Abstract
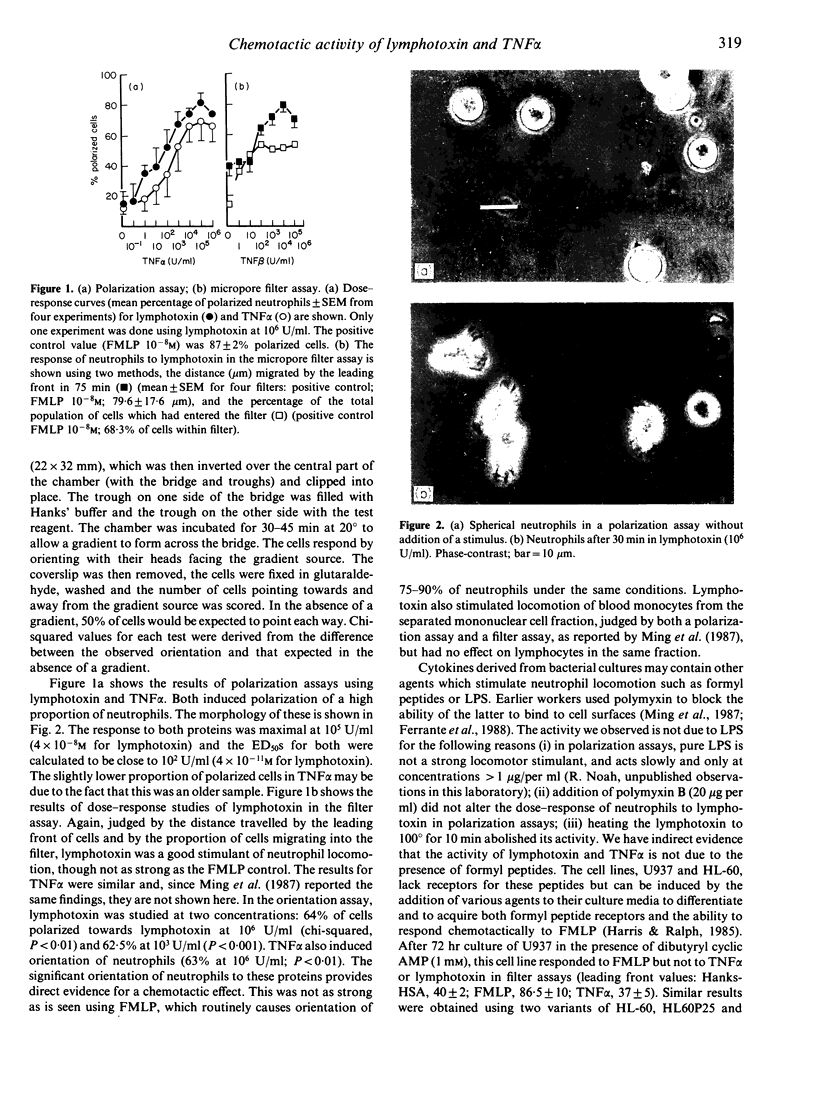
Lymphotoxin (TNF beta) and tumour necrosis factor alpha (TNF alpha) stimulate locomotion and chemotaxis of human blood neutrophils as measured in three assays. Both cytokines stimulate morphological polarization of neutrophils in suspension; both stimulate locomotion of neutrophils into micropore filters; both cause orientation of neutrophils towards a gradient source. Orientation in a gradient suggests a chemotactic effect. The action of both cytokines is similar but is not as strong as that of formyl peptide used as a positive control. Myelomonocytic cell lines (U937 and HL-60) develop responsiveness to formyl peptides on maturation but not to TNF alpha or beta.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Atkinson Y. H., Marasco W. A., Lopez A. F., Vadas M. A. Recombinant human tumor necrosis factor-alpha. Regulation of N-formylmethionylleucylphenylalanine receptor affinity and function on human neutrophils. J Clin Invest. 1988 Mar;81(3):759–765. doi: 10.1172/JCI113381. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrante A., Nandoskar M., Bates E. J., Goh D. H., Beard L. J. Tumour necrosis factor beta (lymphotoxin) inhibits locomotion and stimulates the respiratory burst and degranulation of neutrophils. Immunology. 1988 Mar;63(3):507–512. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris P., Ralph P. Human leukemic models of myelomonocytic development: a review of the HL-60 and U937 cell lines. J Leukoc Biol. 1985 Apr;37(4):407–422. doi: 10.1002/jlb.37.4.407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haston W. S., Shields J. M. Neutrophil leucocyte chemotaxis: a simplified assay for measuring polarizing responses to chemotactic factors. J Immunol Methods. 1985 Aug 2;81(2):229–237. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(85)90208-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ming W. J., Bersani L., Mantovani A. Tumor necrosis factor is chemotactic for monocytes and polymorphonuclear leukocytes. J Immunol. 1987 Mar 1;138(5):1469–1474. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zigmond S. H. Ability of polymorphonuclear leukocytes to orient in gradients of chemotactic factors. J Cell Biol. 1977 Nov;75(2 Pt 1):606–616. doi: 10.1083/jcb.75.2.606. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zigmond S. H., Hirsch J. G. Leukocyte locomotion and chemotaxis. New methods for evaluation, and demonstration of a cell-derived chemotactic factor. J Exp Med. 1973 Feb 1;137(2):387–410. doi: 10.1084/jem.137.2.387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



