxic cells into functionally active cytotoxic lymphocytes. The data presented here demonstrated that activation of peripheral blood lymphocytes with CCRF-HSB-2, 3163 and other allogeneic lymphoid cells for 5 days in mixed lymphocyte culture (MLC) renders them cytotoxic to the respective target cells. Both 4-AP and TEA (2-4 mM), when added to cultures, inhibited the development of cytotoxic effectors in a dose-dependent manner. Maximum inhibition of the generation of cytotoxic lymphocytes occurred when 4-AP was present at the start of cultures. Little or no inhibition was, however, observed when 4-AP was added 1 day of incubation. The results also demonstrate that the addition of recombinant IL-2 (rIL-2) overcame the 4-AP- or TEA-mediated inhibition of the generation of cytotoxic lymphocytes in a dose-dependent manner. The maximum reversal of 4-AP-induced inhibition occurred when exogenous IL-2 was added at Day 0 or 1. Taken together, these data suggest a role of K+ channels in the generation of cytotoxic lymphocytes.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Chandy K. G., DeCoursey T. E., Cahalan M. D., McLaughlin C., Gupta S. Voltage-gated potassium channels are required for human T lymphocyte activation. J Exp Med. 1984 Aug 1;160(2):369–385. doi: 10.1084/jem.160.2.369. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeCoursey T. E., Chandy K. G., Gupta S., Cahalan M. D. Voltage-gated K+ channels in human T lymphocytes: a role in mitogenesis? Nature. 1984 Feb 2;307(5950):465–468. doi: 10.1038/307465a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukushima Y., Hagiwara S., Henkart M. Potassium current in clonal cytotoxic T lymphocytes from the mouse. J Physiol. 1984 Jun;351:645–656. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1984.sp015268. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lutz C. T., Fitch F. W. Accessory cell requirements for the generation of cytolytic T lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1979 Jun;122(6):2598–2604. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matteson D. R., Deutsch C. K channels in T lymphocytes: a patch clamp study using monoclonal antibody adhesion. Nature. 1984 Feb 2;307(5950):468–471. doi: 10.1038/307468a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizel S. B. Interleukin 1 and T cell activation. Immunol Rev. 1982;63:51–72. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1982.tb00411.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlichter L., Sidell N., Hagiwara S. Potassium channels mediate killing by human natural killer cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jan;83(2):451–455. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.2.451. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmid D. S., Larsen H. S., Rouse B. T. The role of accessory cells and T cell-growth factor in induction of cytotoxic T lymphocytes against herpes simplex virus antigens. Immunology. 1981 Dec;44(4):755–763. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharma B. S., Elias A. N. Effects of methimazole on human lymphocyte proliferation and natural killer cell activity. Gen Pharmacol. 1987;18(4):449–453. doi: 10.1016/0306-3623(87)90107-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharma B. S. In vitro lymphocyte immunization to cultured human tumor cells: parameters for generation of cytotoxic lymphocytes. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1976 Oct;57(4):743–748. doi: 10.1093/jnci/57.4.743. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharma B., Gupta S. Antigen-specific primary cytotoxic T lymphocyte (CTL) responses in acquired immune deficiency syndrome (AIDS) and AIDS-related complexes (ARC). Clin Exp Immunol. 1985 Nov;62(2):296–303. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharma B., Terasaki P. I. Immunization of lymphocytes from cancer patients. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1974 Jun;52(6):1925–1926. doi: 10.1093/jnci/52.6.1925. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharma B., Terasaki P. I. In vitro immunization to cultured human tumor cells. Cancer Res. 1974 Jan;34(1):115–118. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharma B., Tubergen D. G., Minden P., Brunda M. J. In vitro immunisation against human tumour cells with bacterial extracts. Nature. 1977 Jun 30;267(5614):845–847. doi: 10.1038/267845a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strausser J. L., Mazumder A., Grimm E. A., Lotze M. T., Rosenberg S. A. Lysis of human solid tumors by autologous cells sensitized in vitro to alloantigens. J Immunol. 1981 Jul;127(1):266–271. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vose B. M., Bonnard G. D. Human tumour antigens defined by cytotoxicity and proliferative responses of cultured lymphoid cells. Nature. 1982 Mar 25;296(5855):359–361. doi: 10.1038/296359a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vánky F., Argov S., Klein E. Tumor biopsy cells participating in systems in which cytotoxicity of lymphocytes is generated. Autologous and allogeneic studies. Int J Cancer. 1981 Mar 15;27(3):273–280. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910270304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vánky F., Gorsky T., Gorsky Y., Masucci M. G., Klein E. Lysis of tumor biopsy cells by autologous T lymphocytes activated in mixed cultures and propagated with T cell growth factor. J Exp Med. 1982 Jan 1;155(1):83–95. doi: 10.1084/jem.155.1.83. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagner H., Röllinghoff M. T-T-cell interactions during the vitro cytotoxic allograft responses. I. Soluble products from activated Lyl+ T cells trigger autonomously antigen-primed Ly23+ T cells to cell proliferation and cytolytic activity. J Exp Med. 1978 Dec 1;148(6):1523–1538. doi: 10.1084/jem.148.6.1523. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ypey D. L., Clapham D. E. Development of a delayed outward-rectifying K+ conductance in cultured mouse peritoneal macrophages. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 May;81(10):3083–3087. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.10.3083. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


