Abstract
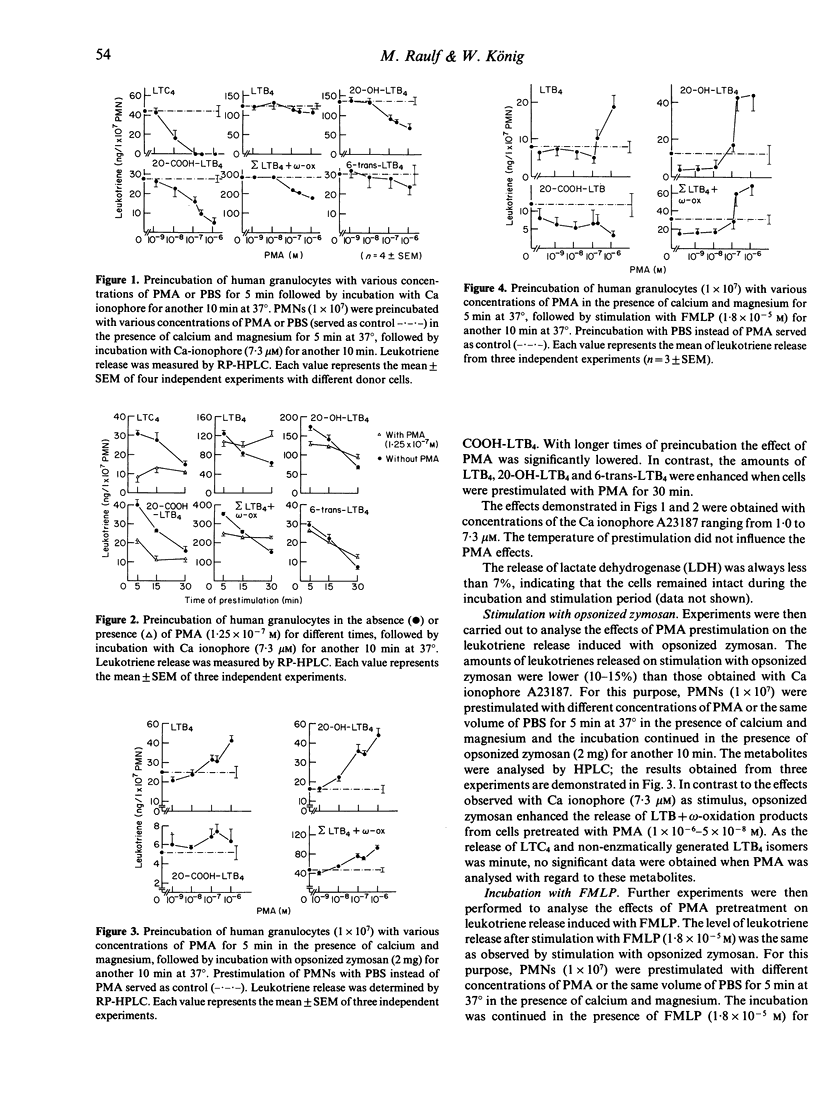
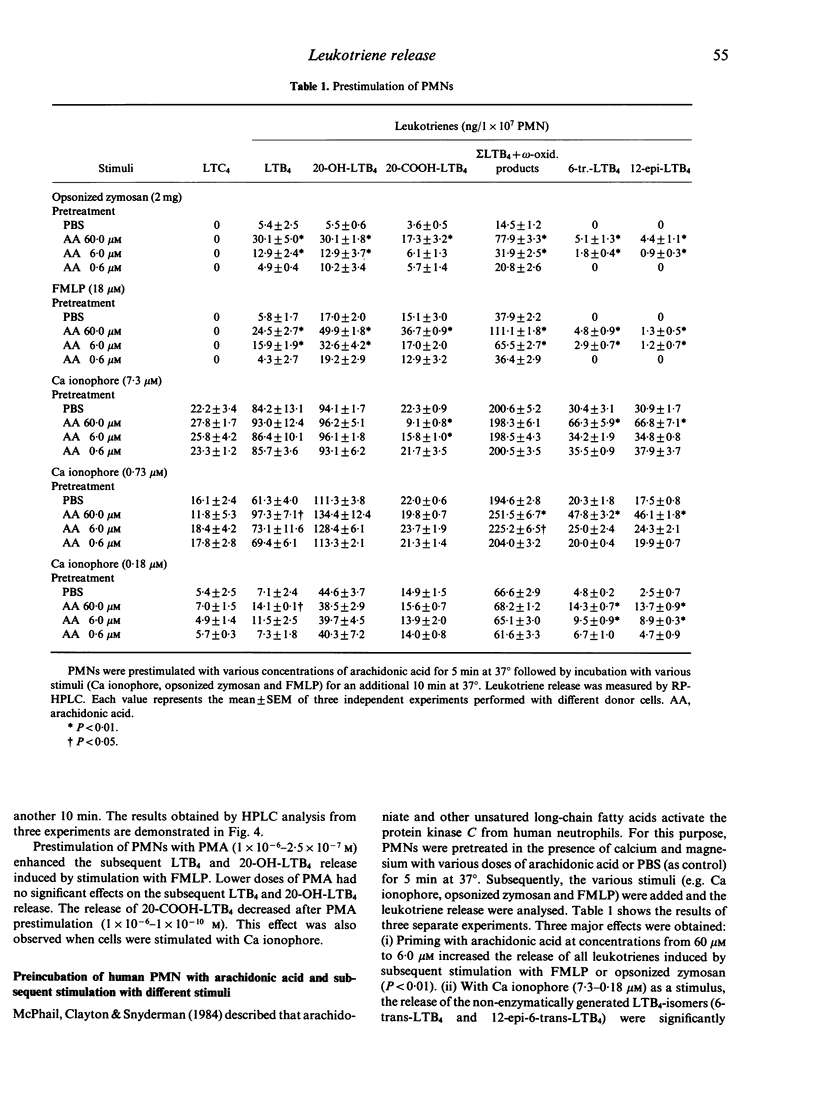
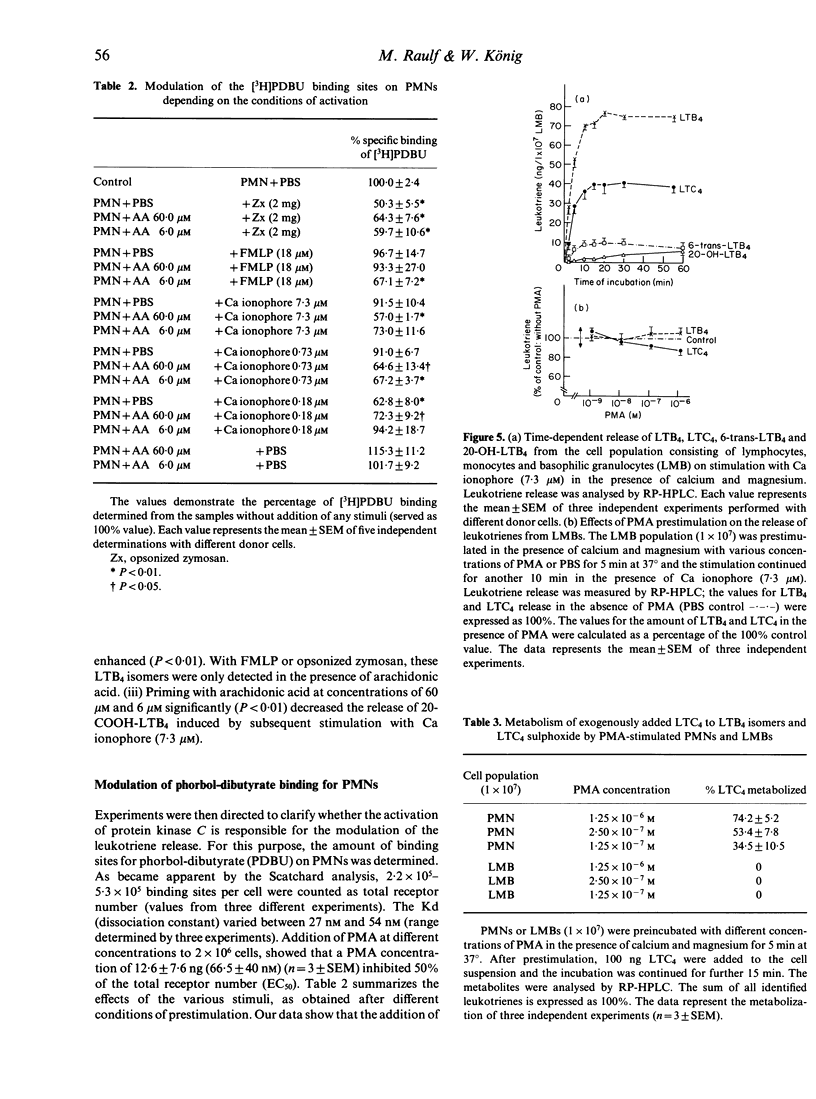
Stimulation of human neutrophils (PMN) with Ca ionophore A23187, opsonized zymosan and formyl-L-methionyl-L-leucyl-phenylalanine (FMLP) led to a time- and dose-dependent release of LTB4, 20-OH-LTB4, 20-COOH-LTB4, 6-trans-LTB4, 12-epi-6-trans LTB4 and LTC4, as detected by reverse-phase HPLC. Preincubation of the PMN suspension in the presence of Ca2+ and Mg2+ with phorbol-12-myristate-13-acetate (PMA) did not release leukotrienes by itself, but modulated the subsequent Ca ionophore-induced leukotriene release. The release of LTC4, 20-OH-LTB4 and 20-COOH-LTB4 was significantly decreased. Lesser effects were observed for the release of LTB4 and the non-enzymatic LTB4 isomers. In contrast, opsonized zymosan and FMLP enhanced the release of LTB4 and LTB4-omega-oxidation products from cells pretreated with PMA. With arachidonic acid as prestimulus, the amounts of the LTB4 isomers (6-trans-LTB4 and 12-epi-6-trans-LTB4) were enhanced significantly on subsequent stimulation with Ca ionophore. Prestimulation of lymphocytes, monocytes and basophilic granulocytes (LMB) with PMA had no significant effects on the ionophore-induced release of LTC4 and LTB4. PMN, but not LMB, suspensions prestimulated with PMA convert exogenously added LTC4 to LTB4 isomers and LTC4 sulphoxide. Our data suggest that preincubation of human granulocytes with PMA modified leukotriene release by activation or inhibition of different metabolic pathways for LTC4 and LTB4.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andersson T., Dahlgren C., Lew P. D., Stendahl O. Cell surface expression of fMet-Leu-Phe receptors on human neutrophils. Correlation to changes in the cytosolic free Ca2+ level and action of phorbol myristate acetate. J Clin Invest. 1987 Apr;79(4):1226–1233. doi: 10.1172/JCI112941. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Badwey J. A., Karnovsky M. L. Production of superoxide by phagocytic leukocytes: a paradigm for stimulus-response phenomena. Curr Top Cell Regul. 1986;28:183–208. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-152828-7.50006-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berridge M. J. Inositol trisphosphate and diacylglycerol as second messengers. Biochem J. 1984 Jun 1;220(2):345–360. doi: 10.1042/bj2200345. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berridge M. J., Irvine R. F. Inositol trisphosphate, a novel second messenger in cellular signal transduction. Nature. 1984 Nov 22;312(5992):315–321. doi: 10.1038/312315a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borgeat P., Hamberg M., Samuelsson B. Transformation of arachidonic acid and homo-gamma-linolenic acid by rabbit polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Monohydroxy acids from novel lipoxygenases. J Biol Chem. 1976 Dec 25;251(24):7816–7820. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borgeat P., Samuelsson B. Metabolism of arachidonic acid in polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Structural analysis of novel hydroxylated compounds. J Biol Chem. 1979 Aug 25;254(16):7865–7869. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brom J., König W., Stüning M., Raulf M., Köller M. Characterization of leukotriene B4-omega-hydroxylase activity within human polymorphonuclear granulocytes. Scand J Immunol. 1987 Mar;25(3):283–294. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1987.tb01074.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- French J. K., Hurst N. P., Zalewski P. D., Valente L., Forbes I. J. Calcium ionophore A23187 enhances human neutrophil superoxide release, stimulated by phorbol dibutyrate, by converting phorbol ester receptors from a low- to high-affinity state. FEBS Lett. 1987 Feb 23;212(2):242–246. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(87)81353-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haines K. A., Giedd K. N., Rich A. M., Korchak H. M., Weissmann G. The leukotriene B4 paradox: neutrophils can, but will not, respond to ligand-receptor interactions by forming leukotriene B4 or its omega-metabolites. Biochem J. 1987 Jan 1;241(1):55–62. doi: 10.1042/bj2410055. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson W. R., Klebanoff S. J. Leukotriene production and inactivation by normal, chronic granulomatous disease and myeloperoxidase-deficient neutrophils. J Biol Chem. 1983 Nov 25;258(22):13522–13527. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- König W., Frickhofen N., Tesch H. Generation and secretion of eosinophilotactic activity from human polymorphonuclear neutrophils by various mechanisms of cell activation. Immunology. 1979 Apr;36(4):733–742. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee C. W., Lewis R. A., Tauber A. I., Mehrotra M., Corey E. J., Austen K. F. The myeloperoxidase-dependent metabolism of leukotrienes C4, D4, and E4 to 6-trans-leukotriene B4 diastereoisomers and the subclass-specific S-diastereoisomeric sulfoxides. J Biol Chem. 1983 Dec 25;258(24):15004–15010. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liles W. C., Meier K. E., Henderson W. R. Phorbol myristate acetate and the calcium ionophore A23187 synergistically induce release of LTB4 by human neutrophils: involvement of protein kinase C activation in regulation of the 5-lipoxygenase pathway. J Immunol. 1987 May 15;138(10):3396–3402. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McColl S. R., Hurst N. P., Cleland L. G. Modulation by phorbol myristate acetate of arachidonic acid release and leukotriene synthesis by human polymorphonuclear leukocytes stimulated with A23187. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Dec 15;141(2):399–404. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(86)80186-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McPhail L. C., Clayton C. C., Snyderman R. A potential second messenger role for unsaturated fatty acids: activation of Ca2+-dependent protein kinase. Science. 1984 May 11;224(4649):622–625. doi: 10.1126/science.6231726. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishizuka Y. The role of protein kinase C in cell surface signal transduction and tumour promotion. Nature. 1984 Apr 19;308(5961):693–698. doi: 10.1038/308693a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Flaherty J. T. Phospholipid metabolism and stimulus-response coupling. Biochem Pharmacol. 1987 Feb 15;36(4):407–412. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(87)90343-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Shea J. J., Siwik S. A., Gaither T. A., Frank M. M. Activation of the C3b receptor: effect of diacylglycerols and calcium mobilization. J Immunol. 1985 Nov;135(5):3381–3387. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powell W. S. Properties of leukotriene B4 20-hydroxylase from polymorphonuclear leukocytes. J Biol Chem. 1984 Mar 10;259(5):3082–3089. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raulf M., Stüning M., König W. Effect of cations on leukotriene release: requirements for the metabolism of peptido-leukotrienes (leukotrienes C4, D4) by human polymorphonuclear granulocytes. Immunology. 1986 Jul;58(3):479–487. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rådmark O., Malmsten C., Samuelsson B., Clark D. A., Goto G., Marfat A., Corey E. J. Leukotriene A: stereochemistry and enzymatic conversion to leukotriene B. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1980 Feb 12;92(3):954–961. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(80)90795-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rådmark O., Shimizu T., Jörnvall H., Samuelsson B. Leukotriene A4 hydrolase in human leukocytes. Purification and properties. J Biol Chem. 1984 Oct 25;259(20):12339–12345. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sando J. J., Hilfiker M. L., Salomon D. S., Farrar J. J. Specific receptors for phorbol esters in lymphoid cell populations: role in enhanced production of T-cell growth factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Feb;78(2):1189–1193. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.2.1189. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shak S., Goldstein I. M. Omega-oxidation is the major pathway for the catabolism of leukotriene B4 in human polymorphonuclear leukocytes. J Biol Chem. 1984 Aug 25;259(16):10181–10187. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tripp C. S., Mahoney M., Needleman P. Calcium ionophore enables soluble agonists to stimulate macrophage 5-lipoxygenase. J Biol Chem. 1985 May 25;260(10):5895–5898. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wey H. E., Baxter C. S. Phorbol diester synergistically stimulates agonist-induced lipoxygenase product formation in murine macrophages. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Nov 14;140(3):861–867. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(86)90714-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


